This article will look at how to quickly and efficiently organize a high-performance wireless network at home with access to.
Simple and cheap wireless connection
So, let's say you have at home desktop computer with a permanent connection to the Internet, and a laptop that you would like to connect to a local network with a desktop computer, and also provide shared access to the Internet. Today, there are several solutions to this problem, but not all of them can be called simple and accessible, especially for users who do not have special network knowledge.
In our opinion, the simplest and in an accessible way is the use of two adapters (the so-called Ad-Hoc or “point-to-point” connection), operating according to the 802.11b standard and providing an exchange rate of 11 Mbit / s, which is quite enough for normal operation.
For our experiments, we used the WNC-0101 USB USB controller and the Realtek RTL 8180 Wireless LAN controller built into the MaxSelect Mission Hammer Wide, Mini - PCI laptop.
Why USB Wi-Fi controller? It really doesn't matter which controller you use, you can choose PCI, PCMCIA, CF or SD. They all provide approximately the same level of functionality and communication quality. Main USB advantage The controller lies in its ease of installation and versatility of use. In other words, to install the controller there is no need to open the computer, and you can use it not only with a regular desktop computer, but also with an old laptop that does not have a built-in Wi-Fi controller, as well as with various compact Barebone platforms, where it is not always possible to find free PCI slot.

As for disadvantages of USB Wi-Fi controllers, then we can note the built-in antenna, which somewhat limits the range, however, given that we are talking about a home network, where the short range of the wireless network is not critical, we do not pay attention to this feature.
Installation features…
First of all, we recommend installing the driver and utility to configure parameters and monitor the connection, and only then connect the LevelOne WNC-0101 USB USB Wi-Fi controller. These recommendations apply not only to the LevelOne controller used, but also to any other USB Wi-Fi controllers.
Once you have installed the USB Wi-Fi controller, you can begin setting up your network. There are two ways to do this. In the first case, you can use your own IEEE 802.11b WPC Utility(USB), and in the second, you can use Windows XP tools. Moreover, it is important to note that before the appearance of the second service pack, which we strongly recommend installing if you really care about the security and stability of your computer, the tools built into XP somewhat limited the capabilities wireless connection, although they were quite functional. In the second service pack, Microsoft has significantly expanded the capabilities and significantly simplified the work with wireless connections.
In order for you to fully understand the configuration features, we present both methods and start with the tools built into XP.

So, first of all, open the properties of the network environment, where everything on your computer is displayed network connections. As you can see, our computer has many different wired and wireless network controllers installed, but now we are only interested in “wireless connection 3”, which is based on the LevelOne WNC-0101 USB controller. Now we open the properties of this connection, where we are interested in the second tab “Wireless Networks”. This is where we will make all the settings for our wireless network.
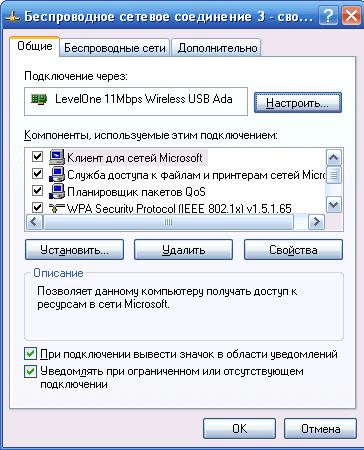
First of all, pay attention to the checkbox in the topmost item “Use Windows to configure the network”; this option allows you to choose which tools will be used to configure the network.
In the next step you should create your first wireless network, why press the button add in the "Preferred Networks" section, where you need to enter the name of your network (we chose the name MyHome), as well as set some special parameters that provide a certain level of security for your wireless network.
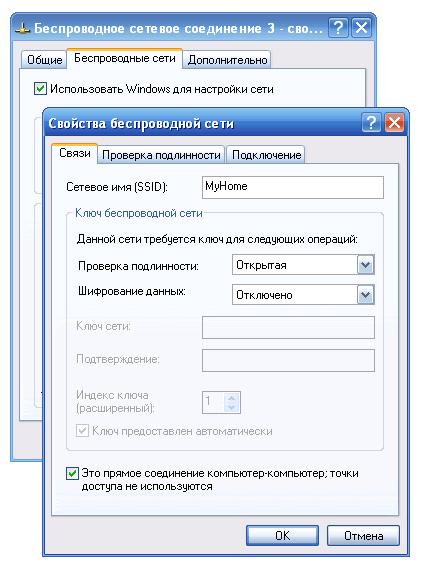
To simplify our first connection we decided to use open network without enabling data encryption. As you understand, such a network does not provide sufficient security for your data, but for a home connection like Ad-Hoc or computer-to-computer it is quite sufficient.
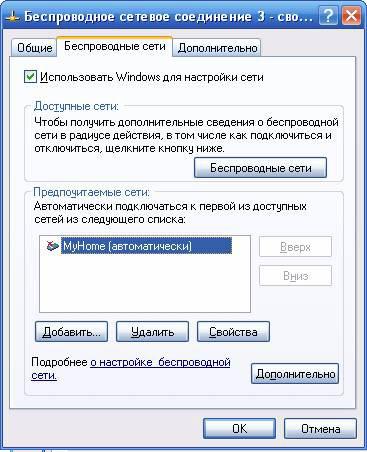
Windows XP tools allow you to create a wireless network using a special wizard available in the " Available networks" To do this, click the “Wireless Networks” button and in the wireless network manager that opens, click the “Set up wireless network” button. The main difference of this wizard is the ability to save wireless network settings on a Flash disk, which greatly simplifies the transfer of the network configuration to other computers on your network, however, for our situation, when we need to connect two computers, this feature is not relevant.

We will return to this manager a little later, but for now we will consider the second configuration method using the utility supplied with the LevelOne WNC-0101 USB controller. Let us remind you that in order to allow the use of a proprietary utility, you must uncheck the “Use Windows to configure the network” checkbox in the “Wireless networks” tab.

The utility includes a slightly larger set of features than Windows tools. There are six bookmarks here. The first tab “LAN Status” displays all wireless networks found around, in our case there are none yet, and also shows the strength and quality of the signal (it is also not displayed for an Ad-Hoc connection).

You can create a new network by opening the “Setting” tab. As you can see here, everything is very similar to what we saw above, but several features make working on wireless networks much more convenient.

First of all, pay attention to the ability to create up to five profiles that allow you to quickly change connection parameters. So, we create the first profile, initially we indicate the network name (SSID), network type (AD - Hoc). The communication channel used and the country can be left unchanged. Additional connection properties are available in the Advance window. Here the user can select the transfer speed, energy saving mode (important for laptops), and encryption mode.

The remaining bookmarks perform informational functions and are not particularly in demand if everything works fine.
In principle, at this point the first stage of setting up a desktop computer can be considered complete, and it’s time to set up a wireless network on a laptop.

In general, this process is completely identical to that described above, and we will not repeat ourselves; we will only remind you that depending on the Wi-Fi controller used, the functionality of the configuration utility may differ, but the basic settings remain identical.
Establishing a connection
It's time to establish a connection between the two computers. To do this, you can use either a proprietary utility or a network manager. Windows connections XP, about which we said a few words above, but before you do this, reboot both computers, which will allow an automatic connection of the two computers to be established, as evidenced by the icon in the system area of the desktop.

If the connection does not occur, open the utility Wi-Fi settings controller or network connection manager Windows XP. Personally, we recommend using the manager. It provides an easier and more intuitive wireless experience.

The main manager window displays a list of detected networks. If you see something similar to our screenshot, then we can assume that you have almost achieved the main goal - connecting two computers to a network.
If this is not the case, we recommend clicking the “Update network list” button. If nothing happened in this case, check whether the second computer is turned on, whether the Wi-Fi controller is working, and whether there is an error in setting up the wireless connection.
Last steps...
So, we have come to the final stage of connecting computers into a network - setting up an IP connection, setting up a gateway and sharing to files and printers. Despite such a complex name for the upcoming procedure, everything is done very simply, for which special thanks to the developers of Windows XP.
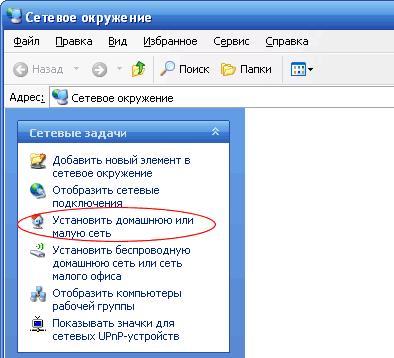
However, before you start setting up, we recommend paying attention to some hidden pitfalls that we encountered when we first set up a wireless network.
If your desktop computer is connected to a dedicated Internet channel and uses an internal IP address (for example, 192.168.0.0…255 or in another internal range), we recommend disabling network cable. The fact is that during setup your wireless controller the desktop computer will be assigned the address 192.168.0.1, which is usually used on the internal network, which will cause an address conflict and you will not be able to configure the gateway.
The second “stone” that made us tinker with setting up a wireless connection is the firewall built into Panda Internet Security. For the wireless network to work, you need to configure the firewall appropriately, both on your desktop computer and laptop, or simply temporarily disable it. By the way, the firewall package built into the second service does not cause any problems.
So, let’s launch the wizard on a desktop computer with an Internet connection. After answering a couple of trivial questions, you need to perform some actions that indicate to the master which connection is used for what.
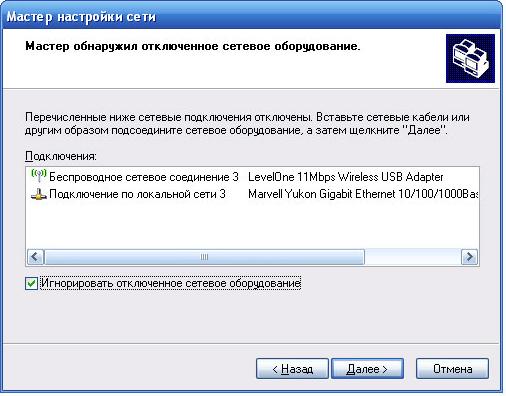
First you need to check the “ignore disconnected network equipment” checkbox, which will allow you to use a wired controller that is disconnected from the network. In the next window, you must select the role of this computer in your network.

Considering that our desktop computer has a permanent connection to an external network, and the laptop will connect to the Internet through it, we choose the first connection method.
In the next step, you specify which connection is used to connect to the Internet. In our case, this is “Local Area Connection”.
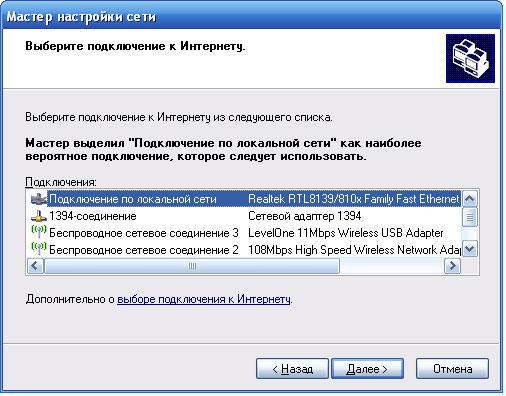
Next, we select which connections are used to connect to other computers on the network. Please note that you can combine wired and wireless connections here. In our case, we selected only “Wireless Connection 3”, which is based on the LevelOne WNC-0101 USB controller.

In the next two windows, you enter a computer name and description (optional), as well as a workgroup name.

Please note that computers on your local network must belong to the same workgroup, otherwise you will not be able to see them on the network.

Finally, the last window allows you to enable or disable file and printer sharing.

After clicking the “Next” button, the wizard will begin configuring the IP connection parameters, as well as sharing and security. If you did everything correctly, a final screen will open, in which you will be asked to save the settings or simply complete the wizard, which we will happily do.

After setup, you will notice some changes in the network connection settings.
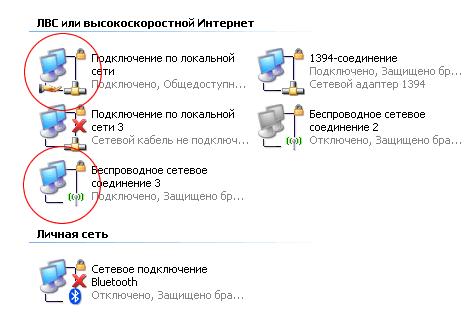
So, in the properties of “Local Area Network Connections” in the “Advanced” tab, all the checkboxes will be checked, and connections for the home network will be defined.

And in the properties of the TCP / IP protocol of “Wireless Connection 3” a fixed IP address and subnet mask will be set.
![]()
Now you can proceed to launch the wizard on your laptop. Here everything happens noticeably faster and you only need to install the second type of connection. The master will do the rest for you.

That's it, the setup process can be considered complete, and you, as the full owner of your home wireless network, can launch any Internet applications, including. In addition, you can easily work with both disks on another computer and printers, providing wireless printing from a laptop located in another room.
A few words about the speed and range of the wireless network...
As we said above, for our first wireless network we used controllers operating according to the 802.11b standard with maximum speed exchange 11 Mbit/s. Of course, in today's times this is not a lot, and against the background of modern controllers operating using the 802.11 g and 802.11 Super G protocol, providing exchange speeds of 54 Mbit / s and 108 Mbit / s, it does not look very good. However, for the first experience, this solution is sufficient, allowing you to achieve quite good capabilities without having to deal with some of the specific features of a high-speed connection, which we will still have to tinker with in the future.
As for the actual exchange speed, to study it we used the ICB 2000 program, which allows you to measure network traffic. Moreover, we are not interested in the speed of artificially generated traffic, but in the speed of actual transfer of files and other information.
So, first we will look at what our wireless network is capable of when copying a large file from a desktop computer to a laptop while simultaneously watching on-line a movie recorded on the desktop computer on the laptop. In this mode, we load the wireless channel as much as possible.

As you can see, the maximum throughput The wireless channel in this mode averages 4636 Kb/s. It is very important to note here that we did not observe any slowdowns when watching a movie, which allows us to conclude that in small home networks, the capabilities of 802.11b networks are quite sufficient.
If you start copying in the opposite direction, i.e. in Download mode for a desktop computer, the maximum throughput of our channel will be slightly higher - 4984 Kb/s with a peak value of 5305 Kb/s.
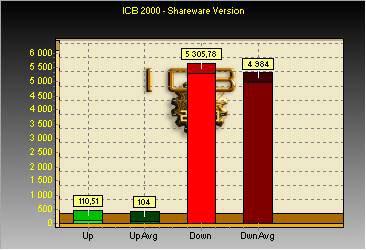
If, while copying a file from a desktop computer to a laptop, we run the same task, but in the opposite direction, the speed will drop slightly. Moreover, the speed in Upload mode does not drop significantly, but in Download mode we observe a noticeable decrease in performance.

And finally, let's see what happens when we run any network application, generating a balanced load on the channel. Here we simply started watching a movie recorded on a desktop computer on a laptop.

As you can see, in this mode the load on the channel is so insignificant that you can easily launch network viewing on a couple more computers. This is what explains the lack of slowdowns when watching a movie while copying a file in parallel. As for the range, in such a network it is not very large, and depends on the configuration of the room. In fact, in a regular apartment or small office everything will work fine.
How many computers can be connected to such a wireless network?
A pleasant surprise for many of you will be that a simple Ad-Hoc network can include several computers at once, which can be easily connected to each other and provide easy access to the Internet. However, remember that an increase in the number of computers working simultaneously on the network significantly reduces network performance, which is due to the need to transfer all data through the desktop computer, which in our case is the gateway.
Conclusion…
So, we hope that the above detailed recommendations will simplify your first experience of creating a wireless home network. Despite the apparent complexity of the process, everything turned out to be more than simple. However, we cannot claim that the presented solution is universal and will be equally correct for all cases. Experience shows that almost every installation of a wireless network with new equipment raises some questions, especially for users who do not have special training. The main thing is that you must clearly understand and imagine the sequence of actions that should lead to the successful launch of a wireless network. In the next article, we will introduce you to equipment that can significantly increase the performance of your home network.
Thank you for your attention!
Leave your review:
Many users of laptops and communicators are accustomed to the fact that airports, business centers, hotels, universities, libraries, cafes or restaurants provide the opportunity to use wireless Internet. This is very convenient because it allows you to more or less constantly stay in touch while moving around the city or building. At the same time, the speed of the communication channel is high, the signal is stable, but you do not need to connect to any wires. You can also get mobile Internet access at home if you configure wireless Internet via Wi-Fi.
Wi-Fi technology was developed for Wireless LAN wireless equipment. Its name comes as an abbreviation for the English Wireless Fidelity, which means “wireless precision”, by analogy with the Hi-Fi standard (High Fidelity – “high precision”) for sound reproducing equipment.

[b]The Wi-Fi trademark belongs to the developer, the Wi-Fi Alliance consortium
Wi-Fi is based on international standards IEEE 802.11, the latest approved release of which, called IEEE 802.11n, allows data transfer rates to increase to 480 Mbps when compatible devices are used simultaneously. When building a home wireless network, you should choose equipment that supports one standard, so as not to encounter a situation where devices simply “do not see” each other. By creating a protection mechanism for a heterogeneous network, we end up with a network in which all devices operate at much lower speeds than if they were all equipped with adapters of even an earlier standard.
Information is transmitted using radio waves emitted by a source in the frequency range corresponding to the IEEE 802.11 standard. Connection is made via wireless points access. The network coverage area around one access point is called a “hot spot” or “hot spot”. The minimum Wi-Fi network configuration is one access point plus one client.
[b] Network equipment
To set up home wireless Internet within a regular apartment, you will need at least one access point. It may well be enough for neighboring apartments, and even for a neighboring house, because the network range indoors is 45 m, and outdoors - all 450 m. An access point is nothing more than a network hub.

[b]The variety of models available allows you to choose an access point that meets all the wishes of users
In addition, the access point may be built into wireless router– this device is also widely used in building wireless networks. A router (router) operates on the border of two networks – internal and external. The local network connects to the internal LAN port, and the Internet to the external WAN port. There are usually several internal ports; they are combined into a switch. An Ethernet cable or ADSL modem is connected to the external port. A wireless router has the ability to connect wireless devices via radio signal, and they, along with those connected to the LAN port, will have access to the external network.
Most modern routers designed for small offices and home use, have built-in firewalls that allow you to protect your internal network from unauthorized access from the outside.
You need to choose based on which of the two devices - an access point or a wireless router - to plan your network, depending on its future purpose.
[b]Building a network
In order to build a wireless home network By Wi-Fi technology, you can go two ways. The first one is called Ad-hoc. It is used to connect several groups of computers with wireless network adapters into separate networks. This mode does not require an access point. If one of the computers does not have a wireless adapter, then it is connected to an access point. This mode is convenient if you need to combine several closely located devices into a single local network. But you won’t be able to access the Internet in this mode.
The second path is called “infrastructure”. It is relevant when Internet access is required. There are two operating modes of this network: basic (BSS) and extended (ESS). In the basic mode, all devices are connected to each other through one access point, which also serves as a network bridge between cable and wireless sections of the network and is a channel for access to an external network. In extended mode, several access points are connected to each other either using a radio signal or via cable connection. Each access point forms its own network, and they can transmit redundant traffic to each other. Each computer is configured to access the Internet via a local network.
There is another way in which Internet access occurs using DSL technology, via an Ethernet connection or using a cable modem. In this case, naturally, you need to choose a wireless router.
[b]Network setup
In order for the local network to have access to the Internet, you need to configure each computer and the selected wireless equipment. All devices must have the same IP address, and it must be entered into the network settings on each of them.
Everyone has it network device, including the access point and wireless router, have factory-set IP addresses. These settings and the password for making changes to the device are presented in the user manual.
Then you need to connect the access point or router to a computer that has an Ethernet controller. If a wireless router is used instead of an access point, the computer should be connected to its LAN port.
Let's assume that the default access point is configured with an IP address of 192.168.1.254. You need to change the IP address of the connected computer to an address from the same subnet, for example 192.168.1.100. To do this, click right click mouse over the " network" on the desktop and select the "Properties" menu - the "Network connections" window will open. In it you need to select "Local network" and "Properties" again. The "Network connection properties" window will open, in which you need to configure the network adapter.

[b]In the "Network Connection Properties" window, select "Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)"
After selecting "Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)", you need to click on the "Properties" button. In the window that opens, you need to mark the “Use the following IP address” checkbox and carefully enter the new IP address and network mask data. In this example, these will be 192.168.1.100 and 255.255.255.0, respectively.

[b]In this window you should change the settings of the computer’s IP address
After setting your computer to a new static IP address, you should go to the settings of your access point or wireless router. Enter in address bar The browser you are using has the factory IP address (192.168.1.254). The settings of the access point or router will open (if the system asks you to enter the login and password contained in the instructions, do so). If you need to make changes to the IP address of the access point, you will then have to assign a new IP address to the network adapter on the computer, otherwise it will become impossible to maintain communication with the point.
In the access point (router) settings dialog box, you should also indicate which standards you are going to use in the wireless network you are creating. If there will be devices on the network that support different protocols, indicate this (for example: 802.11b/g). When selecting frequency channels, it makes sense to specify the automatic selection item. The equipment settings must also reflect the unique identifier of the future wireless network SSID. It must be the same for the access point and for each client on the network. It is better not to manually select the speed of the connection being created, but also to entrust it to automation.
[b] Setting up network computers
After setting up the access point, you should configure all computers on the network. To do this, you need to create a wireless connection on each of them, following the wireless adapter setup wizard. It's pretty simple and universal method. Right-click on the "Network Neighborhood" icon and select "Properties". In the Network Connections list that opens, click Wireless Connections and click Properties. The Wireless Network Connection Properties window opens. In this window, you need to select the “Wireless Networks” tab and click the “Add” button. In the "Wireless Connection Properties" dialog that opens, enter the SSID. There is no need to touch the remaining points.
After completing the configuration of the wireless adapter, it independently establishes a connection with the access point or wireless router.
Next you can create logical drive or shared folder with shared resources, to which all network users will have access. To do this, on each computer you need to select in the “My Computer” window any drive or folder that you are going to share and right-click. From the list that opens, select “Properties” and on the “Access” tab, click the single warning label.

[b]A warning notice indicates the risk of sharing the drive.
In the dialog box that opens, check the boxes to allow clients on your network to use this disk (folder) and change data on it (if necessary).
Now you have a wireless network at home, users of which can access the Internet and share files.
Just imagine: you can browse the web while sitting on the living room couch, chat with friends while lying in bed, and send documents to your home office printer from your computer in the kitchen. The wireless network provides exceptional capabilities and is very easy to set up. This article provides step by step instructions By setting up a wireless network and started using it.
Equipment needed to connect Windows to a wireless network
The following components are required to set up a wireless network:
Broadband Internet connection and modem
Broadband Internet Connection guarantees high data transfer speeds - as opposed to slow remote access, not powerful enough to support a wireless network. Typically, a broadband connection is established using digital subscriber line (DSL) or cable. To get a broadband connection, contact your internet service provider. Typically DSL connections are provided telephone companies, and the cable connection is from the cable television company.
Internet service providers often provide and even install broadband modems. Some ISPs offer a combination of modem and wireless routers. This equipment can also be purchased at computer and electronic equipment stores.
Wireless router
The router transmits data between the network and the Internet. The wireless router allows connect your computer to the network using radio signals rather than cables.
There are several types of wireless network technologies, including 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, and 802.11n. We recommend using a router that supports 802.11g or 802.11n technology because such models can provide adequate data transfer speeds and support sufficient radio signal strength.
Wireless network adapters
Network adapter is a device that connects a computer to the network. To connect a laptop or desktop computer to a wireless network, it must be equipped with a wireless network adapter. Most laptops and desktop computers come with a wireless network adapter pre-installed. To find out if your computer has a wireless network adapter installed, follow these steps:
- Open device Manager
- Double-click the icon Network adapters .
- Find network adapter, which has the word “wireless” in its name.
If your computer requires a wireless network adapter, you can purchase one from a computer and electronics store and install it yourself.
We recommend choosing universal serial bus (USB) adapters: they are small in size, easy to install, and can be moved from computer to computer. Make sure that the type of adapters is the same as the one in your wireless router. Usually the type of adapter is indicated on the packaging and is designated by a letter (for example, G or A).

Setting up a modem and Internet connection
When all the necessary equipment is installed, you need to configure the modem and Internet connection.
If your ISP has not set up your modem, connect the modem to your computer and the Internet by following the instructions in your modem documentation. If you are using digital subscriber line (DSL), connect the modem to the telephone jack. If you are using a cable, connect the modem to the cable connector.
Location of the wireless router on the network
Your wireless router should be located where it can receive a strong signal with minimal interference. For getting best results use the following tips.
- Place your wireless router in the center. The router should be placed closer to the center of the house to provide a strong wireless signal throughout the house.
- Do not place the wireless router on the floor or near walls or metal objects, for example, metal filing cabinets. The fewer physical obstacles there are between your computer and the router, the stronger the router's signal will be.
- Reduce Interference. 802.11g networking equipment uses a radio frequency of 2.4 gigahertz (GHz). Microwave ovens and many cordless phones typically operate on this frequency. When turned on microwave oven or receiving a call on wireless phone The wireless network signal may be temporarily interrupted. Most of these problems can be avoided by using a cordless phone with high frequency(eg 5.8 GHz).
Protecting your wireless network using Windows
Security is always important, and when using a wireless network, this issue becomes even more acute because the signal can spread outside the premises. If you don't secure your network, users of other nearby computers will be able to access data stored on computers on your network and use your Internet connection. To secure your wireless network, follow these steps:
- Protect your router by changing the default username and password. Most manufacturers provide a default username, password, and network name for the router. This information can be used to access the router without the owner's knowledge. To avoid this, change the router's default username and password. Additional instructions can be found in the documentation that came with the device.
- Set up a security key for your network. File cabinets are protected with a key, safes are protected with a code, and wireless networks are protected from unauthorized access with a network security key.
How to set up a network security key in Windows?
- Open Network and Sharing Center .
- Click the item Setting up a new connection or network .
- Menu setting new network and select Next.
The wizard will provide step-by-step instructions for creating a network name and security key. If your router supports secure Wi-Fi access protected access (WPA or WPA2), the wizard will configure it by default.
In addition, WPA2 or WPA technology allows you to use a passphrase, which means there is no need to remember a complex sequence of letters and numbers.
Write down the security key and keep it in a safe place. The security key can be written to a USB flash memory by following the wizard's instructions.
- Use a firewall. A firewall is a piece of equipment or software which helps protect your computer from hackers and malware. Using firewalls on all computers on a network will help control the spread of malware on the network and also protect computers when accessing the Internet. Windows Firewall comes with Windows!
Adding computers to a wireless network
To connect your laptop or desktop computer to your wireless network, follow these steps.
- Open the Connect to Network window.
- Select the network you want to connect to from the list and click the Connect button.
- Enter your security key. You can enter the key or connect a USB flash memory with a record of this key to the USB port of the computer.
File and Printer Sharing
Mostly, a wireless network is installed in order to have access to the Internet from any room in the house, but users also need wireless access to files and printers.
File sharing
The easiest way to provide general access to files on the network - set up sharing for your homegroup. If you don't have a homegroup, you can share files by placing them in a folder in the Public Folders section. Network-connected users automatically share all files or folders in the shared folder. To grant access to a shared folder, follow these steps:
- Open the window additional settings public access .
- Click the double arrow to expand the current network profile .
- In the Sharing of the General folder box, select one of the following options:
- enable sharing so that all users with network access can read and write files in shared folders;
- disable access to the shared folder (users connected to the computer still have access rights to these folders).
- Click the button Save changes . If you are prompted for an administrator password or confirmation, enter the password or confirm.
The above steps are necessary run on all computers, which host files for public access.
To provide access to your own files, save or copy these files to a folder on your computer. For each type of library (Documents, Music, Images and Videos) there is a shared folder. Each person has account on the computer has access to these folders. For example, to open the Shared Documents folder, do the following:
- Open your document library.
- In the Navigation Pane, under Libraries, double-click Documents, then double-click Shared Documents.
Printer sharing
If you have a printer connected to one of the computers on your network, you can print to it from any computer connected to that wireless network. The easiest way to share a printer is to check the Printers when setting up your homegroup. If you don't have a HomeGroup, you can follow these steps.
- Sign in Windows system to which the printer is connected.
- Open the Advanced Sharing Options window.
- Click the double arrow to expand your current network profile.
- Under File and Printer Sharing, click Enable file and printer sharing , then click the Save changes button. If you are prompted for an administrator password or confirmation, enter the password or confirm.
Note: When password protected sharing is enabled, users can use an account with a password to access the printer.
To access the printer from any computer on the network, follow these steps:
- Open the Network folder.
- Double-click the icon of the computer to which the printer is connected.
- Double-click the printer icon. Windows will automatically add and install a printer driver to your computer.
Enjoy your freedom!
That's it - the wireless network is ready to use. Now you can surf the Internet, send email and shop online while lying on the couch or relaxing on the terrace.
Since now every apartment has several computers and mobile devices with Wi-Fi, often ordinary users The question arises about how the wireless network is configured. In this article we will shed light on this slippery issue. An example will be given of setting up a wireless network in Windows 7.
First you need to configure main computer our future network. It can be either a laptop or To do this, we activate the Wi-Fi adapter on our computer. Then open the menu and right-click on the computer, where in the context menu click on properties. After all this we go to Extra options system and click on the name of the computer, and in the “Description” column we give our description, for example, “Vladimir Ilyich’s computer.” Next, select “Change” and give a name to this device, which should not be duplicated by others on the network. In the column " Working group"Indicate the name of this group, which should be the same on all devices on our network, and reboot.
When the computer restarts, wireless network setup continues. Select the wired connection icon and go to “Network Management”, where we click on “Wireless Network Management”. In the menu that appears, select “Add” and then set up wireless. Here you must also come up with the name you want for your network. Then select "WPA2 Personal Security". If there are devices on the network running Windows XP, then select “WEP”.
After that, set a password, click “Next” and in the new dialog that appears, allow Internet sharing for network computers, and then close the window.
But that’s it for setting up a wireless network. Now our task is to set up the remaining computers on this network. Turn on wireless adapter, open the Start button menu. We continue by clicking the button on the right side of the manipulator on the “Computer” icon, where we select “Properties and additional system settings.” Now click on the “Computer name” section and give it your individual name. Next, specify the group name, which must match the group name on the host computer.

Again we go to network management, where we go to the “Changes adapter parameters” section and select “Properties”, after which we jump on the line of protocol version 4. Here we mark the point of setting the IP address. In the “IP address” column we assign ours to this computer, and this must be done based on the IP of the main PC. For example, if the IP of the main device is 192.168.0.1, then the IP of all computers will be the same, except for the last digit. It is very important that there are no identical IPs on the network. In the column we type 255.255.255.0, and the line will contain the IP address of the main computer. In the fields "Preferred DNS server" and "Alternative DNS server" we indicate the addresses of the provider.
After all these manipulations we accept the changes. And only now we go to network connections, select our network, enter the password, and that’s it. If there are no more computers on the network, this completes the wireless network setup. If there are any other computers or laptops, then in this case it is necessary to repeat the procedure for setting up the last computer.

I would like to add my own recommendations for ensuring network security. Recently, cases of intrusion into wireless networks by unauthorized users have become more frequent. Be sure to install on your host computer antivirus program. Also come up with a long and complex password with large and small letters mixed with numbers. This will increase security and minimize the risk of interference by unauthorized persons, and will also prevent the theft of valuable information and the downloading of third-party software.



