As is usually the case with abbreviations used to denote specifics and technical characteristics, there is confusion and substitution of concepts regarding TFT and IPS. Largely due to unqualified descriptions electronic devices in catalogs, consumers pose the question of choice initially incorrectly. So, the IPS matrix is a kind of TFT matrices, so it is impossible to compare these two categories with each other. However, for the Russian consumer, the abbreviation TFT often means TN-TFT technology, and in this case it is already possible to make a choice. So, speaking about the differences between TFT and IPS screens, we will mean TFT screens made using TN and IPS technologies.
TN-TFT- technology for making a matrix of a liquid crystal (on thin-film transistors) screen, when the crystals, in the absence of voltage, rotate to each other at an angle of 90 degrees in a horizontal plane between two plates. The crystals are arranged in a spiral, and as a result, when the maximum voltage is applied, the crystals turn in such a way that when light passes through them, black pixels are formed. No tension - white.
IPS- technology for making a matrix of a liquid crystal (on thin-film transistors) screen, when the crystals are arranged parallel to each other along a single plane of the screen, and not spirally. In the absence of voltage, liquid crystal molecules do not rotate.
In practice, the most important difference between an IPS matrix and a TN-TFT matrix is the increased level of contrast due to the almost perfect black display. The picture is clearer.
The color rendering quality of TN-TFT matrices leaves much to be desired. Each pixel in this case can have its own hue, different from the others, resulting in distorted colors. IPS already treats the image much more carefully.
The response speed of TN-TFT is slightly higher than that of other matrices. IPS takes time to rotate the entire array of parallel crystals. Thus, when performing tasks where drawing speed is important, it is much more profitable to use TN matrices. On the other hand, in everyday use, a person does not notice the difference in response time.
Monitors and displays based on IPS matrices are much more energy intensive. This is due to the high level of voltage required to rotate the array of crystals. Therefore, TN-TFT technology is more suitable for energy saving tasks in mobile and portable devices.
IPS-based screens have wide viewing angles, that is, they do not distort or invert colors if the view falls at an angle. Unlike TN, IPS viewing angles are 178 degrees both vertically and horizontally.
Another difference that is important for the end user is the price. TN-TFT is by far the cheapest and most mass-produced matrix option, so it is used in budget electronics models.
TheDifference.ru determined that the difference between TFT (TN-TFT) and IPS screens is as follows:
IPS screens are less responsive and have longer response times.
IPS screens provide better color reproduction and contrast.
Viewing angles IPS screens substantially more.
IPS screens require more power.
IPS screens are more expensive.
Before the mass distribution of smartphones, when buying phones, we evaluated them mainly by design and only occasionally paid attention to functionality. Times have changed: now all smartphones have approximately the same capabilities, and when looking only at the front panel, one gadget can hardly be distinguished from another. Came to the fore specifications devices, and the most important among them for many is the screen. We will tell you what lies behind the terms TFT, TN, IPS, PLS, and help you choose a smartphone with the desired screen characteristics.
Matrix types
AT modern smartphones Three technologies for the production of matrices are mainly used: two are based on liquid crystals - TN + film and IPS, and the third - AMOLED - on organic light emitting diodes. But before we start, it is worth talking about the acronym TFT, which is the source of many misconceptions. TFT (thin-film transistor) are thin-film transistors that are used to control the operation of each sub-pixel of modern screens. TFT technology is used in all the types of screens listed above, including AMOLED, therefore, if somewhere it is said about comparing TFT and IPS, then this is a fundamentally wrong question.
Most TFT matrices use amorphous silicon, but TFT on polycrystalline silicon (LTPS-TFT) has recently been introduced into production. The main advantages of the new technology are the reduction of power consumption and the size of transistors, which makes it possible to achieve high pixel densities (more than 500 ppi). OnePlus One became one of the first smartphones with an IPS display and a LTPS-TFT matrix.

Smartphone OnePlus One
Now that we have dealt with TFT, let's go directly to the types of matrices. Despite the wide variety of LCD types, they all have the same basic principle of operation: the current applied to the molecules of liquid crystals sets the angle of light polarization (it affects the brightness of the subpixel). The polarized light then passes through a light filter and is colored in the color of the corresponding subpixel. The first to appear in smartphones were the simplest and cheapest TN + film matrices, the name of which is often abbreviated to TN. They have small viewing angles (no more than 60 degrees when deviated from the vertical), and even with small inclinations, the image on screens with such matrices is inverted. Among other disadvantages of TN-matrices are low contrast and low color accuracy. To date, such screens are used only in the cheapest smartphones, and the vast majority of new gadgets have more advanced displays.

The most common in mobile gadgets now is IPS technology, sometimes referred to as SFT. IPS-matrices appeared 20 years ago and since then have been produced in various modifications, the number of which is close to two dozen. Nevertheless, it is worth highlighting among them those that are the most technologically advanced and are actively used in this moment: AH-IPS from LG and PLS from Samsung, which are very similar in their properties, which even caused a lawsuit between manufacturers. Modern IPS modifications have wide viewing angles that are close to 180 degrees, realistic color reproduction and provide the ability to create displays with a high pixel density. Unfortunately, gadget manufacturers almost never report the exact type of IPS matrices, although when using a smartphone, the differences will be visible to the naked eye. Cheaper IPS matrices are characterized by fading of the picture when the screen is tilted, as well as low color accuracy: the image can be either too “acidic” or, on the contrary, “faded”.
As for power consumption, in liquid crystal displays it is mainly determined by the power of the backlight elements (LEDs are used in smartphones for this purpose), so the consumption of TN + film and IPS matrices can be considered approximately the same at the same brightness level.

Matrices created on the basis of organic light-emitting diodes (OLED) are completely different from LCDs. In them, the subpixels themselves, which are subminiature organic light-emitting diodes, serve as a light source. Since there is no need for external illumination, such screens can be made thinner than liquid crystal. Smartphones use a variation of OLED technology, AMOLED, which uses an active TFT matrix to drive sub-pixels. This is what allows AMOLEDs to display colors, while conventional OLED panels can only be monochrome. AMOLED matrices provide the deepest blacks, since it only requires completely turning off the LEDs to “display” it. Compared to LCDs, these matrices have lower power consumption, especially when using dark themes, in which the black areas of the screen do not consume power at all. Another characteristic feature of AMOLED is too saturated colors. At the dawn of their appearance, such matrices really had an implausible color reproduction, and although such “childhood sores” are long gone, most smartphones with such screens still have a built-in saturation setting that allows you to bring the image on AMOLED closer in perception to IPS screens.

Another limitation of AMOLED screens used to be the unequal lifetime of LEDs of different colors. After a couple of years of using a smartphone, this could lead to sub-pixel burnout and afterimage of some interface elements, primarily on the notification panel. But, as in the case of color reproduction, this problem is long gone, and modern organic LEDs are designed for at least three years of continuous operation.

Let's summarize briefly. The most high-quality and brightest image at the moment is provided by AMOLED matrices: even Apple is rumored to use such displays in one of the next iPhones. But, it should be borne in mind that Samsung, as the main manufacturer of such panels, keeps all the latest developments for itself, and sells “last year's” matrices to other manufacturers. Therefore, when choosing a smartphone not from Samsung, you should look towards high-quality IPS screens. But in no case should you choose gadgets with TN + film displays - today this technology is already considered obsolete.
The perception of the image on the screen can be influenced not only by the technology of the matrix, but also by the pattern of subpixels. However, with LCDs, everything is quite simple: in them, each RGB pixel consists of three elongated subpixels, which, depending on the modification of the technology, can be in the form of a rectangle or a “tick”.
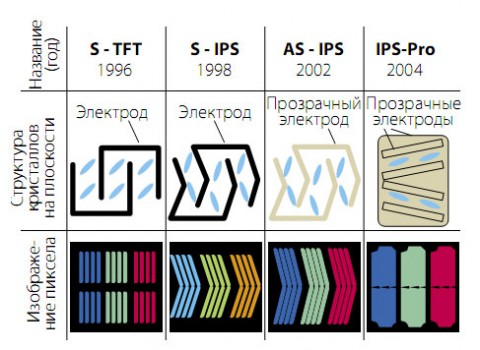
Everything is more interesting in AMOLED screens. Since in such matrices the subpixels themselves are the light sources, and the human eye is more sensitive to pure green light than to pure red or blue, using the same pattern in AMOLED as in IPS would degrade color reproduction and make the picture unrealistic. An attempt to solve this problem was the first version of the PenTile technology, which used two types of pixels: RG (red-green) and BG (blue-green), consisting of two subpixels of the corresponding colors. Moreover, if the red and blue subpixels had a shape close to squares, then the green ones looked more like strongly elongated rectangles. The disadvantages of this pattern were "dirty" white color, jagged edges at the junction of different colors, and at low ppi - a clearly visible grid of the subpixel substrate, which appears due to too much distance between them. In addition, the resolution indicated in the characteristics of such devices was “dishonest”: if an IPS HD matrix has 2,764,800 subpixels, then an AMOLED HD matrix has only 1,843,200, which led to a visible difference in the clarity of IPS and AMOLED matrices with the naked eye. seemingly the same pixel density. The latest flagship smartphone with such an AMOLED matrix was samsung galaxy S III.

In smartpad Galaxy Note II, the South Korean company made an attempt to abandon PenTile: the screen of the device had full-fledged RBG pixels, although with an unusual arrangement of subpixels. However, for unclear reasons, Samsung subsequently abandoned such a pattern - perhaps the manufacturer faced the problem of further increasing ppi.

In their modern Samsung screens returned to RG-BG pixels using a new pattern type called Diamond PenTile. New technology allowed to make the white color more natural, and as for the jagged edges (for example, individual red subpixels were clearly visible around a white object on a black background), this problem was solved even easier - by increasing the ppi to such an extent that the bumps were no longer noticeable. Diamond PenTile has been used in all Samsung flagships since the Galaxy S4.
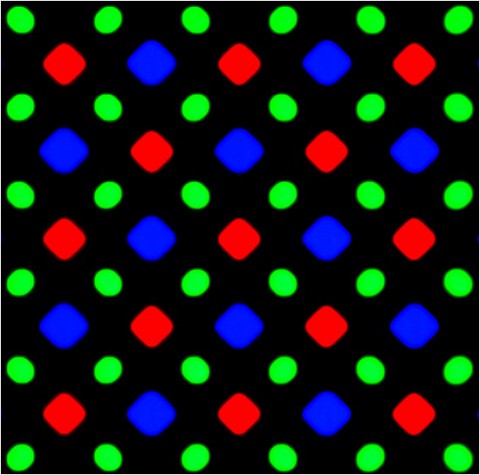
At the end of this section, it is worth mentioning another picture of AMOLED matrices - PenTile RGBW, which is obtained by adding a fourth, white, to the three main subpixels. Before the advent of Diamond PenTile, such a pattern was the only recipe for pure white, but it never became widespread - one of the last mobile gadgets with PenTile RGBW became Galaxy tablet Note 10.1 2014. AMOLED matrices with RGBW pixels are now used in TVs because they do not require a high ppi. To be fair, we also mention that RGBW pixels can also be used in LCDs, but we are not aware of examples of the use of such matrices in smartphones.
Unlike AMOLED, high-quality IPS matrices have never experienced quality problems associated with sub-pixel patterns. However, Diamond PenTile technology, together with high pixel density, allowed AMOLED to catch up and overtake IPS. Therefore, if you are picky about gadgets, you should not buy a smartphone with an AMOLED screen, which has a pixel density of less than 300 ppi. At a higher density, no defects will be noticeable.
Design features
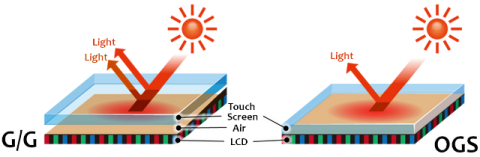
The variety of displays of modern mobile gadgets does not end with imaging technologies alone. One of the first things that manufacturers took up was the air gap between the projection-capacitive sensor and the display itself. This is how the OGS technology appeared, combining the sensor and the matrix in one glass package in the form of a sandwich. This gave a significant breakthrough in image quality: the maximum brightness and viewing angles increased, color reproduction was improved. Of course, the thickness of the entire package has also been reduced, allowing for thinner smartphones. Alas, the technology also has drawbacks: now, if you break the glass, it is almost impossible to change it separately from the display. But the quality advantages still turned out to be more important, and now non-OGS screens can only be found in the cheapest devices.
Recently, experiments with the shape of glass have also become popular. And they began not recently, but at least in 2011: HTC Sensation had a glass concave in the center, which, according to the manufacturer, was supposed to protect the screen from scratches. But such glasses reached a qualitatively new level with the advent of “2.5D screens” with glass curved at the edges, which creates the feeling of an “infinite” screen and makes the edges of smartphones smoother. Such glasses are actively used by Apple in their gadgets, and recently they have become more and more popular.

A logical step in the same direction was the bending of not only the glass, but also the display itself, which was made possible by using polymer substrates instead of glass ones. Here the palm, of course, belongs to Samsung with its Galaxy smartphone Note Edge, in which one of the side faces of the screen was curved.

Another way was proposed by LG, which managed to bend not only the display, but the entire smartphone along its short side. However, LG G Flex and its successor did not gain popularity, after which the manufacturer abandoned the further production of such devices.

Also, some companies are trying to improve human interaction with the screen, working on its touch part. For example, some devices are equipped with sensors with increased sensitivity, which allow you to work with them even with gloves, while other screens receive an inductive substrate to support styluses. The first technology is actively used by Samsung and Microsoft (formerly Nokia), and the second by Samsung, Microsoft and Apple.
The future of screens
Do not think that modern displays in smartphones have reached the highest point of their development: technology still has room to grow. One of the most promising are quantum dot displays (QLED). A quantum dot is a microscopic piece of a semiconductor in which quantum effects begin to play a significant role. Simplified, the process of radiation looks like this: the impact of a weak electric current causes the electrons of quantum dots to change energy, while emitting light. The frequency of the emitted light depends on the size and material of the dots, so that almost any color in the visible range can be achieved. Scientists promise that QLED matrices will have best color rendering, contrast ratio, higher brightness and lower power consumption. Partially, quantum dot screen technology is used in Sony TV screens, and prototypes are available from LG and Philips, but there is no talk about the mass use of such displays in TVs or smartphones.

It is also highly likely that in the near future we will see in smartphones not just curved, but also fully flexible displays. Moreover, almost ready for mass production prototypes of such AMOLED matrices have been around for a couple of years. The limitation is the electronics of the smartphone, which is still impossible to make flexible. On the other hand, large companies can change the very concept of a smartphone by releasing something like the gadget shown in the photo below - we just have to wait, because the development of technology is happening right before our eyes.
Abbreviations are usually used to denote characteristics or specifics. AT this case there is a terrible confusion regarding the comparison of IPS and TFT screens, because IPS technology (matrix) is a type of TFT matrix and nothing more. It is impossible to compare these 2 technologies with each other.
BUT! There is TN-TFT technology - here you can make a choice and compare between it and IPS. Therefore, when we talk about which screen is better: IPS or TFT, we mean TFT screens in any case, but made on the basis of different technologies: TN and IPS.
Briefly about TN-TFT and IPS
TN-TFT is the technology behind the LCD matrix. Here, the crystals, when no voltage is applied to their cells, "look" at each other at an angle of 90 degrees. They are arranged in a spiral, and when voltage is applied to them, they turn in such a way as to form the desired color.
IPS - this technology is different in that here the crystals are arranged parallel to each other in a single plane of the screen (in the first case, spirally). It's all complicated...in practice, the difference between TN and IPS screens is that IPS displays blacks perfectly, resulting in a sharper and more saturated picture.
As for TN-TFT, the color reproduction quality of this matrix does not inspire confidence. Here, each pixel can have its own hue, hence the colors are distorted. IPS-matrices show the picture much better, and also handle colors more carefully. IPS also allow you to observe what is happening on the screen from a large angle. If you look at a TN-TFT screen at the same angle, the colors will be so distorted that it will be difficult to make out the picture.
Benefits of TN
However TN-TFT matrices have their own advantages. The main one is the lower pixel response speed. IPS needs more time to rotate the entire array of parallel crystals to the desired angle. Therefore, when it comes to choosing a monitor for games or for displaying dynamic scenes, when drawing speed is very important, then it is best to choose screens based on TN-TFT technology.
On the other hand, during normal PC operation, the difference in pixel response time cannot be noticed. It is only visible when viewing dynamic scenes, which is often the case in action movies and video games.
Another plus is low power consumption. IPS-matrices are energy-intensive, because. to rotate the array of crystals, they need a lot of voltage. Therefore, TFT-based screens are better suited for mobile gadgets, where the issue of saving battery power is acute.
And yet - TN-TFT matrices are cheap. You won't find a monitor today (other than a used or CRT model) that is cheaper than a model based on TN technology. Any budget electronics device with a screen will definitely use a TN-TFT matrix.
So, which screen is better:TFT orIPS:
- IPS are less responsive due to longer response times (bad for games and action scenes);
- IPS guarantee almost perfect color reproduction and contrast;
- IPS has a wider viewing angle;
- IPS are energy intensive and consume more electricity;
- They are also more expensive, while TN-TFTs are cheap.
That, in principle, is the whole difference between these matrices. Given all the advantages and disadvantages, then, of course, it is easy to come to a specific conclusion: IPS screens are much better.
How to choose from the variety of modern smartphones what is right for you? Today the bad-android team prepared a material with useful tips on display selection.
How not to overpay for the device? How to figure out what to expect from it by the type of display?
Matrix types
Modern smartphones use three main types of matrices.
The first of them, called - is based on organic light emitting diodes. The remaining two types are based on liquid crystals - IPS and TN+film.
It is impossible not to mention the frequently encountered abbreviation TFT.
TFT- these are thin-film transistors that control subpixels of displays (subpixels are responsible for the three primary colors, on the basis of which "full" "multi-color" pixels are formed, which we will talk about a little later).
Technology TFT applied in all three matrix types listed above. That is why the common comparison TFT and IPS is essentially absurd.
For many years, amorphous silicon has been the main material for TFT matrices. At the moment, an improved production of TFT matrices has been launched, in which the main material is polycrystalline silicon, significantly increasing energy efficiency. The size of the transistors has also decreased directly, which allows you to achieve the highest performance. ppi(pixel density).
So, with the base of matrices sorted out, it's time to talk directly about the data types of matrices.
At the moment, this type of matrix is the most common. Also, IPS matrices are sometimes abbreviated SFT.
Story IPS-matrices originates several decades ago. During this period, many different modifications and improvements have been developed. IPS-displays.
When listing the disadvantages and advantages of IPS, it is necessary to take into account the specific subtype. Summarizing, for the list of strengths of IPS, we will take the best subtype (respectively, the most expensive), and for the minuses we will mean the cheapest subtype.
Advantages:
Excellent viewing angles (maximum 180 degrees)
High-quality color reproduction
Ability to produce displays with high ppi
Good energy efficiency
Disadvantages:
Image fading when tilting the display
Possible oversaturation or vice versa insufficient color saturation
AMOLED matrix
The matrix provides the deepest black color compared to the other two types of matrices. But it was not always so. The first AMOLED matrices had incredible color reproduction and insufficient color depth. There was acidity in the picture, too intense brightness.
Until now, due to internal incorrect settings, some displays are almost identical in perception to IPS. But in super-AMOLED displays, all the flaws were successfully fixed.
With a list of advantages and disadvantages, let's take a regular AMOLED matrix.
Advantages:
The highest quality picture among all existing types of matrices
Low power consumption
Disadvantages:
Occasionally occurring unequal life of LEDs (different colors)
The need for careful tuning of the AMOLED display
Let's sum up the intermediate result. It is obvious that matrices are leading in terms of image quality. Exactly AMOLED displays are installed on the most top-end devices. In second place are IPS matrices, but you should be careful with them: manufacturers rarely indicate the subtype of the matrix, and this is what plays a key role in the final image level. An unambiguous and firm "no" should be said to devices with TN+film matrices.
subpixels
The determining factor in the final display quality is often hidden display characteristics. Image perception is strongly influenced by subpixels.
In case of LCD the situation is quite simple: each color ( RGB) a pixel consists of three subpixels. The shape of the subpixels depends on the modification of the technology - the subpixel can be in the form of a "tick" or a rectangle.
In the implementation of displays in terms of subpixels, everything is somewhat more complicated. In this case, the subpixels themselves act as the source of illumination. As you know, the human eye is less sensitive to blue and red than green. That is why the repetition of the IPS subpixel pattern would significantly affect the quality of the picture (of course, in worst side). To preserve the realism of color reproduction, technology was invented.
The essence of the technology is the use of two pairs of pixels: RG (red-green) and BG (blue-green), which, in turn, consist of the corresponding subpixels of the corresponding colors. A combination of subpixel shapes has been applied: green ones are elongated, while red and blue ones are almost square.
The technology turned out to be not too successful: the white color was frankly “dirty”, and notches appeared at the junctions of different shades. With a low rate ppi a grid of subpixels became visible. Such matrices have been installed on a number of smartphones, including flagships. The last flagship that was “lucky” to get a PenTile matrix was Samsung Galaxy S III.
Naturally, it was impossible to leave the situation with poor-quality implementation of subpixels in the same state, so it was soon produced upgrade above the described technology, which received the prefix Diamond.
By increasing ppi Diamond PenTile allowed to get rid of the problem with jagged borders between colors, and white became much “cleaner” and more pleasing to the eye. And it is this development that is installed in all Samsung flagships, starting with the Galaxy S4.
And here IPS-matrices, although they are generally considered weaker than 'ovskih, however, have never encountered such problems.
What conclusion can be drawn? Be sure to pay attention to the number ppi in the case of purchasing a smartphone with a matrix. A high-quality picture is possible only with an indicator of 300 ppi. But with IPS matrices do not have such strict restrictions.
Innovative technologies
Time does not stand still, talented engineers continue to work hard to improve all the characteristics of smartphones, including matrices. One of the latest major developments is the technology OGS.
OGS is an air gap between the screen itself and the projective capacitive sensor. In this case, the technology lived up to expectations by 100%: the quality of color reproduction, maximum brightness and viewing angles increased.
And over the past few years OGS it has become so embedded in smartphones that it is possible not to meet the implementation of a “hamburger” display with an air gap filling only on the simplest devices.
In search of display optimization, designers came across another interesting opportunity to improve the picture on phones. In 2011, experiments began on form glass. Perhaps the most common form of glass among the unusual has become 2.5D- with the help of curved edges of the glass, the edges become smoother, and the screen is voluminous.
Company HTC released a smartphone sensation, the glass of which was concave in the center of the display. According to HTC engineers, this increases the protection against scratches and bumps. But glass concave to the center has not received wide application.
The concept of bending the display itself has become more popular, and not just the glass, as was done in. One of the side faces of the display received a curved shape.
A very interesting characteristic that you should pay attention to when buying a smartphone is sensor sensitivity. A sensor with increased sensitivity is installed in some smartphones, which allows you to fully use the display even with ordinary gloves. Also, some devices are equipped with an inductive substrate to support styluses.
So for those who like to chat in the cold or use a stylus, a sensitive sensor will definitely come in handy.
Known Truths
It's no secret that screen resolution also greatly affects the final level of the image. Without further ado, we bring to your attention a table of correspondence between the display diagonal and resolution.
Conclusion
Each matrix has its own characteristics and hidden characteristics. You should be careful with -displays, or rather, with the ppi pixel density indicator: if the value less than 300 ppi, then the quality of the picture you frankly disappoint.
For IPS-matrices is important subtype, and depending on the subtype, the cost of a smartphone logically increases proportionally.
curved glass 2.5D will significantly increase the attractiveness of the picture, as well as technology OGS.
The question of the size of the display is purely individual, but with multi-inch "shovels" a high resolution will be appropriate.
We wish you pleasant shopping friends!
Stay tuned, more to come lot interesting.
It should be noted right away that each technology has enough fans, and therefore fierce disputes on the Internet do not subside for a moment. This mainly concerns the topic “AMOLED vs IPS”, since TN matrices stand somewhat apart and do not claim to be the “coolest technology” laurels. After reviewing several reviews, we nevertheless made up our opinion, which we will share with you.
Comparison of IPS and TN matrices
The fact that screens created using TN technology have not disappeared from the market indicates that they are still in demand. Their main advantage is the price, since the cost of TN displays is on average 20-50% lower than that of equivalent IPS devices. The second competitive advantage is called low response time: modern TN-matrix screens have a response time of the order of 1 ms, while IPS monitors have a characteristic of 5-8 ms. However, the latter is quite enough to display movies and even 3D games with large quantity dynamic scenes, and therefore you can ignore this parameter as long as it is in the specified range.
Asus MeMO Pad ME172V tablet with TN screen
In contrast to the above, IPS screens show a higher contrast ratio, as well as picture brightness and, most importantly, excellent viewing angles. In addition, the thickness of devices with IPS matrices is slightly lower than that of TN opponents, which is sometimes true for smartphones and tablets. Another advantage is the best quality images when direct sunlight hits the IPS screen, which is again important for wearable devices. Agree, constantly covering the smartphone screen with your hand in order to at least see something on the street is not very convenient, and therefore phones with TN-screens are gradually disappearing into oblivion.
Conclusion: Screens with TN matrices are suitable for the corporate sector, as well as for monitors and tablets of not too demanding customers who do not mind saving. For owners of smartphones and those who are not constrained by funds, it is worth choosing devices equipped with IPS screens.
Comparison of AMOLED and TN
People who do not delve into screen technology too much sometimes refer to displays with TN matrices as TFT. They ask sellers questions like: “What better AMOLED or TFT? ”, Forcing the latter to smile forcedly and explain the materiel to curious customers. We will assume that there are no such people among our readers, and therefore we will move on to the topic of the title.

Ramos W30 tablet with ISP screen
In general, it is difficult to compare these two technologies, since devices made with their use are designed for different categories of customers. AMOLED is primarily a tribute to fashion and a step towards innovation. Customers Considering AMOLED Display Expect to Purchase modern device with top-end features and only secondarily study the price tag and make a decision. On the contrary, buyers of equipment with a TN screen are looking for the maximum for their money, and the budget here is the primary factor when buying. According to the characteristics, AMOLED is closer to IPS, and therefore the conclusions for comparison suggest themselves appropriate.
Conclusion: Since AMOLED displays are even more expensive than IPS, you probably shouldn't look at them when choosing a budget or mid-budget option. If your goal is a device with a high level of image quality, then you go straight to the next subheading.
Comparison of AMOLED and IPS
So we got to the main question of the article: "What is better AMOLED or IPS?". And, of course, in order to draw a conclusion, you need to consider the strengths and weaknesses of each technology.
viewing angles. Both technologies have excellent viewing angles, and smartphone-tablet owners vying to say that their AMOLED / IPS screen is definitely better. There really are no big differences, however, users and experts note that at large viewing angles, the difference between IPS and AMOLED screens is manifested in a bluish or greenish tint of the image in the latter.
Energy saving. The fact is that here it is necessary to say about one feature of these two technologies. Screens with IPS matrices produce the best white color among competitors, while AMOLED displays are leaders in displaying black colors (by the way, because of this they are called even more contrast). If the AMOLED screen has to display white colors frequently, for example when using a browser, then its power consumption increases by about 5 times.

Hybrid samsung tablet ATIV Smart PC with AMOLED screen
Image clarity. Most AMOLED displays use a PenTile subpixel arrangement. Although the developers claim that this does not affect the image, however, many users, when compared, call the picture of IPS screens clearer. On the other hand, maybe they are just suspicious?
Screen thickness. Here the advantage of AMOLED displays is undeniable. The absence of a separate backlight layer makes such screens really thinner.
Brightness and contrast. These characteristics have AMOLED screens really higher than the competition. On the other hand, quite a few people find them oversaturated and tiring on the eyes, especially with prolonged use. It seems that this item remains a matter of taste for each individual user.
Screen burn-in. This item applies mainly to organic displays. The sad fact is that when a static image is displayed for a long time, its “traces” remain on the screen. So, for example, “images” of permanently displayed icons appear on the screens of smartphones.
Response time. AMOLED screens are said to have slower response times than IPS screens. In practice, this difference is insignificant and is suitable only for marketing techniques.
Conclusion: Let the fans of AMOLED technology throw tomatoes at me (that is, the author), but my subjective opinion leaned in favor of IPS. The technology has more advantages, but the price of devices is still lower. We believe that organic displays will still prove themselves after several years of technology improvement in all its glory, however, so far, their characteristics lose out in the price-quality category.
Thank you for your attention to our site, if you liked the published information, you can help in the development of the resource by sharing the article through social networks.
