Resolution in Photoshop
Do you want to change the resolution in Photoshop? For this tutorial, I specifically saved from the Internet a wallpaper from the Spider-Man movie, a small size of 800 x 600px. Before proceeding, let's define the terms of Photoshop, as they are very important in this matter. If you have an order with the terms, immediately proceed to the part on how to change the resolution in Photoshop.
What is Resolution
Permission (resolution) is the number of pixels (pixels) by 1 inch (inch) . Parameter linking virtuality with reality. It is he who is responsible for the quality in which the image will be printed, because it is one thing when 300 pixels fit into an inch and quite another when 72 pixels fit into an inch.
If you print an image with a resolution 72ppi (pixels per inch) then most likely you will be able to see the pixels on the printout, in some particularly sensitive places the image will look like a mosaic. Just as the image on the grandmother's monitor in 1998 looked like a mosaic in the images of icons from Windows 98 and not only them. Low print resolution is evil and needs to be changed, that's what we're here for.
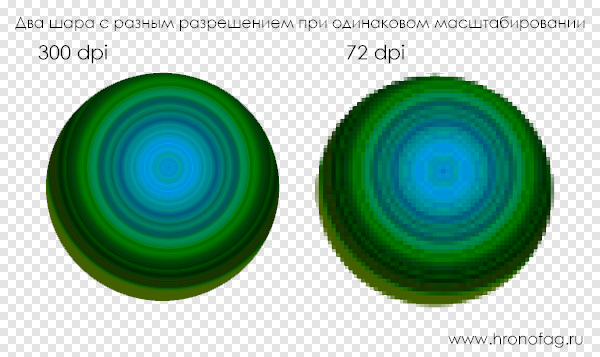
The actual size of the photo when transferring it from the monitor to paper depends on the resolution value. Since if the image is 500 on the 500px and his permission 100ppi then the actual size of this image is 5 on the 5 inches. Let me remind you that in inches 2.54cm. 100ppi of course not enough for printing, so we change the resolution to 300ppi but the physical size will also decrease along with the change in resolution, since resolution is actually the ratio of pixels to physical size (cm inches, centimeters). We increase the quality by laying in an inch more pixels, but the physical size also becomes smaller, since there are only 500 pixels and there is nowhere to take additional ones from. But we'll talk about this later.
I note that Photoshop adopted a different resolution designation (resolution). Instead of ppi received dpi, which stands for drops per inch. This is the subject of a completely different topic and eternal disputes between supporters of the correct formulations. Drop(a drop) this is the point that the printer puts when printing. And if you want to learn more about print preparation, check out my articles: Print Preparation in 10 Minutes and How to Make a Flyer
What is the size (dimension)
Size (dimension) is the total size of the image in width and height. It is measured in pixels. For example, the photo with which we will work 800 on the 600 pixels. Between two terms - size and resolution (resolution, dimension) there is an all-out battle. In the monitor size settings in windows size The screen is described by the term - resolution. Although we are talking about the usual obtuse size in height and width, and not about its resolution. The real resolution of monitors is still not very high, different monitors she fluctuates from 100 before 120ppi. That is, for 1 inch of the monitor screen in width and height, approximately from 100 to 120 pixels fit.
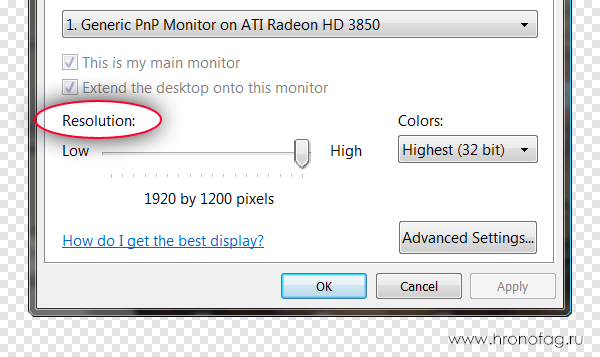
Numerous advertisements for optics, TVs and monitors are confusing, where the physical size of the screen is called the pixel size (dimension), then the resolution is called the size, then the ability of the lens to photograph a larger photo (dimension) again called resolution. In a word, in this confusion it is difficult to understand what is what. Especially when a third term is introduced - resolution, shifting English into Russian, and then they immediately say - permission, meaning something fourth. So, in Photoshop, Illustrator and a number of other graphic programs:
Dimension- the actual size of the photo in pixels in height and width. For example 100
on the 100
pixels.
Resolution is the number of pixels in one inch. For example, 100dpi means one inch 100
pixels. That is, the physical and actual size of the image 100
on the 100px with permission 100dpi will 1
inch.
How to change resolution in Photoshop
Our task is to prepare a picture downloaded from the Internet for high-quality printing, and the generally accepted resolution for such 300dpi. Open the image and go to Image > Image Size
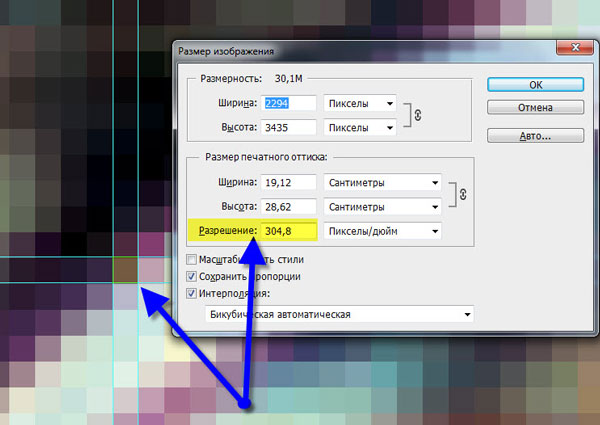
In the dialog that appears, we see three areas. This is, first of all Pixel Dimension , which tells us how many pixels are in our picture and Document Size (document size), which tells us what resolution is in the image, and what physical size will be printed based on this resolution.
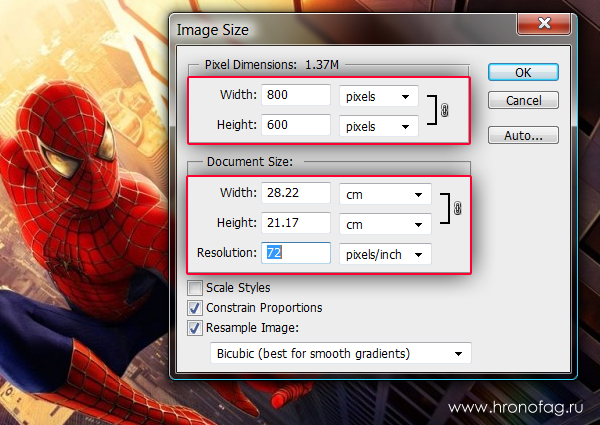
Physical size of my wallpaper 28 on the 21cm . Quite a lot, almost on a whole sheet A4 and this is not surprising, because only 72 pixels fit into 1 inch. Let's change the resolution to more and see what happens.
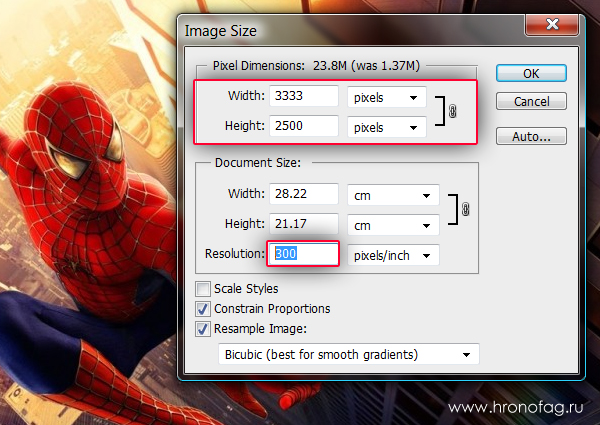
As soon as we change the resolution, all parameters change. Dimension Options Pixel Dimensions jumped 3 times. Instead of 800 pixels in width became 3333 pixels . It is not difficult to guess that the photograph is actually enlarged by 3 times. What's happening?
When I first started working with Photoshop, this property of changing the resolution plunged me into horror. I didn't want to change the size, I just wanted to change the resolution. But size and resolutions behaved like they were related. You know what, they really are connected. The fact is that Photoshop tries to preserve the physical size 28 on the 21 cm . But how to do this if the resolution changes?
Let me give you an example: here we have a picture 100 on the 100 pixels and resolution 100dpi. Accordingly, its physical size 1 inch, but suddenly it occurred to me to increase the resolution to 300dpi. How can Photoshop save the physical size in 1 inch, but increase the number of pixels. Where can he get extra 200 pixels ? You know where, come up with it yourself. If Photoshop doesn't add the pixels itself, it won't be able to save the physical size. Therefore, the image size increases along with the resolution. These are related parameters.

So I will press OK. The image is enlarged. Permission 300dpi, the physical dimensions remain the same 28 on the 21cm . Fine. But what is happening now? Photoshop enlarged the image. He is not a magician and a wizard, he just added pixels of similar color. In fact, the small image has stretched in the same way that the pattern on a balloon stretches when inflated. Its contours stretched and blurred. Moreover, the image was not of very high quality, it was subjected to JPG compression, and when enlarged, all small compression artifacts blurred and became visible. While it remained small, the defects were not noticeable, but when it was enlarged, everything came out. How do I know this?

It's not hard to notice when you zoom in on a photo with the tool. zoom tool. This is not difficult to notice by going through the channels of photography. The Blue channel was subjected to the greatest distortion, but that's not about it now. If you are interested in channels, read my article Channels in Photoshop.

There is another way to increase the resolution, which I will now discuss.
Many people ask questions such as "What is this resolution?", "How do I change the resolution of an image?" and “What is the minimum resolution needed to print beautiful photos?”.
A fairly common operation in Photoshop is resizing an image: if you want to print an image, send it to e-mail, publish it on a website, or simply as part of your work on a project in Photoshop.
Each of these tasks requires a version of the image of a particular size.
Resizing an image is not difficult: the program provides many options. The difficulty lies in doing this without ruining the quality of the image.
Here you will come across resolution, i.e., a unit of measure that determines the size of the pixels in the image.
It can be argued that resolution in photoshop is one of the most difficult digital imaging concepts to understand.
Below you will find all the details you need to answer the questions at the beginning of the article.
The smallest element of a bitmap is a pixel.
A pixel (short for picture element) is the smallest indivisible component of a bitmap that can be manipulated. It has two characteristics: position and color.
Zooming up to 3200 percent, you can see the individual pixels that make up a tiny part of this image.

Pixels form an image.
Pixels don't have given size and that's where the resolution comes into play.
Resolution is a unit of measurement that determines how many pixels will be placed in a certain space, which in turn determines how large or small the pixels will be.
You should understand resolution as pixel density, i.e. how closely the pixels are stacked.
Image resolution is the number of pixels (dots) per unit length.
Thus, the higher the resolution, the smaller the pixel size. The higher the resolution, the more pixels per inch. The higher the resolution, the better quality Images.
Digital photos are made up of pixels and therefore have a fixed resolution. You can enlarge such images, but only until the pixels become noticeable.
Objects created in vector graphics programs, such as Illustrator, for example, are specified mathematically; so, for example, a rectangle is defined by the aspect ratio, relative coordinates on the page, and the fill color. A vector graphic object can be printed at any resolution: both on a computer screen and on a huge poster, this object will be displayed with the same amount of detail.
One of the most significant benefits of working with vectors is that the "size-or-quality" problems you run into when working with bitmaps, don't touch them: you can make vector images as large or small as you like and they will always look great.


Photoshop is a raster graphics editor, but it also contains many features for working with vector graphics. This opens up interesting possibilities for creating various graphical elements - outline text, shapes, and resolution-independent layer clipping paths - all of these vector elements can be arbitrarily scaled without loss of detail.
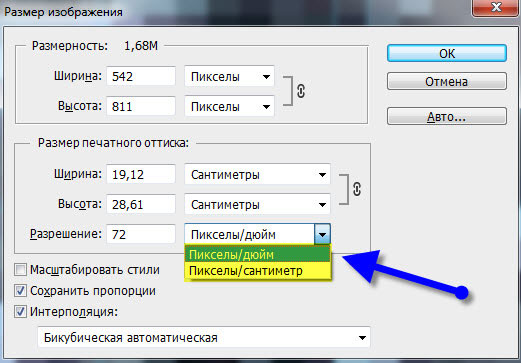
Resolution is usually measured in pixels per inch - ppi (pixels per inch) and sometimes in pixels per centimeter (pps).
You may also hear the resolution sometimes referred to as dpi, which means "dots per inch" (dots per inch). This notation is not entirely accurate, because technically dpi is the unit of measurement used by printers (since they actually print dots). However, many people mistakenly say "dots per inch" when referring to "pixels per inch".
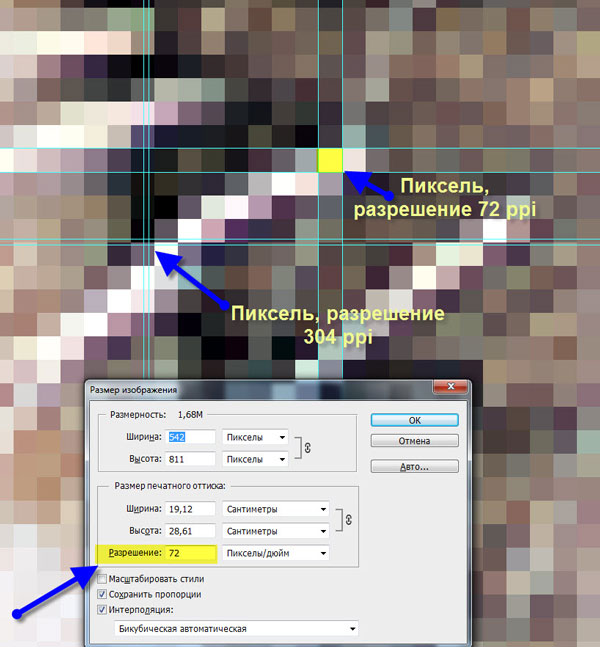
To understand the concept of permission, try to relate it to something in the real world. Imagine that you are pouring cubes into a glass to the very top. Then these cubes are reduced by 2 times and again same quantity pour into a glass. It will be filled with them only up to the “1/2 cup” mark. The number of cubes (read, pixels) has not changed, they have become smaller, as they are packed more tightly together (increased density - the same as higher resolution) in a cup (read, Photoshop document).
The cubes you started with are like low res, and the tightly packed ones are like high res.
Since increasing the resolution from, say, 72 ppi to 300 ppi reduces the size of the pixels and packs them more closely together, this results in a printed image that physically takes up less space, but is smoother and of better quality.
Downscaling, on the other hand, means more size and less pixel density, resulting in a physically larger image that, you guessed it, looks like it's made out of Lego bricks because the pixels are so big you can see them. each of them separately.
The printer is capable of producing images at a much higher resolution than your computer monitor (thousands of dots per inch instead of hundreds) and is one of the few devices that can change the printed document based on the resolution of the image.

In other words, send to jet printer lower resolution versions of the image high resolution, and it will produce two images that differ significantly in size and quality.
Resolution on a computer monitor, on the other hand, is handled by the graphics card driver, not the resolution specified in the image. That's why a 72 ppi image looks exactly the same on the screen as a 720 ppi image when you apply the View - Show Full Screen command to it.
Bottom line: printers can take advantage of the higher resolution (as can scanners), but monitors can't.
Resolution doesn't matter if you're not sending an image to a printer. If you're not going to print it, don't worry about resolution - focus on pixel size instead.
Resolution is selected for each image individually and depends on where it will be used. For example, if you plan to use a photo on the Internet, then the resolution is 72 ppi. This choice is dictated by the monitor from which your image will be broadcast. The main criterion for the Internet is the speed of downloading images, not their amazing quality, so appropriate file saving formats are chosen, where quality is far from the first place.
If you want to print your favorite photo on photo paper, then the resolution should be 300 ppi. By the way, this is the main requirement of photo centers and printing houses.
The most dangerous thing is that the monitor (its resolution is 72 ppi) does not show the future poor quality when printing photos with a resolution of 72 ppi.
If you open a photo with a resolution of 300 ppi on your computer, then it is clear that the monitor cannot place three points of the image at one point of its own. Therefore, it will display each point of the image in one of its own. And, as a result, the picture on the monitor will be about 4 times larger than it actually is.
Printed photos with a resolution of 72 ppi will be fuzzy, blurry.
That's all I wanted to say about resolution in photoshop.
I hope now this concept is completely clear and understandable for you.
And one more answer to the question that was raised at the beginning of the article: "How to change the image resolution and not lose the quality of the photo."
Very simple:
- Go to "Image - Image Size". This operation is performed quite often, so it is better to remember the hot key combination - Ctrl + Alt + I.
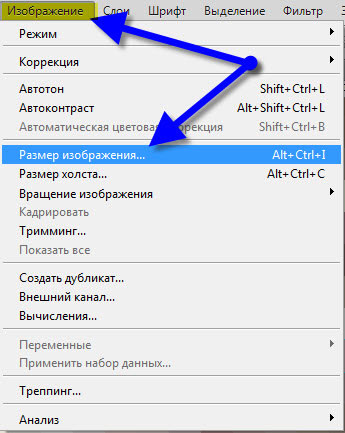
- Uncheck "Interpolation".
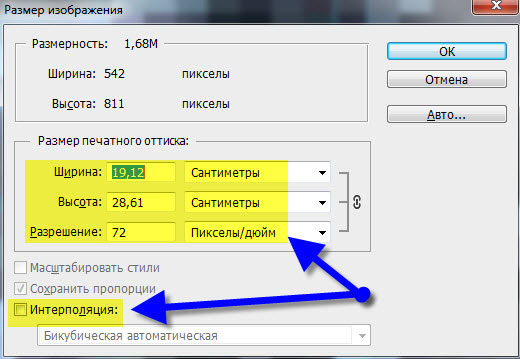
- Now completely free, without loss of quality for the photo, we change the resolution to the one you need. As noted above in the article, this only changes the physical size of the future print of the photograph.
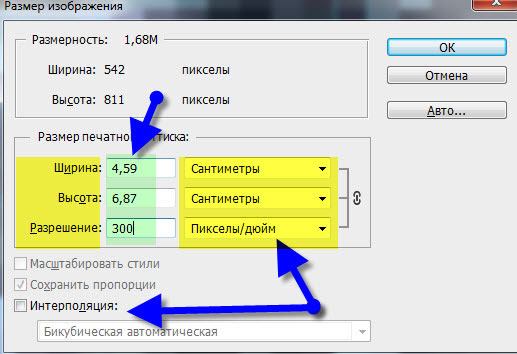
Thanks for attention.
Let's discuss the issues raised in the article in the comments below.
You can receive site news to your address.
To do this, enter your details in the form below:
Instruction
To reduce the file size, the image resolution is usually also reduced. To change the resolution of a picture, you will need any, even the simplest, graphics editor. For example, a fairly feature-rich, free Russian-language photo editor Paint.NET. You can download it here: www.paintnet.ru/download/. The installed Paint.NET takes up very little hard disk space, and its interface is clear even to an inexperienced user.
Install Paint.NET, run it, open the picture you want to resize. To do this, go to the menu "File" - "Open". After the picture opens, select "Image" - "Resize" from the toolbar. In the window that appears, select "Percentage" to change the resolution of the image as a percentage. If you want a predefined resolution, such as 800 pixels wide, select "Absolute Size" and enter your desired dimensions. Check the box "Keep aspect ratio" so that the picture does not stretch or flatten.
The picture with the new resolution is ready. In order not to lose the original file, which may be useful in the future, do not overwrite it, but select "File" - "Save As" and save the resulting image with a new resolution in the format you need to any convenient place, for example, on the desktop or to the My Pictures folder.
With magnification, you can see that the image perceived by the human eye at a distance as a complete picture consists of dots. The designation dpi (dots per inch) or the number of dots per inch serves as a unit of measurement for resolution Images. The more dots placed on one inch, the sharper the image looks, that is resolution it is customary to call the unit of measurement describing the density of points Images. To increase resolution Images, several steps must be taken.
Instruction
If you are working in graphics editor, for example, Adobe Photoshop, in the top menu bar, select "Image" (Image), in the drop-down menu, left-click on the item "Image Size" (Image Size), - a new dialog box will open. In the window that opens, in the fields for designating units of measurement, set (select using the drop-down list) the value "Pixels" (pixels) and enter the value you need. Click OK.
To increase resolution Images on the monitor screen, call the Screen component. To do this, open the “Control Panel” through the “Start” menu and in the “Appearance and Themes” category, left-click on the “Screen” icon. Another way: click in any place free from files and folders on the "Desktop" right click mouse, select "Properties" from the drop-down menu. A new "Properties: Display" dialog box will open.
In the window that opens, go to the "Settings" tab and drag the slider in the "Screen Resolution" group. The higher the screen resolution, the smaller the size of various on-screen elements (folder and file icons, labels, buttons in windows, and so on) will be. After selecting the desired resolution, click on the "Apply" button. The screen will briefly turn black, after which you will see how the elements will be displayed with the new resolution. Confirm your actions and close the display properties window.
How to enlarge a photo?


![]()
Many modern users ask the question: how to enlarge a digital image without losing quality? It happens that the photo is simply of poor quality and it is impossible to see all the details of the picture. We will talk about this problem in our article.
Digital Image Enlargement Process
The process during the increase digital image associated primarily with the presence of pixels in the photo. Let's say we have a photo of a certain size. The quality of a photo depends on the number of pixels it contains. When you expand a photo, its physical size will increase, but the number of pixels will remain the same. Therefore, the clarity of the image deteriorates, and the color gamut becomes blurry.
In order for the image to retain its original appearance, it is necessary to fill in all the empty pixels. This process is called interpolation. Interpolation is the count of missing pixels. Exist special programs, thanks to which you can enlarge a digital image without losing quality. We will talk about them a little later.
dpi
The logical unit of measurement is the dpi resolution. The abbreviation dpi (in English dots per inch) refers to the number of dots per inch. For example, for any image, you can set the resolution from one dpi to infinity. But the linear size of the image will change in inches or centimeters. The higher the resolution is set, the smaller the image will become.
Resolution Formula
Resolution (dpi) = pixels / inch, where pixels is the size of the image in pixels, inch is the size in inches. As the formula shows, we will not immediately know what resolution the photo will have if 2 sizes (in inches and dots) are not indicated.
Let's say the picture has a resolution of six dpi, and the width and height are twelve pixels. To find the physical height, you need to divide the height in points by the resolution. That is, twelve divided by six. We'll get two inches.
You can learn more about how to change image resolution in our article.
Enlarge a photo in Photoshop
You can enlarge a digital image using the graphic editor Adobe Photoshop (Photoshop). In order to enlarge an image in Adobe Photoshop, you must do the following:

How to enlarge an image in PhotoZoomPro
You can also enlarge a digital image using PhotoZoomPro. Thanks to built-in interpolation algorithms and modern technology S-Spline this program gives nice results. It works with many formats: BMP, JPEG, TIFF, PNG, TGA. gif. And if there is a need to prepare files for interior or large-format printing, the program becomes almost indispensable. You can download the PhotoZoomPro program on the official website  benvista.com.
benvista.com.
Image magnification principle
If you have a high-quality source image, you can get large-sized photos without losing quality. Consider the principle of enlarging a digital image using the PhotoZoomPro program.
