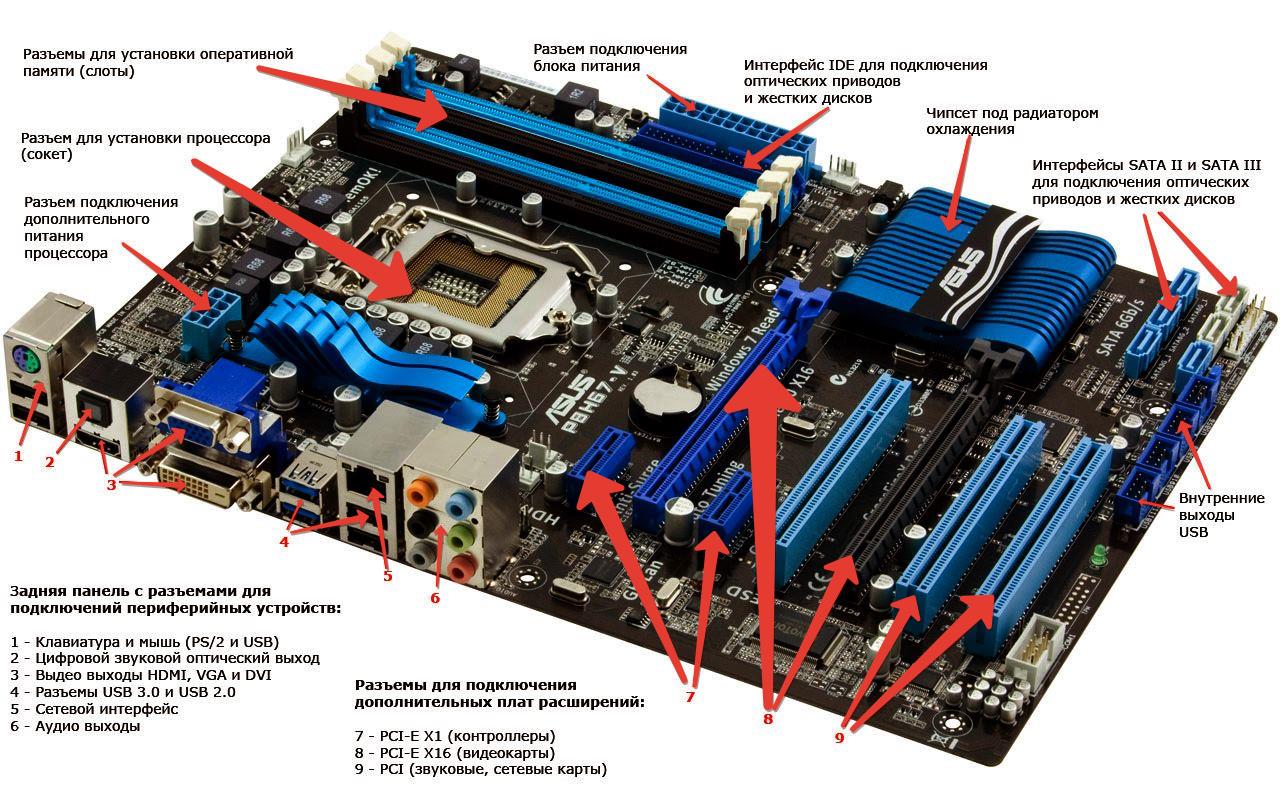
In this article I want to tell you how to choose a motherboard when buying. I will also tell you what the motherboard consists of and how to perform the initial diagnostics. motherboard.
What is the motherboard made of?
Each user should know what a motherboard is, and where what connectors are located, what they are for. Using the foxconn motherboard as an example, I will try to tell you where everything is, and why they are there.

- 1 - a processor is inserted here, and a cooler (fan) is put on top;
- 2 - north bridge;
- 3 - south bridge;
- 4 and 5 - inserted here RAM;
- 6 - a floppy drive is inserted here (there were such before);
- 7 - connector for connection hard drive IDE;
- 8 - connector for connecting hard SATA drive
- 9 - PCI slots (for connecting network, sound cards, TV tuner, etc.);
- 10 - PCI-Express x16 slots (for connecting network, sound cards, Sable, video cards, etc.);
- 11 - PCI-Express x1 slots (for connecting network, sound cards, etc.);
- 12 - connector for the power supply;
- 13 - additional power connector for the processor;
- 14 - power connector for cool video cards;
- 15 - voltage stabilizer;
- 16 - controller for the Fire-Wire interface;
- 17 - controller responsible for audio;
- 18 - controller responsible for the network;
- 19 - BIOS's brain;
- 20 - battery, which is needed for safety BIOS settings;
Motherboard classes
You can divide motherboards into three classes - budget, medium and heaped to the max. Let's break down each class:
budgetary- the motherboard, "truncated", only the main connectors are soldered one at a time, they are well suited for office computers, there is nothing superfluous, not even radiators.

Medium- For ordinary users personal computers, there are all the necessary slots, the bridges are hung with radiators, there are already four memory slots, pci-x in the amount of one piece.

heaped up- It costs absolutely everything that is needed and not needed. Such a motherboard is usually bought by people who do not rummage around in computers at all, sellers just plug it in for them and that's it, gamers and people who are engaged in video editing, design, etc. also love such motherboards.
How to choose a motherboard
When choosing a motherboard, you need to clearly understand what you want to get as an output, as well as provide for the development option. Let's say you have four hard drives, and you plan to buy another one in the future, you need to take into account the fact that there is another additional connector for a future hard drive.
When choosing a motherboard, pay attention to the brand. Let's look at a couple of brands and compare them with each other.
Intel
Global manufacturer. Everyone loves it, the quality is at the highest level, it gives a long-term guarantee for its hardware, but it is expensive in price. The price is too high because this is one of the first companies to enter the market with this product, I would not take the motherboard of this manufacturer, since I am from the middle class.
Asus
A good company that sells high-quality and inexpensive iron. My choice falls on this brand, I always take it. Designed for the middle class of the population.
gigabyte
I came across this company, iron, to put it mildly, disposable. This company loves to release multi-colored parts, so if you see a motherboard in all the colors of the rainbow, pass by.
I had a case: I bought a Gigabyte motherboard, installed it in my computer. Everything worked fine, after half a year I decided to do preventive maintenance of the system unit, disassembled it, cleaned it, lubricated everything, assembled it, and “no signal” =) after that I don’t buy this brand anymore, because. they have low-quality textolite, now there are rumors that everything has been fixed, but I did not check, it was enough for me once.
How to determine if the motherboard burned out
One fine day, you turn on the computer, and it writes “no signal” to you. There can be two reasons: the monitor burned out or something happened to the motherboard.
I think you can guess how to check the monitor, just plug in another one or come up with something else.
How to make an initial diagnosis of the system blog? Let's unwind the system unit, remove the side cover, there you will see your motherboard. We look at it carefully, if there are any swollen capacitors, and these are such round barrels:

Look at the south bridge, if it has been corrected, in general, we look carefully at every detail and, if there is nothing suspicious with the naked eye, then feel free to go to service center and let it be tested. New motherboards are not so easy to burn to see the result, but this is what the motherboards of the past generation looked like after a short circuit.

Or was she put on fire?
I had a case when I was just beginning to learn about the computer. The power cable was disconnected from the floppy disk, and it was necessary to throw off the information from the floppy disk, without hesitation, I open the cover of the system unit, and on a hot one, that is, the computer was turned on, I plug the power connector into the floppy disk, it burned out: the power supply, RAM, hard disk, floppy disk, the processor burned out by half (when it was plugged into another motherboard, windows 98 was not installed on it only windows 95), the motherboard.
Gaming PC Assembly - Motherboard
Also on the motherboard are a sound chip, an I/O chip, a BIOS chip, DIMM slots, and expansion slots.
The I/O chip performs the function of serving the I/O ports.
BIOS (Basic Input / Output System) - a basic input / output system, includes a set of programs, thanks to which the operating system and programs running under this operating system can communicate with devices connected to the computer, as well as with all internal components.
IDE connectors are used to connect drives.
AGP slot - for connecting a video adapter.
PCI slots are used to connect various devices such as a sound card, an additional port card, LAN card and etc.
FDD connector - for connecting a floppy drive.
Expansion slots can be found on older motherboards: ISA, EISA, MCA, VLB.
On modern motherboards, PCI Express x16 slots are installed (used to connect a video adapter); PCI x4, PCI x1 (application similar to PCI).
|
Figure 2.1. Motherboard components(s)

Figure 2.2. Motherboard components (b)
Figure 2.3. Layout of motherboard components
Figure 2.4. Appearance ATX motherboard.

Figure 2.5. External view of the BTX motherboard.
Work order
- Learn how to install the processor.
- Examine the location and purpose of the components of the motherboard.
- Schematically sketch the components of the motherboard.
2. Report on the work according to the order of work.
Control questions
1. List the main installation steps CPU.
2. What is a socket?
3. List the names of the main sockets for Intel platforms that are in use today.
4. List the name of the main sockets for the AMD platform in use today.
5. Which devices and buses are interconnected by the northbridge of the motherboard? Show it on the motherboard.
6. Which devices and buses are interconnected by the southbridge of the motherboard? Show it on the motherboard.
7. What are DIMM slots for? Show them on the motherboard.
8. What is AGP, for which devices is this connector on the motherboard used? Show me this connector.
9. Show the PCI bus connectors on the motherboard. What devices are installed in this bus.
Lab 3
TESTING AND BENCHMARKING
COMPUTER SYSTEMS
Goal of the work: master the SiSoftware Sandra testing program to conduct a comparative analysis of several PCs.
There are many programs for testing PC components.
Classification of testing programs:
1) Determining the characteristics of PC components.
A) Characteristics of hardware components.
An example of testing programs:
SiSoftware Sandra;
B) Definition of system resources.
C) Checking the correct operation of the devices.
2) Performance analysis.
A) Determining the performance of the C.P.
An example of testing programs:
All these tests are "synthetic"
B) Testing in real applications.
An example of testing programs:
C) Test of the graphics subsystem.
An example of testing programs:
D) Encoding, decoding video.
An example of testing programs:
D) archivers.
The CPU-Z program is designed to get information about your processor.
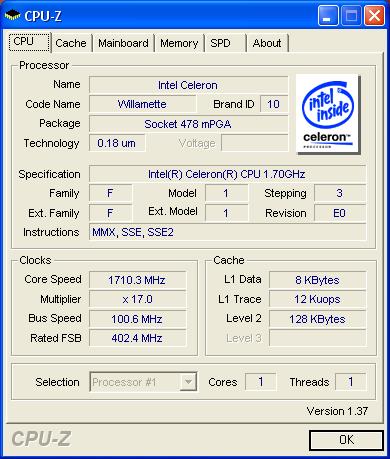
Figure 3.1. CPU-Z test main window
Also in CPU-Z you can find Additional information about the memory cache, some information about the motherboard, memory.
Report creation:
Open About; Select the format in which you would like to receive the report:
Registers Dump - in the form text file;
SiSoftware Sandra
The SiSoftware Sandra program is designed to obtain detailed information about a personal computer, its hardware and software settings.
The program contains the following types of tests:
Information tests
Benchmarks (tests of comparative performance)
Tests of software settings of the computer system
· System resource tests
The working window of the program is presented as a set of shortcuts corresponding to a particular test. To complete the task, we do not need everything, but only those marked in the figure:
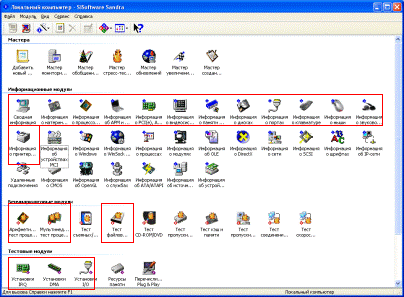
Rice. 3.1. SiSoftware Sandra Testing Paragraph Main Window
By clicking on one of the labels, you will receive a message to wait, then display the information of the selected module on the screen, for example:
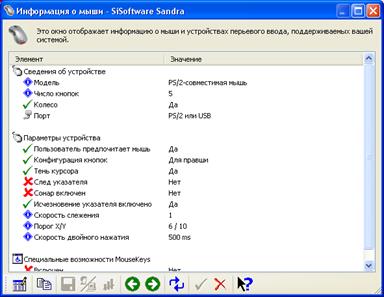
Rice. 3.2. Reference information on the device.
Test all selected labels and carefully review all the information provided.
Pay special attention to benchmarking modules. When they start, you must click the "Update" button (marked in red) and wait for a long enough time.
Compare the performance of your system and several reference systems (select other reference systems from the lists).
These modules are not included in the report in full, so take screenshots of them or rewrite the data of your system and reference ones in the form of a table
Rice. 3.3. Processor Arithmetic Test module window
Create a report
Consider the process of creating a report.
1. Select "File - Report Creation Wizard" from the menu.
3. Select the type "Select parameters and generate a report". And click the "Next" button.
4. Check the required modules (see above). Benchmarks do not need to be marked; it is better to do them manually (see above).
Rice. 3.4. Report Creation Wizard Window (Select Modules for Testing)
5. For all other module selection windows, click the Reset All button.
Rice. 3.5. Report Creation Wizard window
(Choosing where to save the report)
7. Set all parameters as shown in the figure.
Rice. 3.6. Report Creation Wizard window
(Selecting the report data saving format)
8. Enter a name for the file to be saved. Click "OK" and wait a few minutes. After running the program, click "Close".
9. The resulting file is very large, so edit it (in Notepad or other text editor), leaving only the most significant data about the hardware device of the computer.
Work order
2. Create a report on the computer system using the "wizard" of the program. Edit the report, leaving only the most important information.
3. Make screenshots of several benchmarks.
4. Collect information about PC system resources.
1. Theme and purpose of the laboratory work.
2. Report on work according to the order of work.
3. Conclusions on the work on the acquired skills and abilities.
Control questions
1. List the main modules of SiSoftware Sandra.
2. What components are tested by SiSoftware Sandra?
3. What programs can be used to test the graphics subsystem of a computer?
4. What programs test the computer's RAM?
5. What type of programs does the computer's CPU test?
6. What programs do you know for comprehensive testing of the entire PC?
Laboratory work4
CONNECTING DRIVES
Goal of the work: study the features of connecting drives - hard drives, CD ROM drives and floppy drives magnetic disks
Information to get the job done
Hard Disk Drive
Rice. 4.1. Internal view of a hard drive.
Rice. 4.2. The appearance of the hard drive.
Rice. 4.3. The reverse side of the hard drive.
Rice. 4.4. Internal view of an optical drive CD-ROM, DVD-ROM.
Motherboard (system) board- This is a printed circuit board, which is the basis of a computer, located at the bottom of the computer case. It distributes power to the processor, RAM, and other hardware components. Most importantly, the motherboard allows hardware components to communicate with each other.
The first motherboard was used in a personal computer from IBM, released in 1981. Further, the motherboard will become the standard for IBM computer technology.
Below is a photo from the ASUS P5AD2-e with the names of each of the main components of the motherboard.
motherboard components. Below is information for each of the above motherboard components.
- PCI Express. The PCI Express connector is a serial bus designed to replace the PCI and AGP bus and is available in various formats: x1, x2, x4, x8, x12, x16 and x32. PCI Express x16 supports throughput up to 4000 Mbps in both directions.

- PCI. Used in computers from the late 1990s to the early 2000s, the PCI bus has since been replaced by PCI Express. As you can see, there are three PCI slots: PCI4, PCI5, and PCI6.

- AGP. AGP is a port designed for video cards and 3D accelerators. Developed by Intel and introduced in August 1997.

- 3-pin fan connector (3-pin fan Connectors). I think there is no need to explain why a fan is needed in a computer. But it looks like this:

- (Back panel connectors) designed to connect external devices(monitor, speakers, other devices connected to the usb port)
- Heat sink, radiator (heatsink) on the motherboard, as a rule, passive, that is, without a fan.

- P4 power connector. P4 - power connector with constant voltage 12V.
- Inductor (Inductor) used to smooth out the voltage on the board.

- (capacitor) is an element made of two or more conductive plates with a thin insulator between them and wrapped in a ceramic and plastic container.
- Processor socket (Soccet)- This is a connection that allows you to connect a processor to the motherboard.
- Northbridge (northbridge) is a microcircuit responsible for communication between the CPU, AGP and memory.
- (memory slot) designed to connect the RAM to the computer. The motherboard can have from 2 to 4 slots. The most common types of RAM are SDRAM and DDR memory.
- Super I/O integrates interfaces of various low-frequency devices.
- Floppy connector slot is a computer ribbon cable slot that allows you to connect one or more drives to a single controller.
- ATA (IDE) connector— interface for hard disks and CD/DVD drives.
- ATX connector- the computer's power supply is connected to it.
- sATA came to replace the ATA connector, capable of delivering 1.5 Gb / s (1500 Mb / s) through a disk array. Has an external eSATA option.
- CMOS battery, sometimes called a real time clock (RTC), is designed to power the board when the device is turned off to save basic information (date, time, basic system settings). Standard CMOS battery life is about 10 years.
- ATA Raid allows you to create an array of hard drives, used on servers and high-performance computers.
- System connector panel contains connectors for the power button, reset, feeds the LED.
- Firmware Hub (FWH)- a hub containing the system BIOS and a hardware random number generator (data encryption).
- Southbridge (southbridge)- this microcircuit on the motherboard is responsible for the hard drive, controller, I / O controller and complex equipment. Integrated equipment may include sound card and video card.
- Serial port(also asynchronous port) on a computer is used to connect a serial device to a computer and is capable of transmitting one bit at a time.
- 1394 header/ usb headers— connectors are designed to connect additional IEEE 1394 and USB ports.

The main and most important elements of a personal computer, or to be more precise, the system unit: a video card, a central processor, RAM modules and a large number of microcircuits are located on the system board, and its more common name is the motherboard.
Getting close to the question what is a motherboard, you can answer this way - this is the main motherboard of the computer, which has connectors for installing additional expansion cards and serves as the mechanical basis for the entire electronic circuit of the computer. Thanks to the motherboard, the full interaction of the components of the computer system is ensured.
What might a motherboard be used for?
It is simply impossible to underestimate the value of the motherboard, all the components of the computer system unit interact with each other thanks to the motherboard, so the data from the hard disk cannot be processed in the processor before it gets into the RAM, and the graphics adapter will have nothing to receive from the computer system and subsequently transferred to the monitor. The most common input devices, such as a mouse and keyboard, also exchange information through connectors on the motherboard.
A good example would be the already obsolete IDE connectors and all SATA revisions, because an optical drive is connected to them, HDD or solid state drive with the help of special loops, and subsequently they participate in the information exchange with the processor, and then with other devices.
Maybe earlier the overall performance depended on the processor, but now the situation has changed. You need to focus on the capabilities of the motherboard, the bandwidth of its bus, the supported volumes and frequencies of RAM, the ability to get maximum performance from a modern PCI-Express x16 connector and a video card, etc.
Used motherboard form factors and processor sockets
The form factor of the motherboard determines its position for subsequent fastening to the computer case, the location and type of its power connectors, even the number of interfaces for connecting devices and their location. Here is a list of the main used forms - factors of the motherboard:
- Mini ITX - has the smallest average dimensions of 17 by 17 cm, very often already has an integrated processor, the smallest number of connection interfaces, is very rarely used in independent assemblies, more often it is sold already as part of a finished computer.
- mATX (Micro ATX) - a fairly full-featured board with acceptable average dimensions, is the best component for budget computer, although with a fairly small number of interfaces, they should be enough for a home or office computer. Often, these motherboards have a chipset installed that has some limitations, but which are not primarily reflected in the operation of the entire computer.
- ATX - as common as mATX, but larger in size, such boards can have both a fully functional chipset and with slight limitations, usually the largest number interfaces connection, but this is also not mandatory, it is distinguished by more convenient installation and connection options.
The dimensions of the motherboard must be taken into account when choosing a suitable case, because if you think logically, you can install not large motherboards in larger cases, but the opposite will not work.
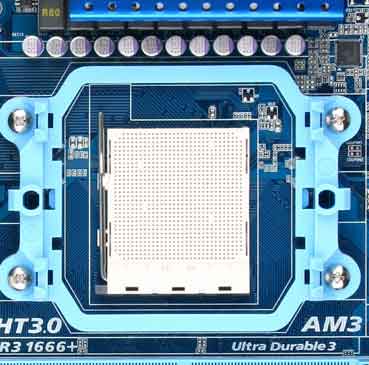
Socket (Socket) is used to install the central processor or replacement. Socket should be considered when choosing the right components for your computer.
The variety of sockets is quite large and each processor will suit its own, for example, the latest Intel processor lines use socket markings LGA 1150 or 1155, and their competitors from AMD - FX2 and AM3, AM3 +. If AMD AM3 and AM3+ sockets are interchangeable, that is, AM3+ processors can work on AM3 motherboard sockets, but performance will be limited by the chipset, then Intel doesn’t have this, you can’t go wrong.
Chipset - the basis of the capabilities of the motherboard
Chipset- this is a microprocessor kit for the interaction of the central processor with the rest of the electronic component of the computer. It is from the chipset that all the possibilities and further operation of the motherboard depend.
Today's chipsets consist of two microcircuits, called the southbridge and northbridge, they can be easily found, these are the largest microcircuits after the processor, usually hidden under cooling radiators. The chipset itself must be matched with the processor, which may mean that not every motherboard will be able to unleash the potential of the processor and vice versa.
The very knowledge of the brand and model of the chipset largely determines the future performance of a computer system, therefore, when choosing a motherboard, it is not bad to know its capabilities. The purity on which the system will work also depends on the chipset of the motherboard, as well as the amount of memory, the possibility of installation and the number of additional devices.
What is a BIOS and what is its need
BIOS (from the English. Basic Input Output System), is considered one of the most important microcircuits of the motherboard, because it contains important programs directly from the manufacturer's factory that are required for the initial boot of the computer. After the computer is turned on and power is supplied to the processor, it first of all accesses the BIOS chip and does not stop working with it until the computer is turned off.
To see the BIOS in operation, when starting the computer, you only need to pay attention to white inscriptions on a black background - this will be the BIOS in operation.
What does the BIOS do? This program is necessary to check the main systems of the computer immediately after turning it on, and also provides interaction with the keyboard and mouse, as well as with the monitor, in the case of a laptop, with its display.
To restore the default BIOS settings, you need to remove the independent power battery or use a special jumper, although the jumper and the battery on different boards may be in different places, but most likely they are in the middle or in the lower right corner.
Motherboard tires
How does the processor communicate with other computer devices? In fact, like all wire-based electronics, a group of wires on a system board is called a bus. Buses differ in functionality: command bus, data bus, address bus.
For 32-bit processors, these are 32 parallel conductors, through which programs send commands for processing by the processor through RAM. It is the address bus that should be considered as controlling the rest, because it serves to select both data from RAM and commands.
If you do not take into account external devices, then we can conclude that the processor receives commands from the RAM and exchanges data with it. The processor, except for RAM, considers all other devices external, even if they are part of the system unit. All buses connecting the processor and RAM can be considered as one main bus - FSB (Front Side Bus). Speaking about the fact that the motherboard operates at a frequency of 2000 MHz, it is precisely the frequency of the main bus that is meant, it is from it that the processor receives its frequency and multiplies it by the internal multiplication factor.
Plug-and-play bus
The main and at the same time important advantage of this bus is its high performance and ease of installation of equipment, thanks to it it became possible to create self-controlled devices (plug-and-play).
The bottom line is that after another expansion board, a daughter board, is connected to the motherboard, the device itself is automatically detected and the necessary resources necessary for its correct operation are allocated to it.
PCI and PCI Express buses
Thanks to PCI, even today it is possible to expand the capabilities of your computer by installing TV tuners for watching analog television, which is important in the absence of a permanent connection to the Internet, or an audio card to increase the sound recording functionality of a computer, or maybe a PCI splitter to increase the number USB connectors, which is even more true for outdated or budget motherboards.
But computer technology is developing at an immediate pace, and the usual PCI bus, or to be more precise, its bandwidth has become insufficient for high-performance components. The video card will probably be the most self-sufficient representative of devices for which the appearance of PCI Express 16x became necessary, although other devices, such as a network card, needed an increase in bus frequency.
It became unprofitable to increase the frequency of the PCI bus, since a large number Parallel conductors required their high precision manufacturing, which was costly. In this regard, 2004 marked the beginning of the introduction of PCI Express 16X and PCI Express X1. As a result, the production of motherboards has become easier, and along with this, cheaper, besides, PCI Express 16X has become the only bus for connecting video cards, and PCI Express X1 is an alternative to PCI.
AGP connection interface
At one time, the AGP bus provided high-performance data exchange, but over time, this connector ceased to satisfy video card manufacturers. This connection interface has become widespread, due to the containment computer graphics regular PCI. Although the interface is still used on outdated computers, modern manufacturers have abandoned it in the same way as they once did from PCI in favor of PCI Express.
USB - connection interface
Each user wants convenience when working at a computer, so that the devices are very easy to install, without neglecting to disassemble the system unit itself to install it, this was the reason for the emergence of the Universal Serial Port (USB).
The USB connector in our time is part of any computer, from a desktop, laptop, to a tablet and smartphone, as well as keyboards, monitors and many other devices. This connector makes it easy to use; for even greater convenience, such USB connectors are displayed on the front panel of system units.
In budget motherboards, it happens that there are not enough USB connectors to connect all devices, but for this you can use a splitter or in another way USB hub, there will be much more ports. Thanks to the USB bus, a lot of devices are connected to the motherboard: 3g / 4g modems, printers and scanners, not to mention computer mice and keyboards.
USB 3.0 is read modern, but USB 2.0 is also used, and USB operation- This is a function of the southbridge of the motherboard chipset. As it has already become clear, all the work of the motherboard is tied to the work of its chipset, and every year more and more functional duties fall on the motherboard.
Integrated motherboard components
A lot of computers these days, especially office ones, are equipped with an integrated video adapter, which can properly save money on the purchase of equipment, of course, if special video performance is not required in the future. Thanks to this, VGA, DVI and HDMI, network and audio boards appeared on many motherboards, and they also became an integrated component of the motherboard.
Before buying a motherboard, you should definitely familiarize yourself with its specification on the manufacturer's website, then, for example, you will not have problems with the maximum frequency of operation and the number of RAM module slots, and maybe the ability to connect several video cards will also not be superfluous.
Now the question of what is a motherboard has become less relevant, because there is an understanding that the motherboard is the basis of the entire internal mechanical world, located in system block. The motherboards themselves change every year, supplemented, and it’s simply not possible to describe everything in one article, you have to limit yourself to the main points.
System (motherboard) board of a personal computer
Motherboard ( System board ) - the second most important component in the device of a personal computer. In addition to the term "system board", the name " motherboard" ( mother board ) . The main purpose of the motherboard is to connect all the nodes of the computer into one device, so, by and large, this is just a set of wires between the contacts of the processor and the contacts of the memory modules and peripherals. All other elements located on it have secondary functions, serving only for decoupling and signal coordination. Of course, some block on the motherboard can be proudly called "controller", but even in this case, its purpose is to perform auxiliary functions.
As a rule, the thickness of the conductors is two times less, so the increase in the thickness of the copper bars improves the cooling of the elements of the motherboard, but at the same time there are a lot of technological difficulties. Since modern processors operate with external devices at a frequency of several hundred megahertz, the length and location of printed conductors is now calculated according to the same principles as for microwave devices, when every extra centimeter of the conductor plays a huge role.
Between the processor, RAM modules and external devices is located chipset(chipset) - a set of chips that perform service functions for distributing signals between all blocks. When the supply voltage is applied, the chipset generates a certain sequence of commands that activates the processor. The processor, in turn, BIOS program tests and activates other devices installed and connected to the system board. If the start of the computer was successful, then the chipset chips connect the processor, memory and peripheral devices into a single whole - a computing device ready to execute user commands or react in a certain way to the appearance of signals in the interface lines. The flow of information from the processor to the RAM and vice versa passes through the electronics of the chipset. Even if the chipset has only buffer circuits, they, alas, introduce a small time delay, even if ideally in one clock cycle system bus. For modern computer systems such a delay is already a lot, so first AMD and then Intel transferred the memory controller to the processor chip. With this principle of construction, the processor works directly with the memory, and unnecessary links are eliminated, which increases the overall performance of the system. There are other options for building motherboards, which depend on the architecture of the processor. For example, recently it has become popular to transfer the interface of a video card (for PCI-E) from chipset on circuits located on the processor chip, which speeds up the graphics subsystem. In particular, it is permissible to mount all controllers of external devices on a processor chip, note that such a scheme has been used since Intel processors 80186, but did not take root in desktop computers.
ATX form factor
Oddly enough, the most constant in PC personal computers is the form factor (overall dimensions and arrangement of elements), which, as it were, makes new and old models related to each other. Due to the fact that all developers of motherboards and peripherals adhere to the same rules for fixing boards and locating nodes in the case, users can independently upgrade their computer by installing the necessary peripherals, replacing an old processor with a new one, etc. There are two main standards for motherboards- AT and ATX. The first - the AT form factor - is a board for a computer with an obsolete processor. The second, the ATX form factor, is the standard by which new computers are designed. The difference between these two standards is in the location of the processor and interface connectors, which necessitates the use of different cases. But everything else - fixing the motherboard to the case, the location of the slots, etc. - coincides in one way or another. As a transitional option between AT and ATX, for example, motherboards were produced that could be installed both in a case with an AT power supply and in an ATX case. Below is the location of the main elements of a personal computer according to the ATX specification, including version 2.2. In particular, one of the main differences in this version of the ATX specification is that the power supply is out of the circuit system board, which turned out to be necessary due to the huge size of the cooling system of a modern processor. Note that previous versions of the specification allowed for a PSU above the processor, but this caused huge problems with processor cooling.
The situation is somewhat more complicated with small-sized and proprietary computers that use motherboards, the dimensions of which differ from the standard ones (other form factors are used, which are developed on the basis of the ATX form factor). To reduce the size, various techniques are used, for example, reducing the number of slots for peripheral devices, using various adapters to be able to arrange peripheral boards not vertically, but horizontally, parallel to the motherboard plane. For such motherboards and enclosures, there is always the problem of upgrading, often resulting in what is easier to buy new computer rather than looking for suitable elements for the old one. Below are the maximum dimensions PC motherboards, which are most common in Russia.
Form factor |
Max width |
Max, depth |
12.0" (305 mm) |
||
11.2" (284mm) |
Form Factor BTX
In 2004, Intel published the BTX (Balanced Technology Extended) specification, which is an evolution of the ATX standard for new high-performance processors. The main purpose of the specification is to improve cooling and increase the mechanical strength of the motherboard; as defined by the BTX specification. In addition, the specification standardizes the methods of connecting I / O interfaces to the motherboard, the design of the case. Since the appearance of computers made according to the BTX specification implies the development and production of new motherboards, even five years later, the matter has not yet reached any significant industrial production. It can be noted here that the modification PC motherboard- this is a lot of work of developers and engineers, plus a huge amount of product testing, fixing bugs and problems. True, today, when processor developers have finally taken care of the problem of reducing heat dissipation, the introduction of the BTX form factor turned out to be not as relevant as it was necessary for latest versions processors Intel Pentium 4 Prescott and for a range of Intel and AMD quad-core processors.
sockets
Over the past three decades, a wide variety of processors have been released for use in PC personal computers. Some types of processors were so successful that they were produced for a wide variety of applications, such as for installation in laptops and industrial devices. When changing the type of processor or its purpose, a silicon crystal with millions of transistors was mounted in a new package, which had different dimensions and methods of attachment to system board. Unfortunately, the main path of modern microelectronics goes in the direction of increasing the number of contacts supplied with the processor package. Naturally, when the number of pins changes, the design of the processor socket, which is installed on the system board, also changes. If the ancestor of the current processors had only 16 pins and was installed in a very simple connector - a "crib", then the models modern processors overcame the milestone of a thousand contacts. The connector for installing modern processors is called a socket (socket ) . It is also called a ZIF-Zero Insertion Force socket, and the numbers in the marking, starting with the Socket 370 model, indicate the number of contacts. In the recent past, the most popular socket for installing processors was Socket 7, designed for Pentium processors, and Socket 370, in which Pentium III processors were installed. It can be noted that it was permissible to install both Intel processors and AMD processors in Socket 7. For some time, processors mounted on printed circuit boards, which were designed to be installed in special slots, reminiscent of slots for memory modules. For Intel processors, this socket was called Slot 1, and for AMD - Slot A. The earliest models of Pentium 4 processors were designed for installation in Socket 423. Later, Socket 478 (mPGA478) was used for Pentium 4 processors,
In new processors Intel Core i7, released in late 2008, use the same processor and socket pin design, only the number of pins is significantly increased, and the socket name is LGA 1366. In 2009, an LGA 1156 socket was proposed for Intel Core i5 processors
In 2006 for dual-core AMD processors Athlon 64 FX and AMD Athlon 64 X2 with DDR2 memory controller now use Socket AM2 , which differs from previous models in the location of the keys and the additional number of contacts (it has 940 of them); in addition, the cooler mount has changed. Phenom processors use an upgraded socket called AM2+, which is compatible with the AM3 socket. For processors that work with DDR3 memory, the AMZ socket is intended .
 |
Currently, almost the same type of processors are offered for sale. Socket AM2/AM2+/AMZ.In any case, in 2010, as well as in 2007-2009, users will have to make a difficult choice, including for the wallet, for the selection the best option"processor-socket-memory", since an absolutely correct solution is not expected (we should not forget that new processors appear, and with them new sockets). For powerful processors Opteron and AMD64FX designed 1207- Socket F pin connector. Since the sockets look similar to each other, although they differ in the number of contacts and their location, when choosing a "processor-mother" pair, you should definitely study the documentation on personal computer motherboard. The documentation always indicates which types of processors a given motherboard supports. Installing the wrong processor is very likely to damage the processor and motherboard. Of course, in some cases flashing the BIOS can help, but this information You should look on the motherboard manufacturer's website.
Expansion slots
To expand the functions of a personal computer, connectors called expansion slots are installed on the system board. Since the interface for video cards is currently being changed, motherboards are being produced with two options for slot sets: AGP or PCI-Expres x16 , plus a set of regular PCI slots and PCI Express x l . Additionally, a slot option with Wi-Fi functions (for creating wireless networks) can be installed. Other types of slots are found only in obsolete computers or on special-purpose boards.
To install most types of peripheral devices in a modern personal computer, PCI slots(Peripheral Component Interconnect). Most often there are 2-3 PCI slot, but there are variants with 5 and 6 PCI slots. In small-sized designs, the number of PCI slots can be reduced to one or two. Despite the fact that there are several options for PCI slots that differ in the supply voltage for peripheral boards, clock frequency and bit depth, in practice, in most cases, only one option is used, which is designed for 5-volt boards with a clock frequency of 33 MHz. True, sometimes there are motherboards with PCI slots with a clock frequency of 66 MHz, but it is quite acceptable to install ordinary peripheral devices in such slots.
The AGP slot is intended for installing video cards with AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) interface. When using an AGP slot, users should be aware that a special plastic latch must be used to securely fasten the card so that the AGP card does not come out of the slot when installing PCI cards. It makes sense to buy a motherboard with an AGP slot only for upgrading an old computer. ATTENTION! There are three variants of the AGP slot, differing in electrical parameters and keys (jumpers on the slot). Unfortunately, a number of video cards with AGP interface are not compatible with motherboards that do not have their version of the AGP specification. In severe cases, not only the video card, but also the motherboard can burn out.
In 2004, Intel Corporation began implementing the specification PCI Express slot, which turned out to be very convenient for developers and users. Accordingly, at present, most motherboards are produced with PCI Express slots. There are several options for this type of slots: x16, x8 or xl. The PCI Express x16 slot is designed to install a high-performance video card. Differs from its successor, the AGP slot, with increased bandwidth and direct bi-directional data transfer. Together, these two parameters increase the bandwidth of the bus at least twice. Recently, 2 PCI Express slot x16 (or 2 PCI Express x8 slots), which allows using two video cards in synchronous mode, for example, for NVIDIA SLI (Scalable Link Interface) technology. The PCI Express xl slot is designed to install other peripherals. PCI Express slot x8, is intended for installing peripheral devices that require bus speed, such as RAID controllers, as well as video cards. .
According to AC97 specification on a number of motherboards one AMR (Audio/Modem Riser) or CNR (Communications and Networking Riser) slot can be mounted sound cards or internal modems. Its location is not specifically specified. In some cases, such a slot is installed close to the slot PCI, which is not always convenient for the user. Indeed, it should be noted that given type The slot has not received any wide distribution, and is now quietly "died".
ISA (Industry Standard Architecture) slots, which should still be mentioned, since users still have many boards with such an interface, appeared in the very first IBM PC computers. For a long time, ISA slots were the most popular among all categories of users, but the efforts of the corporation Intel this type of slot has now become "persona non grata" in the modern computer.
Of course, motherboard manufacturers are experimenting with the arrangement of slots on the board, while remaining within the limits allowed by the ATX specification. As an example, a motherboard manufactured by Gigabyte is shown below. It has 1 slot PCI Express x16 and 2 slots PCI Express x8, which allows you to use two video cards to work together (in .CrossFire mode from AMD, or NVIDIA SLI). Such systems are characterized by increased energy consumption and dissipated thermal power. Two slots for external devices PCI Express xl and x4, and one traditional slot PCI modestly crowded among his "young descendants". At the bottom are connectors for connecting "miscarriages" (cables designed to transfer the interface connector outside the motherboard) of various interfaces. If you read the documentation, you will find that the board is equipped with numerous LED indicators to control the operation of nodes (not only POST operation, but also the level of overvoltage of the central processor, memory, north and south bridges), as well as a huge number of a wide variety of new technologies.
 |
From the novelties that new processors have brought Intel Core i7, three-channel memory can be noted, which allows you to mount 6 slots for installing memory modules. In addition, we can say that, oddly enough, the FDD interface for the floppy drive remains, although now only a few users use it, but for compatibility with old equipment, the board is equipped with only one IDE connector. But in the near future, it will most likely be difficult to find a new system board with a connector for a floppy drive.
Chipset
In order for the processor in a personal computer to work at full capacity, it needs the help of specialized microcircuits that take over the routine work with RAM and peripherals. A set of such chips is called chipset (chipset). The chipset kit may include a different number of microcircuits, but recently the most popular solution is 1-2 microcircuits.
For two basic chips of modern chipset, purely conditionally, the names South Bridge (south bridge) and North Bridge (north bridge) were coined, which originated from the location of the chips on the block diagrams: top-north, bottom-south. The most curious thing is that such names have taken root and have become widely used not only by specialists, but also by users.
From the point of view of specialization, the functions of the exchange between the processor and high-speed devices, such as memory and the PCI Express or AGP bus, fall on the north bridge. The south bridge is designed to work with low-speed interfaces. To exchange information between the north and south bridges in modern computers different types of high-speed buses are used, which are different for each chipset developer, for example, for VIA chipsets, this is V-Link, SiS - MuTIOL (Multi Threaded I / O Link). Previously, communication between bridges was carried out through the PCI bus, but the data transfer rate through it is simply not enough for modern technologies.
When studying the capabilities of chipsets, users should pay attention to the fact that if earlier the development of a new chipset was marked by a significant increase in computer performance and the emergence of new functions, then at present developers profess the ideology of "creeping" modernization, when the next type of chipset differs little from its predecessor. In other words, the new chipset improves one function or adds support for one or another standard, for example, work with one or another memory. In addition, there is a development within one type of chipset of a whole set of chips (several options for south and north bridges), which manufacturers motherboards can be arbitrarily combined. In particular, microcircuits developed for the previous type of chipset can be used as the south bridge.
Chipsets Intel Express have advantages in comparison with earlier released chipsets at the expense of a number of the latest improvements and technologies. For example, the chipset Intel X38 Express, which is also advertised in late 2009, supports the following technologies:
- System bus frequency 1333/1066/800MHz supports processors Intel Core 2 Duo and Intel Core 2 Quad with virtualization technology Intel (Intel VT), dual-core processor Intel Pentium and processor Intel Celeron.
- Interface PCI Express 2.0 16 Gbps per port, twice the throughput PCIe 1.0. Interface PCI Express 2.0 used in all new chipsets, and is fully electrically and mechanically compatible with previous version 1.0.
- Technology Intel Fast Memory Access(advanced backbone memory controller hub architecture, Memory Controller Hub, MCH) improves system performance by optimizing the use of available bandwidth and reducing memory access latency.
- Support for dual-channel memory modules DDR3 provides throughput up to 21.2 GB/s(RAM DDR3 1333 with throughput 10.6 GB/s 8 GB 64- bit computing.
- Dual channel memory support DDR2 provides throughput up to 12.8 GB/s(RAM DDR2 800 with throughput 6.4 GB/s operating in dual-channel mode) and memory addressing up to 8 GB for faster system response and support 64- bit computing.
- Technology Intel Flex Memory Provides easy upgradeability by supporting various sizes of memory modules operating in dual-channel mode.
- Technology Intel high definition Audio (Intel HD Audio)- built-in audio subsystem that provides highest quality digital audio and advanced features such as support for multiple audio streams and jack reassignment.
- Technology Intel Matrix Storage (Intel MST) with addition additional hard disk provides faster access to digital photos, audio and video files using RAID arrays levels 0, 5 and 10, as well as increased protection data hard disk using RAID arrays levels 1, 5 and 10. External interface support eSATA provides external throughput up to 3 Gbps.
- Technology Intel Rapid Recovery To protect information, it provides for the creation of a restore point, which will be used to quickly resume the system in the event of a hard drive failure or damage to a large amount of data. To restore selected files, the disk with backup data can be connected in read-only mode.
- Port disable SATA allows you to enable and disable ports as needed SATA. This function Provides additional data protection by preventing illegal withdrawal or insertion of data through ports SATA. This feature will be especially useful for external ports. eSATA.
- Port disable USB allows you to enable and disable ports USB depending on the need. This feature provides additional data protection by preventing illegal withdrawal or insertion of data through ports. USB.
Chipsets with an integrated graphics subsystem, which is still suitable only for office computers, are characterized by the following:
- Graphics adapter Intel Graphics Media Accelerator X3500- this advanced 3D graphics support provides compatibility with the latest games and high realism, thanks to hardware processing of vertex shaders, support Microsoft DirectX 10,Shader Model 4.0 and OpenGL 2.0. Graphics adapters Intel Graphics also support work in the interface AeroMicrosoft Vista OS And Windows 7 With maximum settings detail.
- Technology Intel Clear Video is hardware and software for video processing allows you to use advanced high-definition video playback, crisp images with improved interlacing and rich color.
- Interface High Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) with support for copy protection technology HDCP is used to transmit an uncompressed video stream in the format HD along with uncompressed audio stream over a single cable and supports all formats HD, including 720p, 1080i and 1080p.
The new chipsets have abandoned the old technology AS "97 in favor HDA (High Definition Audio) .
Technology High Definition Audio corporations Intel- built-in audio subsystem that provides the highest quality digital audio and advanced features, such as support for multiple audio streams and reassignment connectors. Supports anti-copy protection technology High Bandwidth Digital Content Protection to play paid content (be careful not to get in trouble...). For new Intel processors Core i7-800 and Core i5, in which the control circuit of video adapters (bus PCI Express x16) is integrated on a chip, a new type of chipset has been developed R55 block diagram is shown. In fact, the chipset is only responsible for managing low-speed nodes that were previously assigned to the south bridge, so there is only one chip left in the chipset, and there is no division into the south-north bridge. The chipset chip uses a high-speed bus to communicate with the processor. DMI. And, despite the "revolution" in chipset building, the new chipset does not bring any technological innovations to users, and all the most interesting features memory and video work is now directly related to the processor architecture.
Characteristics of VIA chipsets
Corporation VIA develops and manufactures a series of chipsets for its now famous processors Nano, as well as for processors manufactured by corporations Intel and AMD. For northbridge ( VIA North Bridge Solutions) are intended for the following series: for processors K8 production corporation AMD characteristics are given, for processors Intel Core 2 Duo, Pentium and Celeron- . For the south bridge ( VIA South Bridge Solutions) microcircuits are produced, the characteristics of which are given.
Characteristics of NVIDIA chipsets
Corporation NVIDIA produces a large range of chipsets for production processors Intel and AMD with the support of their original technologies. chipset characteristics are given NVIDIA nForce for processors AMD and Intel. For information, see below short description technologies that are used in motherboards based on corporation chipsets NVIDIA:
- Technology NVIDIA ActiveArmor- increases network security and at the same time provides the highest level security by removing CPU packet filtering load, which guarantees fast and reliable network. Supported in MSR-processors NVIDIA nForce Professional, nForce4 SLI and nForce4 Ultra.
- Technology NVIDIA SLI- technology SLI (Scalable Link Interface) uses increased bus bandwidth PCI Express and has dedicated hardware and software solutions, providing amazing PC performance in products based on multiple NVIDIA GPU. NVIDIA SLI only supported on some GPUs GeForce PCI Express and MCP-processors nForce4 SLI/SLIxl6/SLI XE.
- Technology NVIDIA LinkBoost (NVIDIA nForce 590 SLI MCP)- automatically increases bandwidth when working with certain video cards NVIDIA GeForce.
- System Disk Alert- In the event of a drive failure, MediaShield users will see on the monitor which drive has failed so that they can easily replace or repair it.
- Technology NVIDIA FirstPacket- with technology NVIDIA FirstPacket you will get crystal clear telephone conversations and the gaming performance you want. Technology NVIDIA FirstPacket ensures that your game data, VoEP conversations and large files will be transferred according to the preferences you set.
- Utility NVIDIA nTune 4.0- through this utility based on Windows more settings are now available. performance manager NVIDIA nTune supports automatic tuning for optimal performance and the ability to customize to your needs. Once configured utility nTune will always automatically select correct settings systems for running application according to your profiles and rules.
- RAID morphing (MediaShield)- allows users to instantly change the current configuration raid, eliminating the need to back up data and perform multiple actions. Support RAID and SATA- drives. MediaShield automatically selects the configuration RAID 0, 1.0+1 or 5 according to your needs. Advanced users can change options directly RAID.
AMD chipset specifications
Corporation is currently AMD offers chipsets for all classes of computers.
- Chipsets AMD 7th series designed specifically for quad-core processors AMD Phenom and next generation graphics devices. Performance, scalability and personalization are combined with an innovative and efficient design solution that implements new technologies.
- Chipset AMD 580X CrossFire- the fastest single-chip platform 2x16 PCI Express for processors AMD AM2- provides the following advantages: the widest possibilities for overclocking enthusiasts, full system controllability, functionally rich southbridge ATI SB600.
- AMD 480X CrossFire- this is a massive chipset AMD for platforms with multiple graphics accelerators. Combined with external graphics accelerators ATI Radeon this chipset provides the highest performance.
- Chipset series ATI Radeon Xpress 1100 for processors AMD have a faster graphics subsystem and are ready for use . When used in desktop PCs, these chipsets provide extensive peripheral connectivity and secure data management.
- Chipset series ATI Radeon Xpress 200 for desktop personal computers built using integrated graphics chipsets ATI Radeon based on technology PCI Express.
Chipsets designed for Southbridge use ATI SB600, which provides superior performance, support for modern data access features, compatibility with Windows Vista Premium and Windows 7 and advanced power management features to create the most energy efficient platforms. The most interesting at present are the chipsets of the seventh series, designed specifically for multi-core processors AMD Phenom and next generation graphics devices: AMD 790GX, AMD 785G, AMD 780V, AMD 780G, AMD 760G and AMD 740G. Chipset introduced in 2009 AMD 785G takes! intermediate position between the gaming platform on the chipset AMD 790GX and AMD 780V, which is intended for the conservative part of users. Characteristics of the 7 series chipsets are given.
New chipsets use Newest technologies, For example, PCI Express 2.0 and HyperTransport 3.0. Chipset designed for professional use AMD 790FX, which supports three or four graphics devices with technology ATI CrossFireX on one system board. For the gaming segment, chipsets of the series are positioned AMD 790, which are optimized for games with high resolution And HD video. Today it is very difficult to talk about which platform AMD, Intel or NVIDIA the best, because this term refers to a complex of a processor, chipset, motherboard, memory modules, video card and hard drive, as well as an operating system. A simple comparison by individual characteristics, such as the frequency of the core and buses or the amount of memory, does not reflect the real state of affairs. To some extent, you can focus on various synthetic tests with which you can check the performance of iron for certain areas of application.
Motherboard manufacturers
The production of motherboards involves less technical difficulties and requires less financial capacity than the production of microcircuits, so there are an order of magnitude more firms that design and manufacture motherboards than manufacturers of processors and chipsets. Based on the same system logic - the chipset - you can produce a wide variety of motherboards that will differ in their functionality and reliability. Accordingly, motherboards of the same type (for a specific type of processor and on a specific type of chipset) from different manufacturers may have very different consumer qualities. Moreover, even eminent firms can have unsuccessful motherboards, and a little-known manufacturer is sometimes able to develop and release a board that will have specifications outperforming the leading companies. Since there are a lot of motherboard manufacturers, it is simply impossible to list the technical characteristics of even the most popular motherboards in a small book. Therefore, when choosing a new motherboard, you should be guided by information on manufacturers' websites, as well as user reviews that can be found on the Internet. When choosing a motherboard, you should keep in mind that now there is a regular change of generations of processors and sockets, so motherboards are made for a wide variety of combinations of sockets and processors. In addition, a number of companies produce motherboards for Socket 370. Periodically, a number of companies offer motherboards for desktop computers, which use mobile versions processors Intel and AMD. Accordingly, in the specification you can find unfamiliar names of chipsets, for example Socket R for processors Intel. In particular, the Taiwanese company AOrep, founded in 1996, offers a fairly large selection of form factor motherboards ITX. When choosing a motherboard, it should be taken into account that all companies whose products are sold in Russia can be divided into two groups. The first group - the most famous manufacturers whose motherboards are popular with a large number users. The second group are manufacturers whose products rarely appear in stores for various reasons. With that said, here are the website addresses of the most popular motherboard manufacturers. Please note that almost all of the listed companies have Russian-language sites in RuNet, where you can find both technical documentation, and drivers for boards:
