Each owner personal computer periodically encounters specific terms from the field A striking example is “chipset motherboard". Although understanding the meaning of this term is not necessary for the daily use of a computer, this information broadens the user's horizons. the chipset makes it easy to classify motherboards by generation, which makes it possible to exclude fraudulent attempts by dishonest sellers.
Everyone is familiar with the main components of a computer. This is a video card, modules random access memory, motherboard, etc. All these components are sold in the respective stores, so visitors have at least a general idea, which cannot be said about the chipset. No wonder the question "what is a chipset" is asked so often on the Internet. V this case there is nothing difficult to understand. To better understand this issue, let's start from afar.
As you know, almost all components are connected to the motherboard. It is the basis through which it is possible to tie all the knots together. Obviously, the banal placement of connectors on a rectangular PCB plate is not enough. The processor must have access to all ports and sockets peripherals. In this case, you can not do without an intermediary. Although, in fairness, it should be noted that there was a special VESA bus, many of the lines of which were connected directly to the processor stages, but such a solution had a number of limitations. You can answer the question of what a chipset is as follows - this is a node that combines all the main data lines of the motherboard.
Physically, motherboard chipsets are represented by one or more microcircuits. More recently, there were two of them, bearing the names of the North and South Bridges. Such unusual names are due to the peculiarity of placement on the board - one microcircuit (chip) at the top and the other at the bottom. Accordingly, the first is the North Bridge, and the second is the South. In the light of the foregoing, the answer to the question of what a chipset is can be this - it is a set of integrated circuits that ensure the smooth operation of all components.
It is the connecting link between the central processor, RAM (the controller is located here) and the video adapter bus. The speed of operation is relatively high, therefore, due to heat dissipation, a cooling system is often located on this microcircuit.
Performs more functions, but at lower speeds. Interaction with BIOS chips, support for an audio codec, synchronization with microcircuits additional features(USB 3.0, iTE) - this is an incomplete list of tasks performed. In addition, the South Bridge contains controllers for USB, SATA ports, and the common one connects the bridge and the central processor.
In order to reduce signal transmission delays and improve overall performance, all major manufacturers CPUs their latest models integrate memory and video controllers directly into the processor die. In fact, this means the abolition of the classic concept of the "North Bridge", since now its functions are assigned to the processor. That is why on all modern motherboards there is only one large microcircuit (except for the processor) - the South Bridge. The instructions for the board always have a sheet with a block diagram. It schematically indicates the communication lines of all components among themselves. It is enough to at least get acquainted with it so that some questions about the chipset disappear by themselves.
As you probably already know, the main devices of a computer are the processor and random access memory (RAM), and they are located on the motherboard. But besides them, there is another important component on the motherboard, namely, the motherboard chipset. The chipset is a set of several microcircuits designed to control the operation of all functional elements. In addition, the chipset is an element in which one or another set of functions and capabilities that the motherboard has is “hardwired”.
Chipsets in the modern sense of the word first appeared in personal computers of the Amiga Atari platform. On the Intel platform the first chipset appeared in PC/AT computers (based on i80286 processors).
Generally speaking, the word "chipset" (chipset) in translation from English is translated as "chipset". As a rule, however, in modern computers this set consists of a small number of elements - usually 2, sometimes 3 chips. And many modern chipsets, in particular some Intel chipsets, generally manage with just one controller.
In the traditional scheme, the chipset consists of two microcircuits with a well-established set of functions. Traditionally, these two microcircuits are called "south bridge" and "north bridge". This name comes from the fact that usually the “north” chip is located at the top of the motherboard, and the “south” one, respectively, at the bottom. These microcircuits are not called bridges by chance, since it is through them that the connection between all elements of the computer, such as the processor, RAM, I / O buses, drive buses, etc., goes. But the north and south bridges are rather a common term. The formal name given to the north bridge is the memory controller hub, and the south bridge is the I/O controller hub.
The north and south bridges are connected by a special bus for data exchange. Whereas earlier this data was transferred over an I/O bus such as PCI, now each chipset manufacturer has a high-speed bus of its own format for this purpose.
Scheme of interaction of the chipset with all elements of the motherboard.
Main functions
As already mentioned, the functions of the chipset include integration various devices located on the system board - memory, processor, I / O buses, ports, etc. and coordination of their interaction. Also, the chipset often contains an integrated video and audio output system and a network controller.
The south and north bridges are responsible for different functions. The Northbridge is in charge of high speed devices, such as processor, memory, . Also in the north bridge is a built-in video system. The southbridge is responsible for the rest of the periphery, usually low-speed. These are PCI, SATA, USB and many others. By the way, if you remember that the northbridge is called the memory controller, then this rule is often not observed, since in many chipset models memory management is not included in the functions of the northbridge, but is carried out due to the capabilities of the central processor.
Many motherboards also have a small Super I/O chip responsible for low speed ports such as LPT and PS/2. A special bus connects the south bridge and the Super I/O controller.
Northbridge, chipset Intel 815
south bridge
Manufacturers and models
The production of a chipset is a high-tech process, a little less complicated than the production of processors, since the characteristics of a computer, as well as its uninterrupted operation, depend on the quality of the chipset and the set of functions that it supports. Therefore, there are not so many manufacturers of these chipsets in the world now - as a rule, these are companies that produce the processors themselves - Intel and AMD, as well as NVIDIA, VIA and SIS.
A lot has been developed so far various models chipsets. As a rule, certain chipset models are designed to work with certain processors or processor lines. If you want to know the chipset model name of your motherboard, then you should remember that the chipset model name is written on the northbridge chip.
Conclusion
A chipset is a set of chips that integrates and coordinates the operation of the main systems of a personal computer located on the motherboard. The chipset determines the capabilities of a personal computer and the functions that it supports, in addition, the performance of the computer and its uninterrupted operation depend on the reliable operation of the chipset.
Which ensures the operation of all elements of the computer. The chipset also determines the performance and power of the computer.
Physically, a chipset consists of one or more large microcircuits on the motherboard and several smaller auxiliary microcircuits. These microcircuits heat up during operation, so motherboard manufacturers install heatsinks on them for cooling.
Due to the established engineering traditions, the main microcircuits of the chipset were named: North Bridge and South Bridge.
The main function of the North Bridge:
The connection of the processor with memory, video card and south bridge.
The main function of the South Bridge:
Provides communication between the processor and all other devices (hard drives, expansion cards, usb devices etc).
Currently, there are processors that themselves can perform the functions of the north bridge. Therefore, in motherboards for such processors, there is no north bridge, there is only a south bridge!
Major Chipset Manufacturers:
- Intel
- Nvidia
The main manufacturers of desktop chipsets are Intel and AMD. Some time ago, Nvidia also produced chipsets.
It is impossible to say unequivocally that some direction is better. Both companies have products on the basis of which you can assemble an office and powerful gaming computer.
Therefore, when choosing an architecture, that is, Intel or AMD, a big role is played by the personal preference of the buyer or seller.
Chipset characteristics that affect computer performance

Data bus- this is a bus designed to transfer data between PC nodes.
All computer components interact with the chipset via data buses. Each bus works at its own speed, but the performance of the computer is affected by the bus that connects the chipset and processor. This parameter is the speed of the data bus, indicated as bus frequency or bus bandwidth.
The data bus has two characteristics, frequency and width.
Frequency is the actual speed of the bus. Usually measured in Megahertz or Gigahertz. The higher the frequency, the higher the system performance.
For example: 1333 MHz, 1600 MHz
Width is the number of bytes that the bus can transfer at one time or in one cycle. The larger the width, the more information the bus can transfer in one clock cycle.
For example: 1 Byte, 2 Bytes.
Data bus bandwidth
The product of frequency and width gives one more parameter - data bus bandwidth.
Frequency * Width = Data bus bandwidth - the amount of information that the bus can transfer per second.
Example #1: Frequency 4 GHz and Width 1 byte - we get throughput, 4*1=4 GB per second (4Gb/s or GB/s).
Example #2: Frequency 2 GHz and Width 2 bytes - we get the throughput, 2 * 2 = 4 GB per second (4Gb / s or GB / s).
That is, at a lower frequency, but a larger width, we will get the same bandwidth of the data bus. For the processor, these two performance options are equivalent.
Due to the fact that the new chipsets implemented a new data bus architecture. Was introduced new parameter Bus Operations - Transfers per second.
Transfers per second
Transfers per second is the number of data transfer operations per second.
This parameter also refers to the throughput, but it already means not the volume, but the number of operations that the bus can transfer per second.
Usually the number of transfers per second is twice the frequency of the data bus.
For example: 5200 MT/s, 5200 MT/s (Mega transfers per second)
5.2 GT/s, 5.2 GT/s (Gigatransfers per second)
In the description of the motherboard, the maximum possible speed of the data bus that connects the processor and chipset is indicated. In fact, the speed of the bus will depend on the installed processor. This is due to the fact that the processor has the same characteristic as the bus frequency or bus speed. If it is lower than that of the chipset, then the speed of the data bus will be the same as that of the processor.
How is the chipset indicated in the description of the board
Chipset Specifications short description:
ASUS P7H55-V;S1156; without FFD!; Support Core i3,i5,i7; HH5 ; 4DDR3(2200*); 1xP-Ex16, 3xP-Ex1; 3xP; 8ch sound; gigalan; 6xSATAII; 1xATA100; ATX
Usually the chipset is already listed in the name of the motherboard: ASUS P7H55 -V and then it is listed in the short description after , and in more detail in the full description of the board.
Chipset Specifications in Detailed Description:
- System bus frequency
- Bus frequency
- Data gyna frequency
- system bus
- Front Side Bus, QPI, Hyper Transport
Many people think: if you are interested in how to choose a motherboard, they call you “lamer” on our Internet. Specialists and rather savvy amateurs do not need to search for information about the choice due to the already existing baggage of knowledge, ordinary users - due to the lack of need for this knowledge. And lamers are sure of themselves and without knowledge. This is partly true, but sooner or later, any computer user needs to replace the motherboard and the opportunity to contact a specialist disappears. In addition, relying on someone else's competence, you can seriously miscalculate. Well, not all the same to blame on someone else's uncle? Let's figure it out on our own.
First, let's clarify some points. By choosing your own motherboard, you:
- realize that all other existing components may or may not fit it;
- know a little about state of the art component market and its trends;
- soberly assess your own abilities in relation to assembly and the possibility of a wallet;
- exclude for a number of reasons the appeal to specialists;
- assume responsibility for incorrect selection and incorrect assembly.
Do you agree? Then we go to the store or to the catalog.
Focusing on the processor
The motherboard is very closely related to the rest of the components, because the aspects of its choice depend on the aspects of choosing a processor, RAM sticks, drives, a power supply, even a case. It is simply impossible to connect more closely - the whole system is united and interacts precisely thanks to the motherboard. Did you feel responsible? Let's start with the main thing - from the central processor.
This is the very first step of choice - to decide which manufacturer win today. Mutual compatibility of motherboards with processors different manufacturers(fortunately there are only two of them - Intel and AMD) no. Preferences here are only personal, including in relation to system performance. Both AMD and Intel fully present their processors for a variety of tasks. If you have not decided on the “stone” in advance, be prepared that you will have to choose it for the motherboard.
In addition, maternal Intel boards and AMD are not universal even for the lines of one manufacturer. Here they are defined by a socket - a socket into which the processor itself sits. To date, LGA 1150, LGA 1155, LGA 775 (actively obsolete), LGA 2011 for Intel and AM3 +, FM2 for AMD are considered relevant. There are others, they are less common, sometimes designed for very specific tasks or assembly options. It is impossible to put the processor in the wrong socket in any way, so be extremely careful about this. However, motherboard manufacturers report immediately for which processors it is intended specific model and their recommendations must be followed.
Choosing a chipset
If the performance of the system does not depend on the processor socket (you can install any of the suitable ones), then the chipset is the main player in this field. In fact, this is a chipset that provides data exchange between all components. On motherboards for Intel processors and chipsets, they are soldered from the same manufacturer; NVidia also works for AMD. The choice here is from the tasks and from the budget.
Actually, the chipset determines the capabilities of the motherboard, its support for technologies. Most of the current chipsets for current processors can work with the processor's integrated graphics and provide video outputs. This is one of their main advantages, because with a low bar of requirements it allows you to save a lot on a video card due to the fundamental absence of one. The chipset is also responsible for the bandwidth of the memory buses, the maximum and minimum frequencies of its operation, the possibility of overclocking the processor and RAM, and the functionality of the graphics system.
The higher the performance of the chipset, the higher the price. As a rule, the chipset marking is placed in the name of the motherboard, and today you can be guided by it: for example, Intel positions B chipsets as intended for office and undemanding home systems (minimum price with average performance), H for home multimedia and gaming solutions, Z - for overclocking and other abuse of the computer. The more modern the chipset, the higher its serial number. Today, the seventh series of Intel is relevant, but they are updated quite quickly.
Unlike Intel, which reduces the chipset to a single denominator (single northbridge chip), AMD still divides its chipsets between northbridge and southbridge. The fundamental difference is in the implementation of controller control - in the first case, it is given to the processor, in the second (AMD) - directly to the chip. You can only compare on the basis of features and price. Today, chipsets with the 900 series number can be considered promising and relevant, which are also divided by functionality within the line.
The need for a detailed study of chipsets for regular user no: all their main features are listed in the characteristics of the motherboard. You can also focus on price tags: truncated functionality means lower cost, extended functionality means more.
Focus on form factor
Size matters! It's just called the form factor. Most models are presented in ATX and mATX form factors. The first of them is full-sized (usually 30.5 x 24.4 cm), the second is compact (24.4 x 24.4 cm). The number of expansion slots and soldered ports depends on the size of the motherboard. But the main thing is compatibility with the case system block. ATX is for FullTower and MidiTower, mATX is for MidiTower and MiniTower. The mounts are universal, and a small-sized one can be easily installed in a large case, but a full-sized one can be squeezed into a compact version, but with significant inconvenience.
There are also mITX boards designed for desktop system units (17 x 17 cm), they are compatible with full-sized cases, but their capabilities are often cut down to the limit due to energy savings and cost of cooling resources.
Inside view
Power supplies are connected to motherboards via a 24 pin interface (sometimes outdated models after 20 pins). Performance solutions require powering the processor and graphics card, so if you already have a PSU, make sure it has the required cables. For budget and undemanding solutions, almost any power supply is suitable, as long as 24 pins are present.
Slots and interfaces for connecting and powering directly on the board require attention, especially if the motherboard is purchased in the process of upgrading an old system. In addition to studying the manufacturer's recommendations regarding the supported memory and processors, it is necessary to study the motherboard externally. The number of memory slots, SATA ports and their format, the number of PCI-E and PCI slots are important points, although not so critical.
An important detail is the type of RAM that the motherboard supports. Today, the only DDR3 is relevant, and boards with DDR2 may not be available for sale. If we are talking about upgrading an old system, then the memory strips from the dusty block simply will not fall into their intended places.
The more slots for RAM sticks, the more RAM you can add to your system. The more memory, the better the performance. For home and office systems, more than two slots are not required, for gaming systems four are vital (or you will have to buy larger memory modules to replace the old ones). You can put up to 32 bars in server computers, but these solutions are already production ones, you won’t find such monsters either at home or in the office, or at the gamer’s. The more memory slots, the more space they take up, so they don’t fit a lot on small boards.
The same applies to PCI-E x16 slots designed for installing discrete graphics cards. Productive solutions support SLI and CrossFire technologies, allowing installation and parallel operation of two or three video cards. Naturally, this requires an increase in power supply, an improved cooling system and space inside the case. And, of course, the need. If resource-intensive games and applications for working with graphics are not your area, then the number of PCI-E x16 more than one is superfluous. The PCI-E version (the latest 3.0) doesn't really matter, except for solving super-tasks. For home systems, PCI-E 2.0 is more than enough.
PCI-E x8, PCI-E x4, PCI - slots used to connect expansion cards for various purposes. The more of them, the more opportunities to add components that were not originally provided. For example, brackets with USB sockets, SATA controllers with additional ports, TV tuners, modems, sound cards. Naturally, all this wealth takes up a lot of space, and the smaller the board itself, the fewer expansion slots it has.
SATA ports are used to connect drives, optical drives, card readers. When choosing a motherboard, please note that up-to-date interface is SATA 3 (or SATA 6 Gb / s), so it is very unreasonable to purchase a motherboard without its support. It provides a high speed of data exchange, has no compatibility problems, so a few extra hundreds of rubles for its implementation will pay off completely. Also note the number of SATA ports - with the modern amount of file storage, additional hard drives are not at all a luxury, but they need to be connected somewhere. Four is not enough, very few.
outside view
Rear panel connectors are one of the main interests of a potential buyer when choosing a motherboard. It is easy to navigate here - either knowing in advance what peripherals are available, or planning what exactly to purchase. Or already then adjust to the capabilities of the motherboard.
Most users no longer need outdated COM and LPT ports, but if there is a need for them, there are also such board models. If you haven’t found it, don’t panic, the old printer can be connected via an external bracket inserted into the PCI. But the number of USB should always exceed expectations, given the growing number of connected equipment through this interface. If the motherboard supports USB 3.0, at least a pair of blue connectors must be present on the rear panel. The eSATA port is very interesting, allowing hot plugging/switching off devices.
PS/2 input device ports do not give up their positions. True, many motherboard models provide one universal one, so you have to connect either a mouse or a keyboard via USB. When choosing a motherboard, consider how your peripherals are connected.
Motherboards with integrated video are very convenient in terms of the lack of discrete graphics cards. Accordingly, the presence of video outputs is a settled issue, it is only important what they will be. Standard D-Sub does not provide quality, so the presence of HDMI on the rear panel will be a blessing in sight for the future.
Manufacturers outside the filter
Asus not rolling? MSI hot? Gigabyte smart with chipsets? You should not listen to such generalizing maxims when choosing a motherboard in a store. If you want to know about reliability - determine the desired model by its characteristics and get acquainted with the reviews about it. Manufacturers assemble motherboards from identical components, and the differences can only be in the placement of slots and ports and the color of the textolite. Some models are more productive, some less - it does not depend on the vendor, only on the components.
The main difference between motherboards from different manufacturers lies in the attitude towards the consumer. Market leaders supply their products with everything that the soul of the buyer can wish for, offer free branded high-quality software, provide a long-term warranty with other nice “buns”. The laggards are traditionally greedy. Marriage occurs in absolutely everyone, and it is not uncommon for batches of motherboards to be recalled due to flaws or chipset jambs. Reputable vendors make replacements for free or plug holes with some bonuses.
All other components are connected to the motherboard, the service life and stability of the entire computer depends on it. In addition, it should allow you to connect all the necessary devices and make it possible to improve the computer in the future.
Some of the best motherboards are made by ASUS, but they are also the most expensive. Today, mothers are optimal in terms of price / quality ratio. MSI boards, and I will recommend them first of all. Motherboards from ASRock and Gigabyte can be considered as a more budget option; they also have successful models. Gaming motherboards have better sound and network card.
For Intel processors on socket 1151
Optimal option: MSI B250 PC MATE
MSI B250 PC MATE
Or a gaming motherboard: MSI B250 GAMING M3
MSI B250 GAMING M3
Or a gaming motherboard: MSI Z270 TOMAHAWK
MSI Z270 TOMAHAWK
For AMD processors on socket AM4
Optimal option: MSI B350 PC MATE
MSI B350 PC MATE
Or a gaming motherboard: MSI X370 GAMING PRO CARBON
MSI X370 GAMING PRO CARBON
2. The basics of choosing the right motherboard
You should not install a powerful processor on the cheapest motherboard, as the motherboard will not withstand heavy loads for a long time. Conversely, the weakest processor does not need an expensive motherboard, as it is money thrown away.
The motherboard must be selected after all the others have been selected, since it depends on them what class the motherboard should be and what connectors should be on it for connecting the selected components.
Each motherboard has its own processor that controls all the devices connected to it and is called the chipset. The functionality of the motherboard depends on the chipset and it is selected depending on the purpose of the computer.

3.1. Chipset Developers
Chipsets for modern motherboards are developed by two companies: Intel and AMD.
If you chose Intel processor, then the motherboard must be on an Intel chipset, if AMD - on an AMD chipset.
3.2. Intel chipsets
The main modern Intel chipsets include the following.
- B250/H270 - for office, multimedia and gaming PCs
- Q270 - for the corporate sector
- Z270 - for powerful gaming and professional PCs
- X99/X299 - for very powerful professional PCs
For most computers, motherboards based on the B250 and H270 chipsets are suitable. The Q270 chipset features support for special security features and remote control, which is unnecessary for ordinary users.
The Z270 chipset allows you to change the processor multiplier (with the “K” index) and supports memory with a frequency above 2400 MHz, which is not available on other chipsets. In addition, the Z270 chipset has more PCI-E lanes, which is in demand in high-end gaming PCs with multiple graphics cards.
Motherboards based on X99/X299 chipsets are needed only for heavy-duty and expensive professional PCs with processors on sockets 2011-3/2066, respectively (we will talk about this below).
3.3. AMD Chipsets
The main modern AMD chipsets include the following.
- A320 - for office and multimedia PCs
- B350 - for gaming and professional PCs
- X370 - for enthusiasts
The A320 chipset does not have the ability to overclock the processor, while the B350 does. Well, the X370 is equipped with large quantity PCI-E lanes for installing multiple video cards.
3.4. How are chipsets different?
Chipsets have a lot of differences, but we are only interested in their conditional division by purpose in order to select a motherboard that matches the purpose of the computer.
We are not interested in the rest of the chipset parameters, since we will focus on the parameters of a specific motherboard. After choosing a chipset for your needs, you can start choosing a motherboard based on its characteristics and connectors.
4. Motherboard manufacturers
The best motherboards in the above-average price range are made by ASUS, but they are also the most expensive. Motherboards entry level this company pays less attention and in this case it is not worth overpaying for the brand.
MSI's motherboards are distinguished by a good price / quality ratio in the entire price range.
As a more economical option, we can consider motherboards from Gigabyte and ASRock (a subsidiary of ASUS), they have a more loyal pricing policy and they also have successful models.
Separately, it is worth noting that Intel itself produces motherboards based on its chipsets. These motherboards are of stable quality but low functionality and higher price. They are in demand mainly in the corporate sector.
Motherboards from other manufacturers are not so popular, they have a more limited the lineup And I don't think it's worth it to buy them.
5. Motherboard form factor
The form factor is the physical size of the motherboard. The main motherboard form factors are: ATX, MicroATX (mATX) and Mini-ITX.
ATX(305×244 mm) - full-size format of the motherboard, is optimal for desktop computer, It has the largest number slots, installed in ATX cases.
MicroATX(244 × 244 mm) - a reduced format of the motherboard, has a smaller number of slots, is installed both in full-size (ATX) cases and in more compact enclosures(mATX).
Mini-ITX(170x170mm) - super compact motherboards for building very small PCs in appropriate cases. It should be taken into account that such systems have a number of limitations in terms of component size and cooling.
There are other less common motherboard form factors.
Processor socket (Socket) is a connector for connecting the processor to motherboard. The motherboard must have the same socket as the processor.
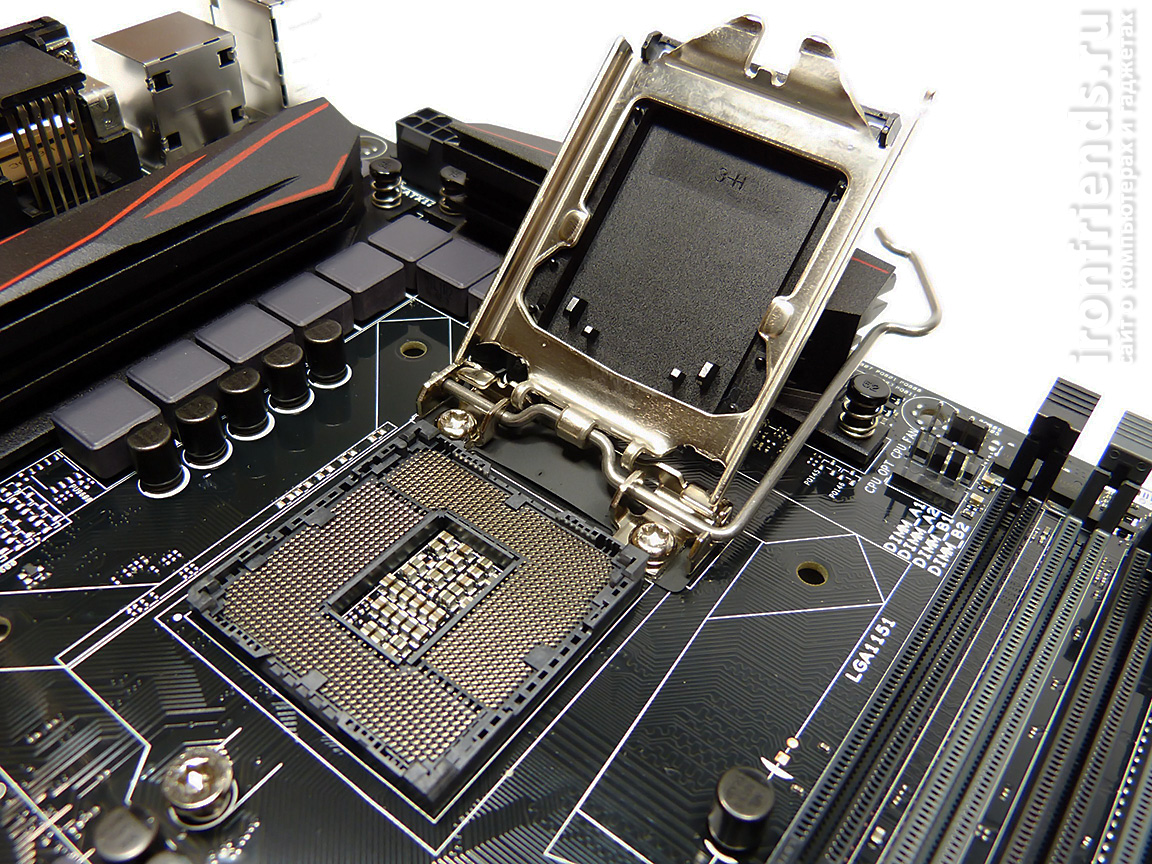
Processor sockets are constantly undergoing changes and new modifications appear from year to year. I recommend purchasing a processor and motherboard with the most modern socket. This will ensure that both the processor and the motherboard can be replaced in the next few years.
6.1. Intel processor sockets
- Deprecated: 478, 775, 1155, 1156, 2011
- Obsolete: 1150, 2011-3
- The most modern: 1151, 2066
6.2. AMD processor sockets
- Legacy: AM1, AM2, AM3, FM1, FM2
- Obsolete: AM3+, FM2+
- Most modern: AM4
Compact format motherboards often have 2 memory slots. Large ATX boards usually come with 4 memory slots. Free slots may be needed if you plan to add memory in the future.
8. Type and frequency of supported memory
Modern motherboards support DDR4 memory. Inexpensive motherboards are designed for a lower maximum memory frequency (2400, 2666 MHz). Medium and high-end motherboards can support more than high frequency(3400-3600 MHz).
However, memory with a frequency of 3000 MHz and higher is much more expensive, while not giving a noticeable performance boost (especially in games). In addition, there are more problems with such memory, the processor can work with it less stably. Therefore, overpaying for a motherboard and high-frequency memory is advisable only when assembling a very powerful professional PC.
Today, the most optimal in terms of price / performance ratio is DDR4 memory with a frequency of 2400 MHz, which is supported by modern motherboards.
9. Connectors for installing video cards
Modern motherboards have a PCI Express slot (PCI-E x16) latest version 3.0 to install video cards.

If the motherboard has several of these connectors, then you can install several video cards to increase performance in games. But in most cases, installing one more powerful video card is the preferred solution.
Also, free PCI-E x16 slots can be used to install other expansion cards with a PCI-E x4 or x1 slot (for example, a fast SSD or a sound card).
10. Slots for expansion cards
Expansion card slots are special connectors for connecting various additional devices, such as: TV tuner, wifi adapter and etc.
Older motherboards used PCI slots to install expansion cards. Such a connector may be needed if you have such boards, for example, a professional sound card or TV tuner.

Modern motherboards use PCI-E x1 slots or extra PCI-E x16 slots to install expansion cards. It is desirable that the motherboard has at least 1-2 such connectors that do not overlap with the video card.
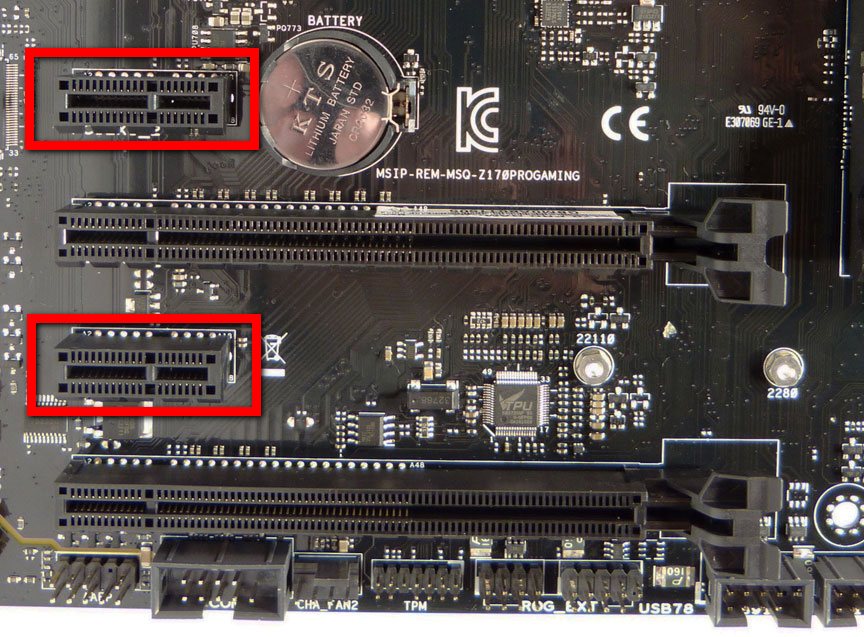
In a modern computer, the old-style PCI connectors are not required, since any device with a new PCI-E connector can already be purchased.
The motherboard has many internal connectors for connecting various devices inside the case.
11.1. SATA connectors
Modern motherboards have universal SATA 3 connectors that are great for connecting hard drives, solid state drives(SSD) and optical drives.

Several of these connectors can be placed in a separate block, forming a combined SATA Express connector.

This connector was previously used to connect fast SSDs, but any SATA drives can also be connected to it.
11.2. M.2 connector
Also, many modern motherboards are equipped with an M.2 connector, which is used mainly for ultra-fast SSDs.
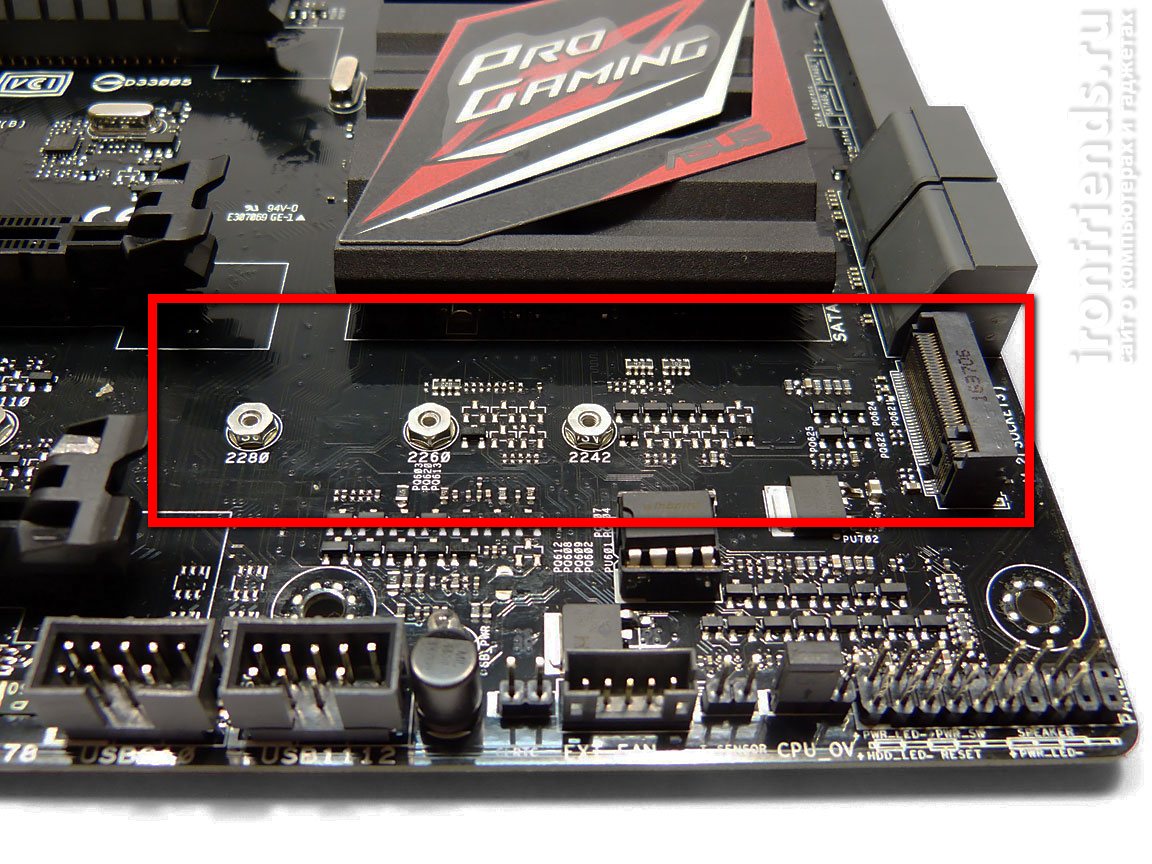
This connector has mounts for mounting cards of various sizes, which should be considered when choosing an SSD. But now only the most common size 2280 is commonly used.
It's also good if the M.2 connector supports both SATA and PCI-E modes, as well as the NVMe specification for fast SSDs.
11.3. Motherboard power connector
Modern motherboards have a 24-pin power connector.

All power supplies are equipped with the same connector.
11.4. CPU power connector
The motherboard may have a 4 or 8 pin CPU power connector.

If the connector is 8-pin, then it is desirable that the power supply has two 4-pin connectors that are inserted into it. If the processor is not very powerful, then it can be powered by one 4-pin connector and everything will work, but the voltage drops on it will be higher, especially during overclocking.
11.5. Location of internal connectors
The picture below shows the main internal motherboard connectors we talked about.

12. Integrated devices
The motherboard, in addition to the chipset and various connectors for connecting components, has various integrated devices.
12.1. Integrated graphics
If you decide that the computer will not be used for games and do not purchase a separate video card, then the motherboard must support processors with a video core and have the appropriate connectors. Motherboards designed for processors with a video core may have VGA, DVI, DisplayPort, and HDMI connectors.

It is desirable that the motherboard has a DVI connector for connecting modern monitors. An HDMI connector is required to connect a TV to a computer. Please also note that some budget monitors only have a VGA connector, which in this case should also be on the motherboard.
12.2. Integrated sound card
All modern motherboards have an HDA class audio codec ( high definition Audio). The corresponding audio codecs (ALC8xx, ALC9xx) are installed on budget models, which, in principle, are enough for most users. Better codecs (ALC1150, ALC1220) and a headphone amplifier are installed on more expensive gaming motherboards, which give higher sound quality.
Motherboards usually have 3, 5, or 6 3.5mm jacks for connecting audio devices. An optical and sometimes coaxial digital audio output may also be present.

For connecting 2.0 or 2.1 system speakers. 3 audio outputs are enough.
If you plan to connect multi-channel acoustics, then it is desirable that the motherboard has 5-6 audio connectors. An optical audio output may be required to connect to a high quality audio system.
12.3. Integrated network card
All modern motherboards have a built-in network card with a data transfer rate of 1000 Mbps (1 Gb / s) and an RJ-45 connector for connecting to the Internet.

Budget motherboards are equipped with corresponding Realtek network cards. More expensive gaming motherboards may have higher quality Intel, Killer network cards, which has a positive effect on ping in online games Oh. But often the work of online games depends more on the quality of the Internet than on the network card.
It is highly desirable to connect to the Internet through, which will repel network attacks and increase the protection of the motherboard from electrical breakdowns by the provider.
12.4. Integrated Wi-Fi and Bluetooth
Some motherboards may have built-in Wi-Fi and bluetooth adapter. Such motherboards are more expensive and are used mainly for assembling compact media centers. If you don't need this functionality now, then correct adapter can be purchased later if the need arises.

13. External motherboard connectors
Depending on the number of integrated devices and the class of the motherboard, it may have different connectors on the rear panel for connecting external devices.
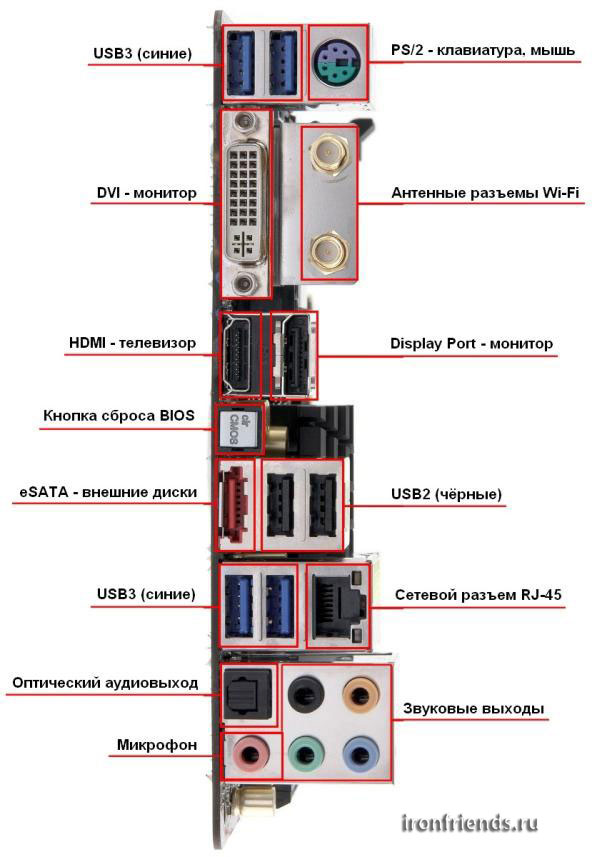
Description of connectors from top to bottom
- USB 3.0- connector for connecting fast flash drives and external drives, it is desirable to have at least 4 such connectors.
- PS/2- the old connector for connecting a mouse and keyboard, is no longer on all motherboards, is optional, since modern mice and keyboards are connected via USB.
- DVI– a connector for connecting a monitor in motherboards with integrated video.
- Wi-Fi Antenna Connectors- available only on some expensive boards with a Wi-Fi adapter.
- HDMI- a connector for connecting a TV in motherboards with built-in video.
- display port– a connector for connecting some monitors.
- BIOS reset button- optional, used when the computer freezes during overclocking.
- eSATA– used for external drives with the same connector, optional.
- USB 2.0- a connector for connecting a keyboard, mouse, printer and many other devices, 2 of these connectors are enough (or USB connectors 3.0). Also on modern motherboards there may be USB 3.1 connectors (Type-A, Type-C), which are faster, but still rarely used.
- RJ-45- socket for connection to local network or internet is required.
- Optical audio output- for connecting high-quality acoustics (speakers).
- Sound outputs– for connecting audio speakers (2.0-5.1 system).
- Microphone- connection of a microphone or headset, there is always.
14. Electronic components
Cheap motherboards use the lowest quality electronic components: transistors, capacitors, chokes, and so on. Accordingly, the reliability and service life of such motherboards are the lowest. For example, electrolyte capacitors can swell after 2-3 years of computer operation, which leads to malfunctions and the need for repair.
Medium and high-end motherboards may use higher quality electronic components (such as Japanese solid capacitors). Manufacturers often emphasize this with some slogan: Solid Caps (solid state capacitors), Military Standard (military standard), Super Alloy Power (reliable power system). Such motherboards are more reliable and can last longer.
15. Processor power circuit
The power scheme of the processor determines how powerful the processor can be installed on a specific motherboard without the risk of overheating and premature failure, as well as power drawdown when overclocking the processor.
A mid-range motherboard with a 10-phase power scheme can handle non-extreme overclocking of a processor with a TDP of up to 120W. For more voracious stones, it is better to take a motherboard with a 12-16 phase power system.
16. Cooling system
Cheap motherboards either don't have heatsinks at all, or have a small heatsink on the chipset and sometimes mosfets (transistors) near the CPU socket. In principle, if you use such boards for their intended purpose and install the same weak processors on them, then they should not overheat.

On mid-range and high-end motherboards with more than powerful processors I wish the radiators were bigger.

17. Motherboard firmware
Firmware is a built-in firmware that controls all the functions of the motherboard. Already, many motherboards have switched from BIOS firmware with a classic text menu to a more modern UEFI with a user-friendly graphical interface.
Gaming motherboards also come with a number of advanced features that set them apart from more budget-friendly solutions.
18. Equipment
Usually, a motherboard comes with: a user manual, a driver disk, a blank for the rear panel of the case, and several SATA cables. The complete set of the motherboard can be found on the website of the seller or manufacturer. If you are collecting new computer, then calculate in advance how many and what kind of loops you need, so that if necessary, immediately order them.
Some models of motherboards have an extended package, which can include many different cables and brackets with connectors. For example, at ASUS, such motherboards used to have the word Deluxe in the title, but now they can be some kind of Pro version. They cost more, but usually all these add-ons remain unclaimed, so it’s more expedient to buy a better motherboard for the same money.
19. How to find out the characteristics of the motherboard
All motherboard specifications, such as supported processors and memory, types and number of internal and external connectors, etc. check the manufacturer's website for the exact model number. There you can also see images of the motherboard, by which it is easy to determine the location of the connectors, the quality of the power supply and cooling system. It would also be nice to look for reviews of a particular motherboard on the Internet before buying.
20. Optimal motherboard
Now you know everything you need about motherboards and you can choose the right model for yourself. But I will still give you a few recommendations.
For office, multimedia or gaming computer In the middle class (Core i5 + GTX 1060), an inexpensive socket 1151 motherboard with an Intel B250/H270 chipset will do.
For a powerful gaming computer (Core i7 + GTX 1070/1080), it is better to take a motherboard on socket 1151 with a powerful processor power system based on the Intel B250 / H270 or Z270 chipset (for overclocking). If you want to better sound, a network card and funds allow, then take a motherboard from a gaming series (Gaming, etc.).
For professional tasks such as video rendering and other heavy applications, it is better to take an AM4 motherboard for multi-threaded processors AMD Ryzen on B350/X370 chipset.
Format (ATX, mATX), types and number of connectors, select as needed. Manufacturer - any popular (ASUS, MSI, Gigabyte, ASRock) or based on our recommendations (this is more a matter of taste or budget).
21. Setting up filters in the online store
Thus, you will receive an optimal motherboard in terms of price / quality / functionality that meets your requirements at the lowest possible cost.
