Preparation of any digital image, read by a graphic editor Adobe Photoshop, be it a PSD file, TIF image or “large” JPEG image, for publication on a website, forum or in social networks, as well as for shipment by e-mail. In other words, "japeg" for the Internet. It worked out in rhyme.
Of course, the image formats that Photoshop can read are hardly limited to the three mentioned above. And what’s nice is that most can be converted to JPEG. Regardless of the source format, there are two ways to "japegize" Photoshop. The opportunity to choose is doubly pleasant. Both ways are different. External differences are detectable with the naked eye; I will specifically highlight the differences in purpose (“Which path to follow?”).
In this lesson I will present two step-by-step instructions with the necessary theoretical inclusions. It is designed to show you how to optimally save your virtual drawing, collage or photograph in the widely used JPEG format. The latter is most effective for images with smooth color transitions.
To consolidate and expand the acquired knowledge, as well as to develop skills, I have prepared appropriate exercises. I suggest you complete them and then publish your results in the comments to this lesson. Test your skill in the field!
First way
1 step
I open the original image in Photoshop. In my case, this is a file called “Example.psd” containing a drawn ball.
I press the key combination “Ctrl”, “Shift” and the key designated by the Latin letter “S” on the keyboard, or select “File” > “Save As...” from the main menu. A dialog box titled “Save As” appears.
Step 2

I choose the location of the future JPEG image. In the “File name” field, enter a new name for the image, if necessary. In the “File type” drop-down list, select the “JPEG (*.JPG, *.JPEG, *.JPE)” format.
I leave the parameters below unchanged, making sure that “standard” sRGB is specified and selected as the color profile embedded in the future JPEG image. If this is the case, then I move on to step 4.
If a different color profile is specified instead of sRGB, such as ProPhotoRGB or AdobeRGB, I will convert the source image to the sRGB color space before starting this tutorial to ensure colors appear consistently across most devices. I'll do it this way.
Step 3

I press the “Esc” key on my keyboard to close the “Save As” window.
I select “Image” > “Mode” from the main menu. If the checkbox is checked opposite “8 bits\channel” (“8Bits\Channel”), then select “16 bits\channel” (“16bits\Channel”). Increasing the color depth is desirable so that conversion from one color profile to another occurs accurately. Visually, changes in color depth are unlikely to be reflected in the original and final images.
Then I select “Edit” > “Convert to Profile” from the main menu. A dialog box appears with the title Convert to Profile.
In my case, the original color profile (“Source Space”) that describes the colors in the drawing is called “Adobe RGB (1998)”. I select the value “sRGB IEC61966-2.1” in the “Destination Space” drop-down list. I check the conversion parameters - they are located below: the “Tool” (“Engine”) parameter is set to “Adobe (ACE)”, “Method (rendering)” (“Intent”) - “Relative Colorimetric”, set There is a check mark next to the “Use Black Point Compensation” option; there is no check mark next to the “Flatten Image to Preserve Appearance” option.
If you increased the color depth (I did this a little earlier), then the “Use Dither” option will be grayed out. If there is only one layer in the open image (when you open JPEG images or “simple” TIF images, this is usually the case), then the “Flatten Image to Maintain Appearance” option is also greyed out.
I click the “Done” (“OK”) button. The Convert to Profile window disappears.
Step 4

A new dialog box with the title “JPEG Options” appears in the main program window. The “Quality” parameter allows you to set the ratio between the quality of the output image and the amount of space that the image will occupy in the computer’s memory. Thus, the price for reducing volume is the degradation of the quality of the original image. How less value“Quality” parameter, the smaller the size of the JPEG image.
In the example under consideration, I will focus on a value of 6.
To evaluate the quality of the image before saving, I’ll check the box next to the “Preview” parameter.
Step 5

I will set the value of the second parameter - “Format Options” - equal to “Standard Optimized” (“Baseline Optimized”). The volume of the future JPEG image has decreased, but the image quality remains the same.
Step 6

I click the “Done” (“OK”) button in the “JPEG Options” window and check the result.
I compare the volumes of the original PSD image (~ 3000 Kb) and the final JPEG image (82 Kb). Thus, the JPEG file turned out to be approximately 36 times smaller than the original image with visually equal quality. Comfortable!
Please note that the size of the final JPEG image remains the same as the original PSD image, it is 2480 pixels × 2480 pixels.
Second way
1 step

I open the original image in Photoshop.
I press the key combination “Ctrl”, “Alt”, “Shift” and the key designated by the Latin letter “S” on the keyboard, or select “File”> “Save for Web...” from the main menu.
A new dialog box with the title of the same name will appear.
Step 2

Step 3

I set the “Quality” parameter to maximum.
Step 4

I reduce the image size using the “Image Size” parameter.
This is an optional operation, but it helps to significantly reduce the size of the future JPEG image, most often with minimal loss in quality. On the one hand, reducing the size will lead to a natural decrease in volume and, on the other hand, to a decrease in detail. The latter, in turn, limits my ability to print the final JPEG image. If I don't plan to print the last one, I'll forget about the restrictions.
In this example, I enter the value 600 in the “Width” field. The value in the “Height” field will automatically change. Also, the size of the output image will automatically change relative to the size of the original image, specified in the “Percent” field. Changes occur automatically and the “Percentage” field is in an active state if the “Width” and “Height” parameter fields are connected, as evidenced by the corresponding icon located to the right of the named fields.
In the preview window on the left I will evaluate the size and quality of the image. And I can find out the approximate volume of the latter by the number indicated, usually in kilobytes (Kb) or megabytes (Mb) under the left corner of the window.
Step 5

I check the box next to the “Optimized” option.
Step 6

If I want to further reduce the volume of the output image, then I reduce the value of the “Quality” parameter. I recommend sticking to values between 45-90.
IN in this case I'll choose a value of 75.
As a result, on average, with an Internet access speed of one megabit (1 Mbits), the time it takes to download my drawing from the Internet will be one second. It is indicated under the volume value of the future JPEG image.
At the same time, visually the picture turned out to be of quite acceptable quality, the tonal transitions are quite smooth.
Step 7

I check the box next to “Convert to sRGB” and select “Monitor Color” from the drop-down list below.
Step 8

Finally, I check the box next to the “Embed Color Profile” option.
Actions in the 7th and 8th steps are desirable so that the future JPEG image is displayed approximately equally on different devices.
Step 9

In the dialog box that appears with the title “Save Optimized As,” I select the location of the JPEG image and set its name, if necessary. I click the “Save” button in the active window. Both windows disappear. Now I can evaluate the result.
I close the original image. In the dialog box that appears asking you to save changes, select “No”.
The image obtained by the second method can be conveniently used for publication on the Internet. And the image obtained by the first method can, in addition to publication on the Internet, be printed. Since the size of the image did not change, it was not subject to interpolation, which means its quality is a priori higher than the quality of the image obtained by the second method.
I will tell you more about interpolation and its impact on the degradation of digital image quality in the lesson “What is interpolation?”

To consolidate the acquired knowledge, I suggest that you not only save several of your own photographs in JPEG format, but also complete the exercises attached to this lesson. The latter cover the challenges you may encounter in your photography career.
Instructions
A beginner should not delve too deeply into the theory, but you should definitely know that JPEG is a format with a compression algorithm. File of this format may have different extensions, for example? .jpeg, .jfif, .jpg, .JPG, or .JPE. It is very convenient because it takes up much less space than a similar image in TIFF or BMP format. Unlike the latter, it has less information about the image. This may not be too noticeable when viewing the original file on a monitor, but when the photo is printed in a laboratory or processed, the result may be of lower quality than formats with complete information.
The way you save JPEGs depends greatly on your needs. Before saving the picture, decide whether you will process it, print it on photo paper, or whether you just need to post the picture on a page on the Internet.
For subsequent processing or printing in the darkroom, save the image at its maximum quality and size. When saving the image you are looking for, open the File menu and select Save as. Select the directory where the file will be saved. Enter the name in the first line, and select the JPEG format in the second line and click the Save button. If you have manipulated the file, a dialog box will pop up in front of you to select the quality of the saved image. You should select the maximum quality using the slider or the corresponding number 12. Confirm your choice by clicking Ok. If you have not manipulated the image, then after saving it, the dialog box for selecting JPEG quality will not open.
When saving a photo for publication on the Internet, modern resources themselves can change the size and quality of the downloaded JPEG. However, in some cases you have to do this yourself. Before saving the picture, change its size by going to the Image menu and selecting Image size. Make sure the Constrain Proportions box is checked. Select a unit of measurement that is convenient for you: centimeters, pixels, inches or millimeters, enter the required value of one of the sides in numbers and click Ok (in most cases, images from 800 to 1500 pixels on the larger side are used for web pages). Save the result, but select a lower quality. With values ranging from 8 to 10 and a small image size, visual differences from the original size are minimal, but the file size is significantly reduced.
Adobe Photoshop also has a special module for optimizing and saving images for web pages, which may be more convenient. From the File menu, select Save for Web. In the dialog box that opens, you will be presented with a window for viewing the saved image and several settings options. Select the 4-up or 2-up tab. The program will present you with four or two possible options for the optimized image. To save the appropriate one, just click on the picture and click Save. If you are not completely satisfied with the options, then first use the tools located to the right of the image.
Working with a graphics editor Adobe Photoshop for 5 years now, I was surprised to learn that not everyone knows about the importance and necessity of saving images correctly. Turning to the Internet, I really couldn't find up-to-date and correct information on this topic. For this reason, I figured out the issue and want to tell you how to save images correctly.
Who needs to know this and why?
Anyone who works with a graphics editor, not necessarily Adobe Photoshop. Illustrator, artist, graphic designer, web designer, interface designer, photographer, student, schoolchild - by learning how to properly save images, reducing the file size, you save not only your own, but also other people’s time.
What time are we talking about?
First, let's make one thing clear:
Using the Internet, you waste time - a lot of time
Loading pages on the Internet is not instantaneous and takes time, but over many years of being on the Internet you have become accustomed to not noticing this. Let's say average page loading speed 3 seconds, where 2 of them are for loading images. Illustrations, interface elements, photographs, advertising banners, PDF presentation or even a picture of a cute cat, depending on the file size, it will take time for the browser to display the image on the screen.
Don't be fooled by "megabytes per second"
Most likely, your Internet provider promises you 100 Mbit/s- this is a brilliant advertising move (read as: deception) that has given rise to many misconceptions, including the topic of site loading speed. I measured the connection speed with a server located in Moscow, the result:
But the page loading speed from the site is much lower:
How many images do you view per day?
Dozens? Hundreds? As an active Internet user, I view several hundred images a day, most of them high resolution. If you reduce the weight of these images and accordingly increase the loading speed, at least by 1 second, multiplying by 500 images per day, then we get about 8 minutes a day and 4 hours per month.
I wait 4 hours a month for a picture to load
Everything you need to know about saving images
With rare exceptions, there is no need to save the final result using the same method as PSD, in this case, additional and unnecessary information from the date of creation and the name of the graphic editor to the weather and camera model.
A bad habit is to set quality to value. 100 , but in comparison with 80 varies visible quality practically equal to zero, but the difference in weight palpable.

To post an image on a website, send it by mail, save it in the cloud, send it in a messenger, etc., you must use Save for Web.


JPEG or PNG?
JPEG - for images with big amount flowers and complex figures: illustrations, paintings, photographs.
PNG - for vector images or images containing text, simple geometric shapes with transparency and a small number of colors: logos, screenshots, stickers, icons.
Which Quality should I choose?
For most images the optimal value would be 80 , for some simple images where a clear transition between colors is not important. you can set the value 60 .
Optimized
The function includes an additional color conversion algorithm, it is recommended always turn on, except when the smallest details are important (for example Pixel Art).
Convert to sRGB
Converts the colors of the image to the corresponding sRGB table.
sRGB is the Internet standard
Resolution(Image Size)
The most common screen resolution is: 1366×768- for computer and 720×1280- for smartphone. Keep this in mind and do not save images larger than 1920 in width.
Metadata
Extra information that I already mentioned. There is no need to provide additional image information, which will only increase the size of the file.
When was the last time you looked at the detailed information of a downloaded image?
Using this method, I managed to reduce the weight of the image by half.
Of course, there are rare exceptions when you may find it useful detailed information or increased detail, but in most cases these rules will be appropriate and will save hundreds of hours.
Thank you, Vladislav.
Hello, dear readers of the Start-Luck blog! Andrey Zenkov and mine are in touch practical advice in web design. Today we’ll talk about those very keys without which your website will never open the door to the world of browser bookmarks (and it’s so important for the user to star their favorite pages).
We will talk, as you might have guessed, about images. Selecting a bright photo is only half the battle. After its processing, colorization, text overlay and other manipulations, a new problem is brewing on the horizon: how to save an image in Photoshop?
Let's say you've created a website about pets and are eager to add an extensive photo gallery. Bang - and you can no longer imagine design without charming menu icons in the form of paw prints. What about the section with funny animations that will lift the mood of site guests?
With enthusiasm, you adjust all the images to fit, save and... see that your efforts are in vain. Pixels completely kill the painstakingly created “paws”, and you can’t look at pictures in motion without tears. Photoshop is automatically moved to the list of programs for removal, and you promise yourself to find a real craftsman. For what? You can do everything yourself by learning the main secret that I always use.
The algorithm for saving images in optimal quality depends on their format. I don’t want to go into details, talking about which ones are raster and which are vector. Moreover, you can change them in a couple of clicks. I already wrote about this in one of my articles, sharing with readers how to change image formats.
Analyzing the sites that the Internet is rich in, I noticed one interesting detail: all graphic elements are represented by only a few universal formats, while the existence of others is completely forgotten. What are they?
Basic groups of images in web design
Graphic content on websites is divided into three categories.
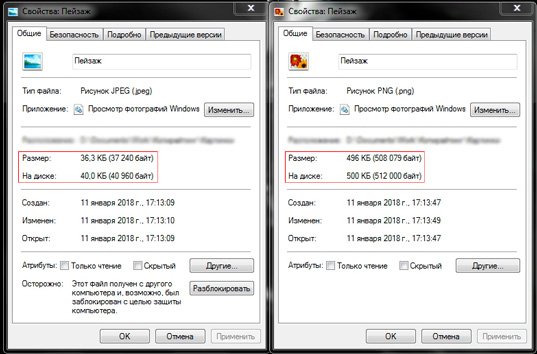
Collages and photographs
They are characterized by the JPG format - by the way, the most common on the web. These images are small in size, which allows you to use them in website design without fear of slow page loading. For example, the same landscape saved in JPG and PNG differs significantly in weight:
Icons, buttons and banners
For these design elements, PNG is preferred. It allows you to cut out an object and save the image without a background, using the site’s “background” instead. I would also recommend this format for images that do not have a huge palette. For example, we create a document in Photoshop and - the name of the site:

We save the image in two formats and compare the result:

Animation
GIF is intended for creating animated images consisting of two or more layers. This can be done not only using Photoshop, but also. I would call this format the most capricious, since when saving in it it is difficult to achieve good quality. Luckily, I have a life hack that will give you animations with minimal pixelation. Intrigued? Read on!
Step-by-step instructions for saving images
Let's start with JPG: with it it is very easy to get a photo without losing quality. To do this, click “File” - “Save As”. If you wish, you can use the key combination Shift+Ctrl+S:

In the window that appears, look for the “File type” drop-down list and select the JPEG line. Usually it is the default:

In the same drop-down list, you can also select the PNG line, thereby simplifying your task. However, I recommend saving images from transparent background differently.

Examine the window that opens. Your task is to make sure that PNG-24 is selected in the drop-down list, and that the “Transparency” and “Interlaced” lines are checked:

Please note: the last checkbox reduces the loading time of the image on the site, but at the same time increases its weight. If this doesn't bother you, click "Save". In the window that pops up, select the file path and press the coveted button again to get a PNG image and upload it to the site as soon as possible!
The animation is saved through the same menu item, but now you need to select the GIF option in the drop-down list. A huge number of parameters and unclear words can cause confusion or even fear. Not worth it! Just set the parameters that I use:

Let's sum it up
Working with graphics requires constant improvement of skills, without focusing on one or two areas. What should I do? At one time it became a real find for me set of five mini-courses from the project "Photoshop Master". I learned more than one byte from them useful information.

The material is presented in an accessible form and free of charge. This is an excellent alternative to studying in computer academies and spending many hours searching for the necessary lessons on the Internet.
That's all. Don't forget to subscribe to VKontakte group and blog updates for a weekly dose of fresh and useful articles.
Andrey Zenkov was with you. See you again!
Adobe Photoshop is a popular multifunctional graphics editor. Many users encounter it, especially when processing photographs and pictures. How to save a document in Photoshop? This is one of the main functions of the graphic editor. Next we will consider all possible methods saving pictures. The tips offered to your attention will greatly facilitate the process of working with Photoshop. They are easy to learn and apply in practice.
Normal saving
How to save a photo in Photoshop? The first option available in graphic editor, is the "Save" command. It is usually used when processing a previously opened document. When the command is executed, the previously existing object will be replaced by the edited image.
- Open the photo and edit it as you wish.
- Click on the "File" button. It is located on the toolbar at the top of the screen.
- Click on the "Save..." button.
Important: if the user created a graphic document from scratch, after the actions taken, a save log will appear on the screen. Here you need to specify the name of the document, its storage format and its intended location on the computer.
Option "Save as..."
Second way to save graphic files- this is the use of the "Save as..." command. This technique is similar to the previously studied algorithm of actions. It features a variety of saving options. The method is perfect for duplicating pictures.

- Click on "File" after editing the document.
- Select the "Save as..." command from the menu that appears.
- Specify the name of the document to be saved.
- Select a saving format. It is located in the "File Type" line.
- Specify the location where the graphic document will be saved.
- Click on "Save".
- Specify photo parameters. Usually here you choose the image quality and format type. You can specify standard or enhanced optimization, or with a gradual improvement in the quality of the image as it loads.
- Click on the "Ok" button.
It is done. We have explored another way to save documents through Photoshop. To quickly activate the option, you can press Ctrl + Shift + S.
With the file closed

- Go to the tab with the selected picture.
- Hover over right top corner tabs with the corresponding document.
- Click on the cross with the left mouse button.
- Agree to save the document by clicking “Yes”.
Important: If you click No, Photoshop will close without saving any changes to the document. "Cancel" will return the user to the editor without any changes.
For Web resources
Photoshop is often used to create graphics for Web sites. All that remains is to correctly save the document. What is needed for this?
- Select "File" - "Save for Web...".
- Specify the graphic set and saving format.
- Set background parameters.
- Specify the quality of the photo and its size.
- Click on the "Done" button.
Quick access to the option is carried out using the keyboard shortcut Alt + Shift + Ctrl + S.
Saving background and pictures without it
How to save the background in Photoshop? This is a fairly simple task. The point is that the user can use any image as a background. All that remains is to set it as the mentioned element of the picture.

Creating a background in Photoshop is done like this:
- Open or create a graphic document.
- Click on the "Add new layer" button.
- Copy the image used as the background.
- Paste the image onto the created new layer.
Now all that remains is to make the necessary adjustments to the image, and then move the background layer to the very bottom.
How to save a picture in Photoshop without background? To do this, you will need to create a document in .gif or .tiff format. It is preferable to work with the first option. To do this, you will have to activate the "Save for Web..." option, and then check the "Transparent" box in the saving options.
