Who benefits? I'm not a big fan of conspiracy theories. Yes, and here it just happened, without anyone's help, but it was quickly picked up by manufacturers and sellers of computer equipment. By convergence of public opinion, we conclude that 1080p resolution is not enough for monitors with a diagonal of 27 inches. There are a lot of comments and feedback on this subject, and most of the people who left them adhere to the position of insufficient resolution of 1080p. But is it really so?
I have two 27 inch monitors in front of me (it doesn't matter which manufacturer, with matrix TFT AH-IPS), one with FullHD resolution 1920x1080p, the other 2560x1440p. I worked with them for about two weeks and I formed a clear opinion, different from what I have seen in hundreds of comments.
I can't identify any particular consumer benefit of the latter. We can say that at a resolution of 2560x1440, more information fits into the screen at 1.8 than at FullHD. But this is nonsense, with akin to dissatisfaction with audio signal delays of as much as ~ 0.002 seconds in wireless headphones. I also had to work in engineering CAD programs, where there can be a lot of information, while there is practically no difference between the two monitors in terms of convenience. Or rather, it is, but so imperceptible that we can consider its absence.
In windows 7 (respectively, in 8) support for different DPI values \u200b\u200bis implemented, which will allow you to configure correct scales in your workspace. Most often, problems arise with higher DPI, cropped text, incorrect font sizes, window size problems, pixelation (which has become a headache for webmasters, especially with the advent of retina displays) bitmaps.
And when I run a game, the 1440p version even loses due to lower performance. At the same time, the picture does not get much better in games. More fun from the game is acquired not because of the density of dots per inch, but because of the diagonal of the monitor. Below is a visual representation of the dependence of the optimal diagonal on the resolution, taking into account the distance from you to the screen.
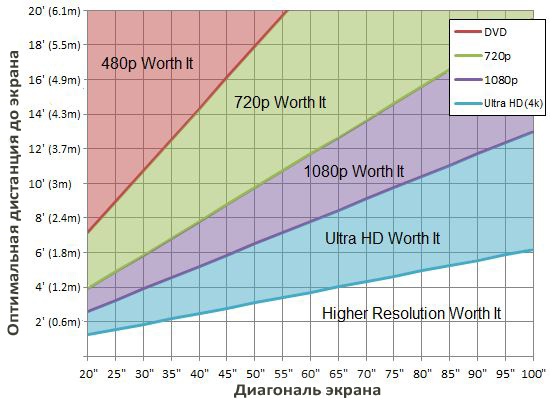
In summary, it is better to buy a monitor with a larger diagonal, rather than a higher resolution. This results in a pretty substantial savings on your budget. 1080p resolution for a 27-inch monitor is enough, but this is already the limit. In the case of 1080p resolution, with large (more than 27 inches) diagonals in games, you will not lose anything, but you may lose comfort in work applications or, for example, when surfing the Internet. If your choice fell on a diagonal of 27 inches, feel free to take a cheaper option with 1080p. And if you are looking at monitors 30 inches or more, then the choice should already fall on monitors with a higher resolution.
Those who say that 1080p is not enough for a diagonal of 27 inches are disingenuous, because most of them have not used such monitors and advise only on the basis of a stable picture that has formed in the Internet space. Fans also support this opinion. Apple products, whose resolution of 2560 × 1600 was shoved into a laptop with a 13-inch screen.
Information about the make, model, and alternative names of a particular device, if any.
Design
Information about the dimensions and weight of the device, presented in different units of measurement. Used materials, suggested colors, certificates.
| Width Width information refers to the horizontal side of the device in its standard orientation during use. | 76 mm (millimeters) 7.6 cm (centimeters) 0.25ft 2.99in |
| Height Height information refers to the vertical side of the device in its standard orientation during use. | 156 mm (millimeters) 15.6 cm (centimeters) 0.51 ft 6.14in |
| Thickness Information about the thickness of the device in different units measurements. | 11 mm (millimeters) 1.1 cm (centimeters) 0.04ft 0.43in |
| Weight Information about the weight of the device in different units of measurement. | 220 g (grams) 0.49 lbs 7.76oz |
| Volume Approximate volume of the device, calculated from dimensions provided by the manufacturer. Refers to devices with the shape of a rectangular parallelepiped. | 130.42 cm³ (cubic centimeters) 7.92 in³ (cubic inches) |
| Colors Information about the colors in which this device is offered for sale. | The black Blue Golden |
| Housing materials The materials used to make the body of the device. | Metal Faux leather |
SIM card
The SIM card is used in mobile devices to store data that certifies the authenticity of mobile service subscribers.
Mobile networks
A mobile network is a radio system that allows multiple mobile devices to communicate with each other.
| GSM GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) is designed to replace the analogue mobile network (1G). For this reason, GSM is often referred to as a 2G mobile network. It is enhanced by the addition of GPRS (General Packet Radio Services) and later EDGE (Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution) technologies. | GSM 850 MHz GSM 900 MHz GSM 1800 MHz GSM 1900 MHz |
| W-CDMA W-CDMA (Wideband Code Division Multiple Access) is the air interface used by 3G mobile networks and is one of the three main UMTS air interfaces along with TD-SCDMA and TD-CDMA. It provides even higher data transfer speeds and connectivity more consumers at the same time. | W-CDMA 850 MHz W-CDMA 900 MHz W-CDMA 2100 MHz |
| LTE LTE (Long Term Evolution) is defined as a technology fourth generation(4G). It is developed by 3GPP based on GSM/EDGE and UMTS/HSPA to increase the capacity and speed of wireless mobile networks. The subsequent development of technologies is called LTE Advanced. | LTE 800 MHz LTE 900 MHz LTE 1800 MHz LTE 2100 MHz LTE 2600 MHz |
Mobile technologies and data rates
Communication between devices in mobile networks is carried out through technologies that provide different data rates.
Operating system
The operating system is the system software that manages and coordinates the operation of the hardware components in the device.
SoC (System on a Chip)
System on a chip (SoC) includes all the most important hardware components of a mobile device in one chip.
| SoC (System on a Chip) System on a chip (SoC) integrates various hardware components such as processor, graphics processor, memory, peripherals, interfaces, etc., as well as the software necessary for their operation. | MediaTek MT6750T |
| Technological process Information on technological process on which the chip is made. The value in nanometers measures half the distance between the elements in the processor. | 28 nm (nanometers) |
| Processor (CPU) The main function of the processor (CPU) of a mobile device is the interpretation and execution of instructions contained in software applications. | 4x 1.5 GHz ARM Cortex-A53, 4x 1.0 GHz ARM Cortex-A53 |
| Processor bit depth The bit depth (bits) of a processor is determined by the size (in bits) of registers, address buses, and data buses. 64-bit processors have higher performance than 32-bit processors, which, in turn, are more productive than 16-bit processors. | 64 bit |
| Instruction Set Architecture Instructions are commands by which the software sets/controls the operation of the processor. Information about the instruction set (ISA) that the processor can execute. | ARMv8-A |
| First level cache (L1) Cache memory is used by the processor to reduce access time to more frequently accessed data and instructions. L1 (level 1) cache is small and much faster than system memory, and other cache levels. If the processor does not find the requested data in L1, it continues to look for them in the L2 cache. With some processors, this search is performed simultaneously in L1 and L2. | 32 kB + 32 kB (kilobytes) |
| Second level cache (L2) L2 (level 2) cache is slower than L1, but in return it has a larger capacity, allowing more data to be cached. It, like L1, is much faster than system memory (RAM). If the processor does not find the requested data in L2, it continues to look for it in the L3 cache (if available) or RAM. | 512 kB (kilobytes) 0.5 MB (megabytes) |
| Number of processor cores The processor core executes program instructions. There are processors with one, two or more cores. Having more cores increases performance by allowing multiple instructions to be executed in parallel. | 8 |
| Processor clock speed The clock speed of a processor describes its speed in terms of cycles per second. It is measured in megahertz (MHz) or gigahertz (GHz). | 1500 MHz (megahertz) |
| Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) The graphics processing unit (GPU) handles calculations for various 2D/3D graphics applications. IN mobile devices it is used most often by games, consumer interface, video applications, etc. | ARM Mali-T860 MP2 |
| Number of GPU cores Like the CPU, the GPU is made up of several working parts called cores. They handle the graphical calculations of different applications. | 2 |
| GPU clock speed The speed of work is clock frequency GPU, which is measured in megahertz (MHz) or gigahertz (GHz). | 650 MHz (megahertz) |
| Volume random access memory(RAM) Random access memory (RAM) used operating system and all installed applications. Data stored in RAM is lost when the device is turned off or restarted. | 4 GB (gigabytes) |
| Type of random access memory (RAM) Information about the type of random access memory (RAM) used by the device. | LPDDR3 |
| Number of RAM channels Information about the number of RAM channels that are integrated into the SoC. More channels means higher data rates. | single channel |
| RAM frequency The frequency of RAM determines its speed, more specifically, the speed of reading / writing data. | 833 MHz (megahertz) |
Built-in memory
Each mobile device has a built-in (non-removable) memory with a fixed amount.
Memory cards
Memory cards are used in mobile devices to increase the storage capacity for storing data.
Screen
The screen of a mobile device is characterized by its technology, resolution, pixel density, diagonal length, color depth, etc.
| Type/technology One of the main characteristics of the screen is the technology by which it is made and on which the image quality of information directly depends. | IPS |
| Diagonal For mobile devices, the screen size is expressed in terms of its diagonal length, measured in inches. | 5.5in 139.7 mm (millimeters) 13.97 cm (centimeters) |
| Width Approximate Screen Width | 2.7in 68.49 mm (millimeters) 6.85 cm (centimeters) |
| Height Approximate Screen Height | 4.79in 121.76 mm (millimeters) 12.18 cm (centimeters) |
| Aspect Ratio The ratio of the dimensions of the long side of the screen to its short side | 1.778:1 16:9 |
| Permission Screen resolution indicates the number of pixels vertically and horizontally on the screen. More a high resolution means sharper image detail. | 1080 x 1920 pixels |
| Pixel Density Information about the number of pixels per centimeter or inch of the screen. Higher density allows information to be shown on the screen in clearer detail. | 401ppi (pixels per inch) 157ppm (pixels per centimeter) |
| Color depth Screen color depth reflects the total number of bits used for the color components in a single pixel. Information on the maximum number colors that the screen can show. | 24 bit 16777216 flowers |
| Screen area Approximate percentage of screen space on the front of the device. | 70.56% (percentage) |
| Other characteristics Information about other functions and features of the screen. | capacitive Multitouch |
| Display manufacturer-Sharp 2.5D curved glass screen 1100:1 contrast ratio 570 cd/m² |
Sensors
Different sensors perform different quantitative measurements and convert physical indicators into signals that are recognized by the mobile device.
Main camera
The main camera of a mobile device is usually located on the back of the case and is used for taking photos and videos.
| Sensor model | Samsung S5K3L8 |
| Sensor type | ISOCELL |
| Sensor size | 4.69 x 3.52 mm (millimeters) 0.23in |
| Pixel size | 1.127 µm (micrometers) 0.001127 mm (millimeters) |
| crop factor | 7.38 |
| ISO (light sensitivity) ISO values determine the light sensitivity level of the photosensor. A lower value means weaker light sensitivity and vice versa - higher values mean higher light sensitivity, i.e. better ability of the sensor to work in low light conditions. | 100 - 1600 |
| Diaphragm | f/2.0 |
| Focal length | 3.5 mm (millimeters) |
| Flash type | LED |
| Image resolution One of the main characteristics of mobile device cameras is their resolution, which indicates the number of pixels in the horizontal and vertical direction of an image. | 4160 x 3120 pixels 12.98 MP (megapixels) |
| Video resolution Information about the maximum supported resolution for video recording by the device. | 1920 x 1080 pixels 2.07 MP (megapixels) |
Information about the maximum number of frames per second (fps) supported by the device when shooting video at the maximum resolution. Some of the main standard shooting and video playback speeds are 24p, 25p, 30p, 60p. | 30 fps (frames per second) |
| Characteristics Information about other software and hardware features related to the main camera and improving its functionality. | autofocus Burst shooting digital zoom geo tags panoramic shooting HDR shooting Touch focus Face recognition Adjusting the white balance ISO setting Exposure compensation Self-timer Scene Selection Mode |
| Phase detection Wide-angle lens - 88° Secondary rear camera - 13 MP (telephoto) Sensor model - Samsung S5K3L8 (#2) Sensor type - ISOCELL (#2) Sensor size - 4.69 x 3.52 mm (#2) |
Additional camera
Additional cameras are usually mounted above the screen of the device and are used mainly for video calls, gesture recognition, etc.
| Sensor model Information about the manufacturer and model of the photo sensor used in the device's camera. | Samsung S5K3L8 |
| Sensor type Digital cameras use photo sensors to take pictures. The sensor, as well as the optics, is one of the main factors in the quality of a camera in a mobile device. | ISOCELL |
| Sensor size Information about the size of the photosensor used in the device. Typically, cameras with a larger sensor and lower pixel density offer better image quality despite lower resolution. | 4.69 x 3.52 mm (millimeters) 0.23in |
| Pixel size The smaller pixel size of the photosensor allows the use of more pixels per unit area, thus increasing the resolution. On the other hand, a smaller pixel size can have a negative impact on image quality at high light sensitivity (ISO) levels. | 1.127 µm (micrometers) 0.001127 mm (millimeters) |
| crop factor The crop factor is the ratio between the size of a full-frame sensor (36 x 24mm, equivalent to a frame of standard 35mm film) and the size of the device's photosensor. The number shown is the ratio of the diagonals of the full frame sensor (43.3 mm) and the photo sensor of the specific device. | 7.38 |
| Diaphragm Aperture (f-number) is the size of the aperture opening that controls the amount of light reaching the photosensor. A lower f-number means the aperture is larger. | f/2.0 |
| Focal length Focal length is the distance in millimeters from the photosensor to the optical center of the lens. There is also an equivalent focal length that provides the same field of view with a full frame camera. | 3.5 mm (millimeters) 25.82 mm (millimeters) *(35 mm / full frame) |
| Flash type The most common types of flashes in mobile devices cameras are LED and xenon flashes. LED flashes give a softer light and, unlike brighter xenon flashes, are also used for video shooting. | LED |
| Image resolution Information about the maximum resolution of the secondary camera when shooting. In most cases, the resolution of the secondary camera is lower than that of the main camera. | 4160 x 3120 pixels 12.98 MP (megapixels) |
| Video resolution Information about the maximum resolution supported when shooting video with the optional camera. | 1280 x 720 pixels 0.92 MP (megapixels) |
| Video - frame rate/frames per second. Information about the maximum number of frames per second (fps) supported by the optional camera when shooting video at the maximum resolution. | 30 fps (frames per second) |
| Wide-angle lens - 88° |
Audio
Information about the type of speakers and audio technologies supported by the device.
Radio
The radio of the mobile device is a built-in FM receiver.
Location determination
Information about navigation and location technologies supported by the device.
WiFi
Wi-Fi is a technology that provides wireless communication to transfer data over short distances between different devices.
Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a standard for secure wireless data transfer between different types of devices over short distances.
USB
USB (Universal Serial Bus) is an industry standard that allows different electronic devices to communicate.
Headphone jack
This is an audio connector, which is also called an audio jack. The most widely used standard in mobile devices is the 3.5mm headphone jack.
Connecting devices
Information about other important connection technologies supported by the device.
Browser
A web browser is a software application for accessing and viewing information on the Internet.
| Browser Information about some of the key features and standards supported by the device's browser. | HTML HTML5 CSS 3 |
Audio file formats/codecs
Mobile devices support various audio file formats and codecs that store and encode/decode digital audio data, respectively.
Video file formats/codecs
Mobile devices support various video file formats and codecs, which store and encode/decode digital video data, respectively.
Battery
Mobile device batteries differ from each other in their capacity and technology. They provide the electrical charge they need to function.
| Capacity The capacity of a battery indicates the maximum charge it can store, measured in milliamp-hours. | 7060 mAh (milliamp-hours) |
| Type The type of battery is determined by its structure and, more specifically, by the chemicals used. Exist different types batteries, with lithium-ion and lithium-ion polymer batteries most commonly used in mobile devices. | Li-polymer (Li-polymer) |
| 2G standby time The 2G standby time is the amount of time it takes for the battery to fully discharge when the device is in stand-by mode and connected to a 2G network. | 480 h (hours) 28800 min (minutes) 20 days |
| 3G standby time The 3G standby time is the amount of time it takes for the battery to fully discharge when the device is in stand-by mode and connected to a 3G network. | 480 h (hours) 28800 min (minutes) 20 days |
| Adapter output power Information about the strength of the electric current (measured in amperes) and the electrical voltage (measured in volts) that the Charger(output power). Higher power output ensures faster battery charging. | 5 V (volts) / 3 A (amps) 7 V (volts) / 3 A (amps) 9 V (volts) / 2.7 A (amps) 12 V (volts) / 2 A (amps) |
| Characteristics Information about some additional features of the device's battery. | fast charging Fixed |
CCTV systems are becoming more and more popular all over the world. Equipment is constantly being improved, and this area is constantly evolving. As in any technical field, there are terminologies and nomenclatures here. Today we will talk about what are the main video resolutions in the field of video surveillance systems and how they differ from each other.
Resolution D1
The lowest resolution matrices. It appeared along with analog cameras more than 10 years ago. Now D1 is practically not used, as a higher resolution has appeared. If translated into pixels, then the resolution of D1 is 720 * 576 pixels. Not the clearest picture. D1 is still used in analog video recorders, and this resolution is set even in AHD systems at remote access, in order to provide more stable video streaming over the network.
Resolution 960H
This type of resolution also applies to analog video recorders. More modern type permission, appeared about 5 years ago. 960H resolution is 960*576 pixels. Compared to the previous resolution, it is slightly higher, and the picture quality is distinctly better.
Resolution 720p
This permit was issued 3 years ago. It applies to digital recorders as well as AHD video recorders. 720p resolution is 1280*720 pixels. This resolution is used in 1 megapixel CCTV cameras.
Resolution 960p
Only slightly different from the previous resolution. If translated into pixels, then 960p is 1280 * 960 pixels. It is used in CCTV cameras with matrices of 1.3 mega pixels.
Resolution 1080p
This type of resolution is also used in AHD systems. 1080p resolution is 1920*1080 pixels. Used in 2 megapixel video cameras.
In this article, we have reviewed the main permissions that are used in video surveillance systems. Which one is better is up to you. Good luck! Be safe!
A professional designer creates a website design, focusing on the screen resolution used by the main part of the audience.
How should the site design be done in order to display perfectly on all screens? The fact is that each of us has different computers and different screen resolutions. And this means that we all see the same site in different ways. For example, if you have a screen resolution of 1920x1080 pixels and you draw a website design with this resolution, "a kind of wide design", then those people whose screen is not 1920 pixels wide, but 1366 pixels wide, your design will not fit. And a person, to see the whole site, will scroll to the right scroll. So, in order to please most people, you need to draw a design with a resolution that can fit on the screen of almost everyone. To date, such a standard is considered to be a resolution of 1024x768 pixels.
Screen resolution statistics around the world. Let's take a look at the statistics provided by the w3counter.com service. These statistics are collected mainly for the US and Europe. But in other countries the statistics are approximately the same. Looking at the statistics, you can see that the smallest resolution that is most often used is 1024x768. Therefore, the design of the site cannot be more than 1024 pixels, otherwise it will not fit. And to be more precise, it should even be a little smaller, namely 960 pixels wide, since 64 pixels go to the indent so that the letters of the site text on the right and left do not stick to the border, and another part is required for the horizontal scroll bar.
Standard 960 pixels- is considered today the world standard of web design, which professional web designers are guided by. The site 960.gs is dedicated to this standard, where you can see examples of many world-famous sites created by this standard. To create a convenient, mathematically accurate and proportionately harmonious website design, a tool called "Modular Grid". A modular grid is used in order to draw a design within it. Thus, maximum convenience and the correct arrangement of design elements are achieved. You can download the modular grid template from this link.
Fixed and rubber design
Fixed site design is a design whose size is clearly fixed in width, such as 1000 pixels, or 800 pixels.
Rubber site design is a design that takes the size of the screen, i.e. stretches. This type of design is mainly used for sites with high traffic, sites that require a lot of information to be placed on the screen.
Partly fluid, partly fixed site design- this is a design that stretches to certain boundaries, and then fixed.
Responsive website design is a design drawn with different screen resolutions in mind. Roughly speaking, as many design options are drawn as there are screen resolutions. And the browser is programmed and shows you the design of the site, which is ideal for your resolution. When developing, the most time-consuming design option, as it requires drawing a large number layouts and their adaptation on the site.
Most often, in the development of a corporate website, an online store, a catalog, a website for business, a fixed website design is used.
Pros and Cons of Fluid vs. Fixed Site Design
Fluid design makes it hard to line up content and images beautifully. If the pictures five in a row at a resolution of 1024 pixels look neat, then when the screen expands, a void forms on the right. Lines and paragraphs become either shorter or wider, and it is visually difficult to build paragraphs that are beautiful for perception. In a fixed one, nothing jumps, and the content lines up neatly and beautifully.
In the rubber design, the texts have such long lines that they are incredibly uncomfortable to read. Why are the sites "Twitter" and "Vkontakte" so narrow? To make them easy to read. Why do e-readers have a screen of only 6 inches? So it is more convenient for a person to read and there is no need to twist the neck. The fixed design is shorter in width, which makes it easier to read.
In rubber design, it is difficult to create a graphic header in the form of a beautiful picture or slider, since such things most often do not stretch. Therefore, a rubber site, as a rule, does not contain a lot of graphics, and often it is practically absent.
Rubber design is most often chosen by those who need to place as much information on the screen as possible. For such sites, the option that left and right remains empty in the form of a background is not suitable. These sites use every pixel of available space.
