YouTube.com is the most famous video hosting site and the third most popular site in the world. He achieved such success thanks to convenience and simplicity. Using YouTube you can watch the most popular videos from around the world - from the hottest new music to latest news, and you can also add video clips on the website www.youtube.com. YouTube will help you have a great time and be entertained, it will be available anytime and anywhere. The decoration is made in dark red colors.
YouTube for Android has several unique features that make the app stand out from its competitors. Firstly, it is possible to pre-boot when the phone is connected to Wi-Fi networks, the application will download the video and save it in cache, so you can easily watch it on a slow connection. Secondly, the ability to connect a smartphone to a TV and broadcast video to big screen.
Google collects tons of information about the user using a smartphone. Location, activity installed applications, contacts, calendar, search history, data backup applications - this is only part of the information that goes to Google servers. It is not at all necessary to link your smartphone to a Google account, but then you will lose the ability to install applications, synchronize contacts, calendar, backups and many other useful functions in everyday life. Is there a way around these problems? Let's try to figure it out.
Here are two links that show only a small part of what Google knows about you: once, two. Even the most insignificant information gets into Google logs, even recordings of voice requests to Google Now and Assistant. Officially, the company uses this data to improve products and display targeted advertising. But she also cooperates with law enforcement agencies and, upon request, will give out as much information about you as you yourself do not know.
Do you want to get rid of surveillance and not lose the convenience of using your smartphone? Then let's go.
So, when you turn on a new device for the first time or after resetting it to factory settings, the smartphone asks Google account data and after their verification, it immediately begins collecting data about your activity. Therefore, there are only three options for bypassing “surveillance”:
The last two actions will disable synchronization of contacts and photos, deactivate Google Play and application backups. Therefore, you will have to look for workarounds to get this functionality back.
So, by skipping account linking or installing lightweight firmware, we got a non-working market in the first case or its absence in the second. Accordingly, we need a convenient way to fill the device with the necessary applications. First of all, let's go to settings and In the “Security” menu, put a checkmark (move the slider) on the “Unknown sources” item. This will allow you to install applications not from the Play Store.
After this, you can download and install applications from anywhere, but you should trust only trusted sources, some of which will be discussed below.
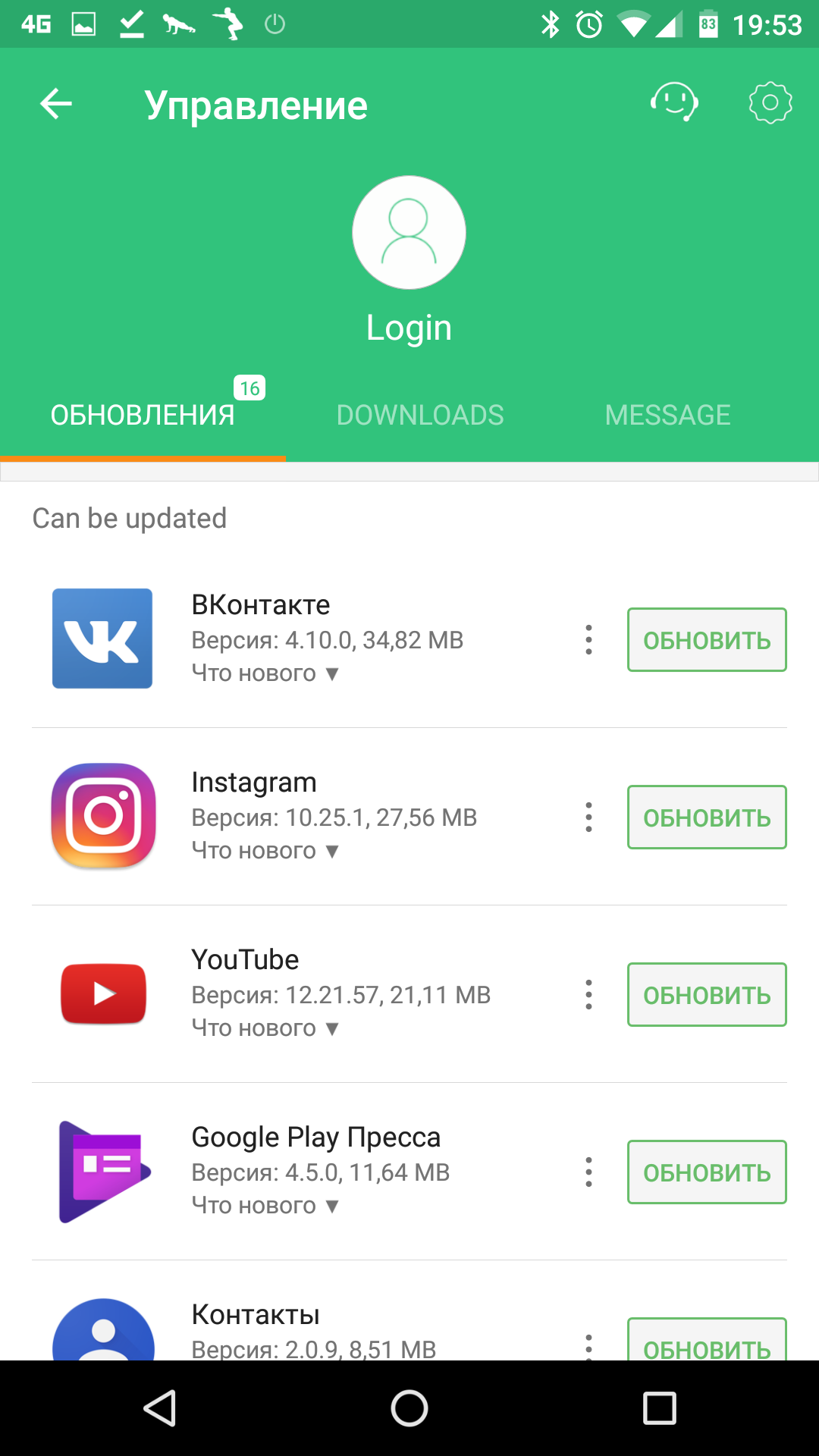
First, let's learn how to download applications from Google Play. It is not so difficult. You just need to find the necessary program in the browser and then replace play.google.com in address bar at apk-dl.com. This will take you to a page with the option to download the package.
And - more well-known sites with similar, but expanded functionality. APKMirror is the favorite file hosting site for Android Police. The download page contains the package name, version number, minimum requirements To Android versions. Available for download previous versions applications, and the main page contains a feed of recent downloads, as well as statistics of the most popular applications based on download results over 24 hours, seven days and a month.
It is worth keeping in mind that both of these sites do not distribute Warez, which means that only free software can be downloaded through them.
Another advantage of apkpure.com is its convenient client. After launching, it scans installed applications and displays a notification in the curtain, prompting you to update them to the latest versions.
Google collects tons of information about the user using a smartphone. Location, activity of installed applications, contacts, calendar, search query history, application data backup - this is only part of the information that goes to Google servers. It is not at all necessary to link your smartphone to a Google account, but then you will lose the ability to install applications, synchronize contacts, calendar, backups and many other useful functions in everyday life. Is there a way around these problems? Let's try to figure it out. The vast majority of this is software produced by Google. And it’s no secret that Google’s main business is collecting our private information. Google is constantly collecting information about us, search queries are carefully logged, movements are tracked, and passwords, emails and contact information are stored for years to come. All this is an integral part of modernity, but we are quite capable of changing it.
Today I will tell you how to remove Google programs from your phone, replacing them with open-source analogues and thereby significantly increasing the level of your privacy.
It's no secret that any device under Android control(at least the one certified by Google) contains not only components assembled from AOSP, but also an impressive number of proprietary Google programs. These are the same Google Play, Gmail, Hangouts, Maps and a bunch of other applications, including a dialer and a camera (starting with KitKat).
For all these components there is not only source code, but also no explanation at all about the principles of their operation. Many of them are initially designed to collect certain types of information and send it to Google servers. This is how, for example, GoogleBackupTransport behaves, which is responsible for synchronizing the list of installed applications, passwords and other data, GoogleContactsSyncAdapter, which synchronizes the list of contacts, or ChromeBookmarksSyncAdapter, whose job is to synchronize browser bookmarks. Plus collecting information about all queries in the search engine.
There is, of course, nothing wrong with the fact of synchronization, and it is an excellent mechanism that allows you to configure new phone in a matter of minutes, and Google Now even manages to give us useful information based on our data (sometimes). The only problem is that all this destroys our privacy, because, as Snowden showed, under the hood of the NSA (and, most likely, a bunch of other services) is not only some evil empire called Microsoft, but also Google, and as well as many other companies from the “we are not evil, but fluffy philanthropists” crowd.
In other words: Google will merge us all without any problems, and it’s not a fact that its employees, sitting in their offices with masseuses and dogs, are not laughing at the names from your contact book (everything is encrypted there, yes), drinking 15-year-old pu-erh from Yunnan Province. Or maybe to hell with Google? Let's take their Android and let them go through the forest?
What is Google Apps?
The latest version of the custom KitKat-based firmware for my smartphone weighs 200 MB, however, in order to get a real experience from the smartphone, I also have to flash the gapps archive on top of it, the size of which is 170 MB. Only after this will I receive a system similar to that pre-installed on Nexus devices, with all the goodies in the form of a desktop integrated with Google Now, a screen lock based on a face shot, a camera with support for spherical shooting and a kilogram of Google software, from Google Play to Google Books.
I repeat once again: all this is closed software from Google, which in a good way cannot be distributed at all without their knowledge (that’s why it is not in custom firmware like CyanogenMod), but since it is quite easy to extract it from the firmware of Nexus devices, you can find it on the Internet a huge number of similar archives, including severely truncated ones. In order to release an Android smartphone with a set of gapps on board, the manufacturer must send it for certification to Google, which, after evaluating the quality and performance of the smartphone, will either give the go-ahead or kick it (but this does not stop the Chinese at all).
This is how Google Apps get to your smartphone. Of the users, 99% either use pre-installed applications or install them themselves on absolutely clean and completely anonymous firmware. And then, from the moment you enter your username and password, synchronization and downloading of information begins.
To figure out how this happens, let’s unpack the same archive with gapps and take a look inside. We are interested in the /system/app and /system/priv-app directories; during installation, their contents are copied to the directories of the same name inside the smartphone. The second directory is a KitKat innovation, apparently invented to store private applications that are accessible only to the administrator (owner) of the device and invisible to other users logged into the system.
In the /system/app directory we will find a large number of various Google applications, easily recognizable by the name of the package: Books.apk, Chrome.apk, Gmail2.apk and so on. Each of them will share information differently, but that's totally fine (yes, Google will know you're reading Paulo Coelho through their app!). The greatest danger here is GoogleContactsSyncAdapter.apk, which is only responsible for sending a list of contacts to the remote server. We write down the name in a notepad and move on.
Most of the files from the /system/priv-app directory are the services and frameworks necessary to run this whole synchronization and surveillance machine:
- GoogleBackupTransport.apk - synchronizes data from installed applications, Wi-Fi passwords and some settings;
- GoogleLoginService.apk - connects the device with a Google account;
- GooglePartnerSetup.apk - allows third party applications gain access to Google services;
- GoogleServicesFramwork.apk - a framework with various auxiliary functionality;
- Phonesky.apk - Play Store (oddly enough);
- PrebuiltGmsCore.apk - Google Services, as the name suggests, is the core of the entire gapps suite;
- Velvet.apk is a Google search that includes a desktop search bar and Google Now.
In essence, this is the part of Google Apps that is responsible for leaking our private information. Let's try to get rid of all this. Method number 1. Disabling through settings
The easiest way to unlink a smartphone from Google is to use standard settings systems. The good thing about this method is that it does not require root rights, installation of custom firmware, or custom recovery. Everything can be done in any stock firmware without losing access to your account and applications like Gmail (if necessary). However, no one will vouch for the efficiency, since it is quite possible that some gapps components will continue to send data.
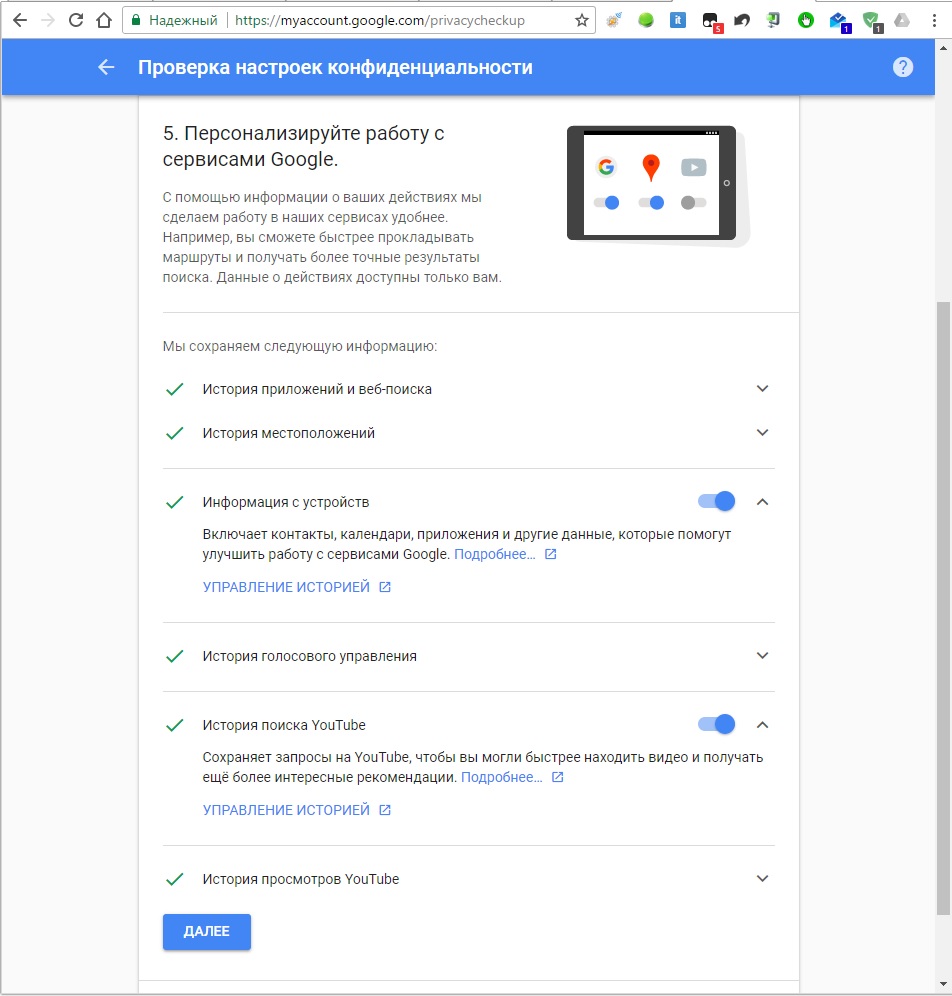
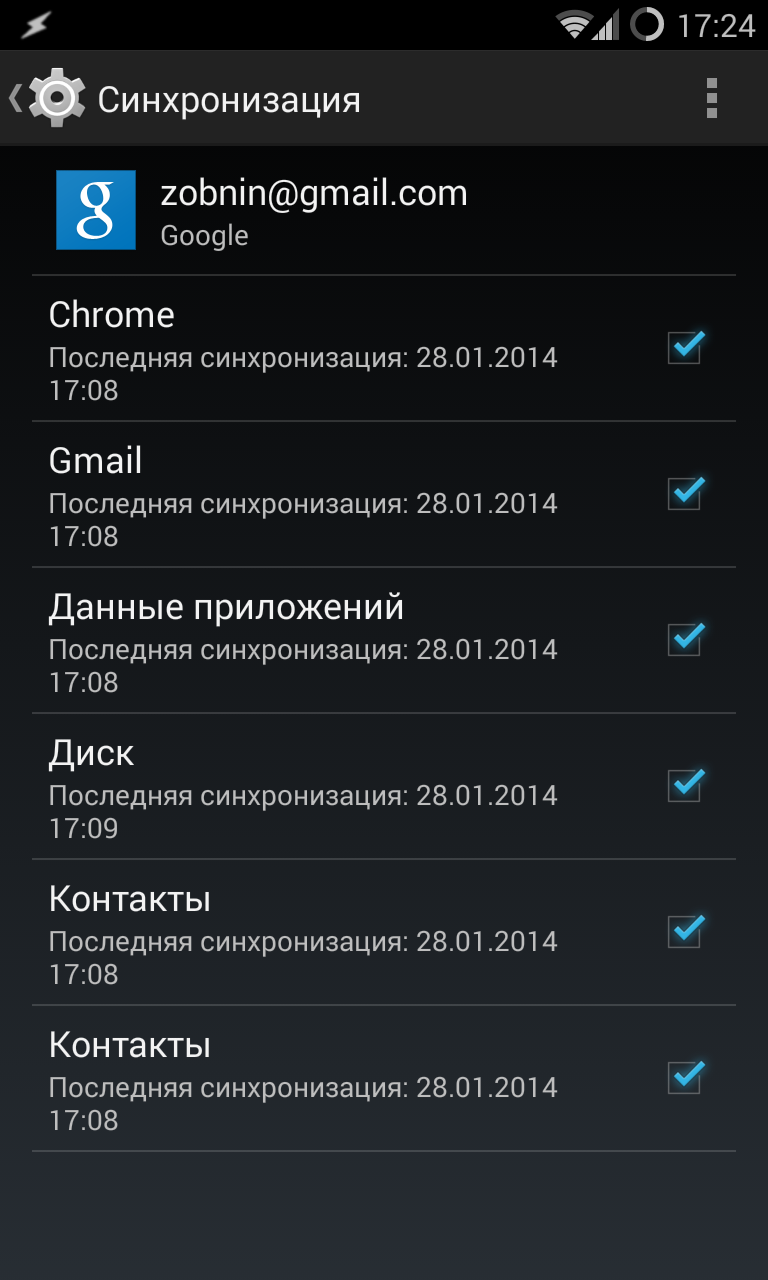
The main location for synchronization settings is the menu “Settings -> Accounts -> Google -> [email protected]" Here you can disable things like syncing contacts, application data, Gmail, Play Music, Google Keep, and more. All you need to do is simply uncheck the desired menu items. Next, go to the “Settings -> Backup and reset” menu and uncheck the “Data backup” and “Auto recovery” items.
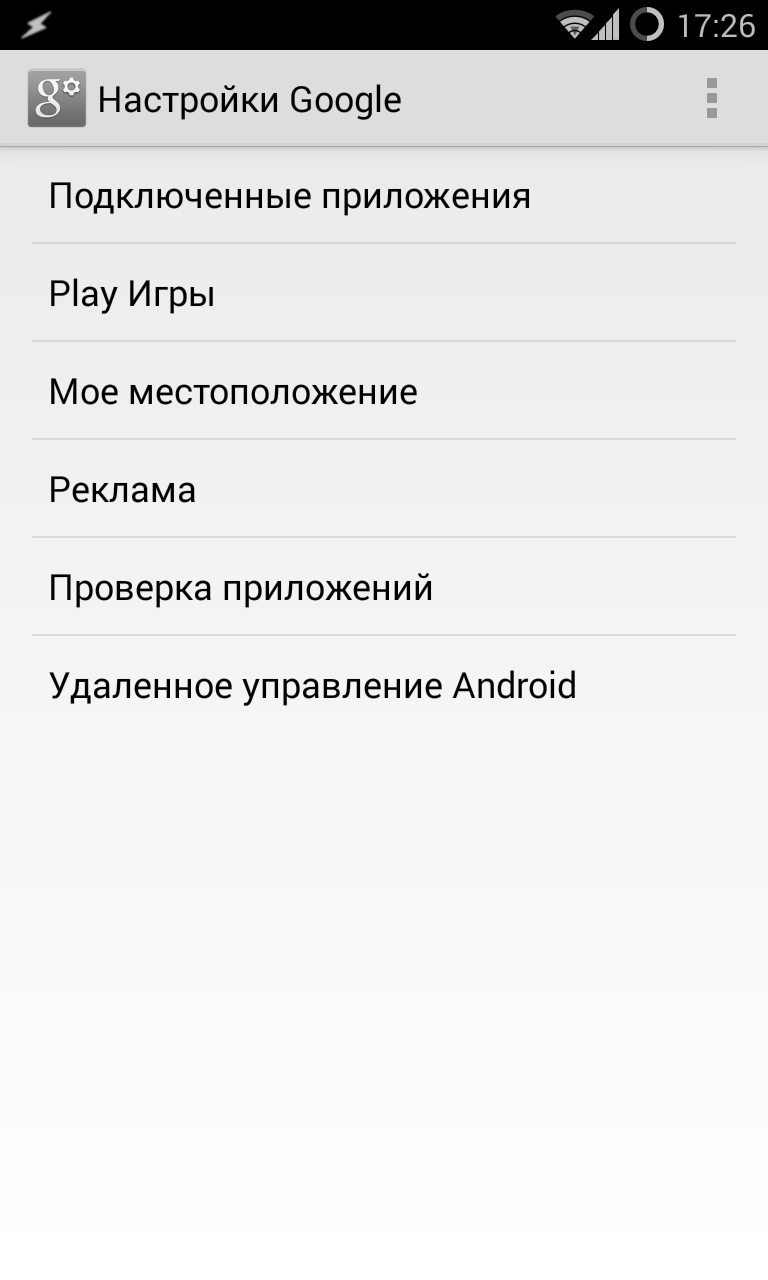
The Google Settings application, which is part of Google Services, is also responsible for many synchronization settings. With its help, in particular, you can disable Google access to the location (“Access to geodata -> Access to my geodata / Sending geodata / Location history”), disable sending personal data to the search engine (“Search -> Personal data”), disable Google Now (“Search -> Google Now”) and disable remote control(" Remote control -> Remote search devices / Remote lock and reset").
In the same " Google Settings"By the way, you can disable any application that uses Google account for authorization. We are talking not only about the software installed on the device, but also about all applications ever used, including websites. For example, I found a lot of sites on this list that I haven’t visited for at least a couple of years.
In the event that you do not intend to use Google services at all, it will be easier to disconnect your smartphone from your account completely, that is, simply delete it through the settings: “Settings -> Accounts -> Google -> [email protected]-> Menu button -> Delete account.”
Most Google applications can be disabled painlessly through the settings: “Applications -> ALL -> the right application-> Disable".
Method number 2. Cleaning the official firmware.
In the event that the stock firmware has root rights, you can get rid of Google Apps by simply deleting them from your smartphone. As I already said, they are all stored in the /system/app and /system/priv-app directories. For example, in the case of KitKat, the list of Google applications in the first directory will be like this:
- Books.apk - Google Books;
- CalendarGoogle.apk - Google Calendar;
- Chrome.apk - Google Chrome;
- CloudPrint.apk - cloud printing system;
- Drive.apk - Google Drive;
- GenieWidget.apk - news and weather widget;
- Gmail2.apk - Gmail;
- GoogleContactsSyncAdapter.apk - contact synchronization;
- GoogleEars.apk - Google Ears (similar to Shazam);
- GoogleEarth.apk - Google Earth;
- GoogleHome.apk - home screen with integrated Google Now;
- GoogleTTS.apk - speech synthesis system;
- Hangouts.apk - Google Hangouts;
- Keep.apk - Google Keep;
- LatinImeGoogle.apk - keyboard with gesture support;
- Magazines.apk - Google Magazines;
- Maps.apk - Google Maps;
- Music2.apk - Google Music;
- PlayGames.apk - Google PlayGames;
- PlusOne.apk - Google+;
- QuickOffice.apk - QuickOffice;
- Street.apk - Google Street;
- SunBeam.apk - SunBeam live wallpaper;
- Videos.apk - Google Movies;
- YouTube.apk - YouTube.
In addition to those listed earlier, the /system/priv-app directory also contains the following files: - CalendarProvider.apk - stores calendar data;
- GoogleFeedback.apk - sends a report about using Google Play;
- GoogleOneTimeInitilalizer.apk - installation wizard for additional Google applications;
- SetupWizard.apk - setup wizard on first launch;
- Wallet.apk - Google Wallet;
- talkback.apk - voice notification about events on the device.
The Gapps kit for KitKat, among other things, also includes a proprietary camera with support for spherical shooting and a proprietary desktop with integrated Google Now.
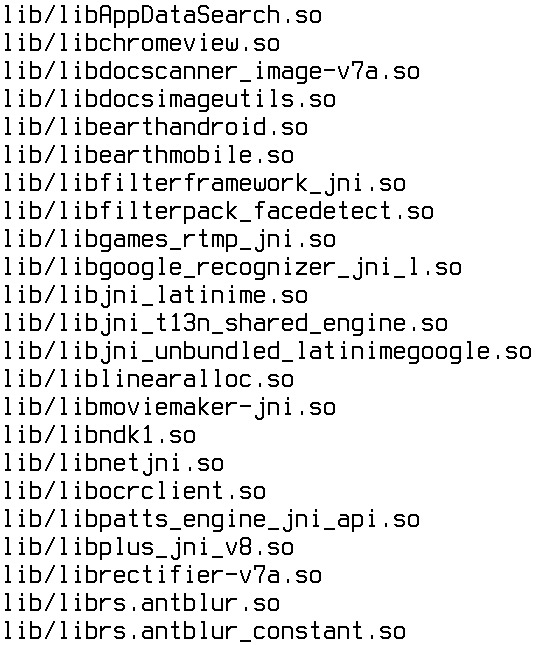
But that is not all. Google Apps depends on several frameworks, which are located in the /system/framework directory. These files are com.google.android.maps.jar, com.google.android.media.effects.jar and com.google.widevine.software.drm.jar. There are also many libraries in the /system/lib directory that are used exclusively by Google applications. It is not at all necessary to remove them, but it is possible. Just to clean up the trash. You can find their list in the comments. In previous (and future) versions of the system, the contents of Google Apps are different, so before deleting, I recommend downloading gapps of the desired version from goo.im/gapps, unpacking it using WinRar and viewing the contents. You should also take into account the dependence of some applications from the market on Google applications, I will talk more about this later.
Method number 3. Custom firmware without gapps
The previous method can be significantly simplified if you simply install custom firmware on your smartphone without Google Apps. In this case, the smartphone/tablet will be crystal clear without any connection to Google. The disadvantage of this method is the absence of Google Play, but you can either replace it with a third-party application store (more on that below), or use the following method, which involves installing a stripped-down Google versions Apps.
Method number 4. Google Play and nothing else
This method of partially decoupling from Google is a kind of compromise. It does not solve the problem of surveillance - at least without the settings from the first method - but it allows you to avoid cluttering the system with a bunch of useless software that will hang in the background and eat up memory. The idea is simple - install custom firmware and upload a minimalist version of gapps on top of it, which includes only Google Play.
There are many such minimal gapps assemblies on the Internet, but I would recommend using the time-tested BaNkS Gapps, namely the “month-dateGAppsCore4.4.2signed.zip” file. They work on any smartphone, are ART compatible and include only the basic gapps files, a list of which is given in the "What are Gapps" section, framework files, as well as several libraries. Essentially, it's Google Play, synchronization tools and nothing else.
Changing the search engine to DuckDuckGo
Even after complete shutdown synchronization, the “built-in” Google search bar will remain on the home screen. In the stock firmware of some manufacturers (Samsung, for example), this is just a widget that can be easily removed from the screen. In pure Android and devices from many other manufacturers, it is “built into” the home screen, but it can be removed by disabling all search from Google (along with Google Now) using the menu “Settings -> Applications -> All -> Google search-> Disable" or by installing a third-party launcher. Next, just download DuckDuckGo from the market or another application store and add the widget of the same name to your home screen.
Third party market
The second and third methods involve completely getting rid of Google Apps, including Google Play and the ability to log in using a Google account, so we must find a way to simply and conveniently install applications that would not force us to download them ourselves, and then dump them on a memory card and install manually. One such way is to install a third-party market.
On this moment There are three more or less viable alternatives to Google Play. These are Amazon Appstore, Yandex.Store and 1Mobile Market. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages, which mainly come down to the number of applications and payment methods:
- Amazon Appstore
- the most famous application store after Google Play. Contains more than 75 thousand applications (compared to 800 thousand on Google Play), the quality of each of which is manually checked, just like iTunes for iOS. You can pay using credit card or Amazon Coins, which are given as a gift for purchasing a Kindle Fire tablet or as a gift from another user. One of the most interesting features of the store is the daily giveaway one of the paid applications.
- Yandex.Store
- a store from the Yandex company. Contains more than 85 thousand applications, each of which is scanned by Kaspersky antivirus. It doesn’t particularly stand out, but it has a killer feature in the form of the ability to pay for purchases using the Yandex.Money service or a mobile phone account.
- 1Mobile Market
- the largest third-party repository of Android applications, including more than 500 thousand software. It differs from others by the presence of exclusively free applications (not to be confused with pirated ones), which is why it allows you not to go through the account registration stage and maintain anonymity.
Applications in all three markets have original digital signatures application developers, allowing them to be used simultaneously. An application installed from one market can be updated without problems from another, and if deleted, it will disappear from the list of installed ones in all of them. However, you will have to buy them separately.


Open Source Market
In addition to those described in the article, as well as many other lesser-known application stores, on the Internet you can find the F-Droid repository, which is different from the rest. It is completely anonymous and contains only free software distributed under licenses approved by the FSF. There are only a thousand applications in F-Droid, but all of them are guaranteed to not contain backdoors or other systems for disclosing personal data. It is F-Droid that is used as the default market in the free Android firmware Replicant.
Solving the problem of application dependence on Google Apps
Even though gapps components are not part of the official Android API, some applications still expect to see them on the system, which can cause a number of problems - from the application not working at all to losing some of its functionality. Some applications will refuse to install due to lack of Google Maps API, others crash immediately after launch without detecting it, others include direct links to Google Play, which can lead to crashes and incorrect operation.
To address these issues, XDA user MaR-V-iN started the NOGAPPS project, which is developing a set of open source components to replace the original Google Apps functionality. There are currently three replacement components available:
- Network Location- Wi-Fi based geolocation service and base stations GSM. Based on Apple's IP address database and open base station database;
- Maps API- replacement of the interface to Google Maps based on OpenStreetMap;
- BlankStore- an open alternative to the Play Store client. Allows you to install free applications from Google store, but is not recommended for use due to possible sanctions from the search engine (this is prohibited by their rules).
The components are installed separately and different ways. Network Location can only be manually copied to the /system/app/ directory in Android 2.3–4.3 or to the /system/priv-app/ directory in KitKat (in this case, you should use the NetworkLocation-gms.apk file). Maps API is installed by flashing the nogapps-maps.zip file via the recovery console. To install the market, you will have to not only copy the file, but also generate an Android ID on a large machine. After all the manipulations, the software should work correctly.
conclusions
For Google, Android is useless without its own apps, so it's not surprising that the company would take out the best parts of the system and leave the code closed. However, in this article I showed that there is life without gapps and it can be even easier and more convenient than with Google.