All modern scanners classified by the method of operation and by the type of reader (optical module).
By way of operation:
- manual
- stationary
By type of optical module:
- LED (CCD)
- laser
- imager (photo)
Moreover, scanners they are also divided according to secondary classifiers: according to the reading principle (linear, multi-plane); location on the operator's table (horizontal, vertical, built-in); connection interface; readable symbols, etc.
Handheld LED (CCD) scanners
CCD scanners have built-in LED matrix, which illuminates the barcode and receives its reflection. LED scanners are divided into two types: contact and non-contact.
Contact scanners characterized by a small scanning field width (up to 80mm) and short distance(from 0 to 2 cm), but at the same time they have a low cost. Non-contact scanners have the characteristics of not expensive handheld laser scanners(long reading distance up to 30 cm, large barcode illuminated area).
When reading a barcode LED scanner key factors must be considered:
- scanning field width;
- reading distance;
- tilt angle;
- surface curvature barcode quality.
CCD scanners have a number of advantages - low cost, high readout speed, high reliability (no moving mechanical parts). The disadvantages include the small width of the scanning field and the reading distance, as well as the poor quality and reliability of reading, both from ordinary and from curved planes. Also, a common disadvantage linear hand (LED, laser and imager) scanners is the need for rigid positioning of the scanner relative to the barcode. Ray scanner must cross all lines of the barcode.
Everything CCD scanners have a built-in decoder that allows you to read most linear as well as stack codes, and support various connection interfaces (keyboard wedge - KBW, USB, RS232, IBM46xx, OCIA, light pen emulation). Greatest application CCD scanners found in retail, in small stores where there is no need to provide large throughput.
Laser scanners can be manual or stationary, in addition, they are divided according to the principle of reading into linear (one scan line) and multi-plane (several scan lines).
Handheld line laser scanners.
Optical laser module hand scanners built on the basis of a laser diode. Scan laser beam scanner provided by a swinging mirror, which reflects the laser diode beam and directs it to the barcode along a certain trajectory. 
Linear laser scanners have high quality, speed and long reading distance (up to 10 meters) of the barcode. The main disadvantage of this type scanners is low reliability. This is due to the presence of moving parts in the optical module, which are subject to external mechanical influences (strong shocks, falls from a great height, etc.). Moreover, scanner must be rigidly positioned relative to the barcode to read it. Scanners have a built-in decoder that allows you to read most linear as well as stack codes, and support various connection interfaces (keyboard wedge - KBW, USB, RS232, IBM46xx, OCIA, light pen emulation). 
Laser scanners are used in almost all industries: wholesale and retail trade, transport and logistics, warehouses and distribution centers, pharmaceuticals and banking, industry and manufacturing, etc.
Largely multi-plane scanners are stationary with horizontal or vertical scanning plane. In addition, there is a separate type of multi-plane stationary scanners – bioptical scanners which have two scanning planes (vertical and horizontal). 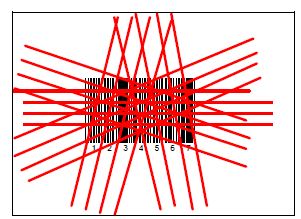
The difference multi-plane scanners from others - the presence of several scanning lines, the number of which can reach up to 20 for horizontal or vertical scanners, and up to 68 for bioptic scanners... Multi-plane scanning scheme provides a dense field of illumination, while there is no need for rigid positioning scanner regarding the barcode. It is enough just to carry the product with a barcode in front of the scanner at a distance of up to 25 cm and the barcode will be read, which increases the productivity of cashiers and the throughput of checkout points, and reduces the number of customer queues in the store.
 Optical module laser multi-plane scanners built on the basis of a laser diode, a set of mirrors, a mirror prism motor and a decoder.
Optical module laser multi-plane scanners built on the basis of a laser diode, a set of mirrors, a mirror prism motor and a decoder.
A laser diode (VLD) emits a laser beam (mostly in the visible red spectrum) that hits a rotating mirror prism. Due to the rotation of the motor and reflection from the mirror prism, the beam changes its direction of movement along a certain path. The reflection of the beam from the plurality of mirrors of the optical unit forms several scanning lines (scanning plane). When the barcode is on one of the scanning lines, part of the laser beam is reflected from the streaks and gaps back to the mirror prism and hits the focusing lens, which focuses the beam on the photodetector. Further, the optical signal is converted into electrical, amplified and digitized. Then the decoder decrypts the data contained in the signal and transmits it to the information system through the interface card.
 Multi-plane laser scanners have a built-in decoder that allows you to read most of the line codes, and support various connection interfaces (keyboard wedge - KBW, USB, RS232, IBM46xx, OCIA, light pen emulation).
Multi-plane laser scanners have a built-in decoder that allows you to read most of the line codes, and support various connection interfaces (keyboard wedge - KBW, USB, RS232, IBM46xx, OCIA, light pen emulation).
Main application multi-plane scanners found in wholesale and retail trade in small-format stores, in super and hypermarkets.
Linear imager scanners
The most advanced linear barcode reading technology available today. It combines the advantages of LED and laser technologies - barcode reading from a long distance and the absence of moving parts in the structure. With wide and clearly focused illumination and no mechanical constraints linear imager scanner captures a wider barcode strip and better than others copes with low contrast and damaged codes, has a faster read speed and more robust design.
Peculiarities:
- Code reading at a distance of up to 2 meters - full compliance with the standard reading distance laser scanner.
- Scanning speed - from 270 to 450 scans / sec, which is much faster LED and laser scanner.
- High reliability and mechanical strength (no moving parts).
Linear Photo Scanners are used in almost all industries: wholesale and retail trade, transport and logistics, warehouses and distribution centers, pharmaceuticals and banking, industry and manufacturing, etc.
Matrix imager scanners.
Reading 2D codes This is a new generation scanners, which are based on photo scanning technology and use miniature digital cameras as an optical module.
Unlike CCD and laser technologies, matrix imager technology is based on the fact that a barcode is initially viewed not as information itself encoded in strokes and spaces between them, but as an image, a picture that can, for example, be photographed. Powerful processor and advanced recognition and decoding algorithms process the image photographed by a mini camera, thanks to which the possibilities matrix photo scanners far exceed the capabilities of conventional LED and laser scanners while having the cost of a quality laser scanner. Photo scanner can read "normal" linear, two-dimensional, composite barcodes, read multiple barcodes with one trigger pull, read a barcode regardless of its orientation relative to the backlight beam. images. The matrix imager scanner has the ability to capture and process signatures, photographing. In addition, the absence of moving parts ensures high reliability of the scanner.
Peculiarities:
- The principle of reading is photographing a barcode with subsequent decoding.
- Reading the code in any orientation of the scanner relative to the code.
- Reading any codes - one-dimensional and two-dimensional, postal and OCR, capturing a signature, photographing images.
- Simultaneous reading of several barcodes.
- Reading the code in any ambient light - from complete darkness to bright sunlight (up to 100,000 lux).
Matrix photo scanners find application in such industries as transport and logistics, pharmaceuticals, banking, industry and manufacturing.

Barcode scanners occupy a very important place in the segment of equipment for trade automation. At the same time, they are universal in their application and can be used in most other industries: medicine, logistics, inventory control, acceptance and shipment of goods, in the service sector, etc.
Each of us has repeatedly seen this scanner at the checkout of the store or at the point of issue of goods. However, not everyone knows how many possibilities a small and seemingly simple device can have.
There are several types of barcode scanners:
- wired
- wireless,
- slotted,
- multi-plane,
- built-in.

Corded scanners belong to the budget category. Such devices are purchased for stationary use. The main advantage of wireless scanners is the ability of employees to move freely around the warehouse.
The types of barcodes known today are:
Linear barcodes are a set of stripes in the same direction.
Linear Barcode Standards:
- EAN - European (EAN-8 consists of 8 digits, EAN-13 - 13 digits are used),
- UPC (UPC-A, UPC-E),
- Code39,
- Code128 (UPC / EAN-128),
- Codabar
Such barcode can carry unique encrypted information about a product (up to 30 characters).

Linear barcodes differ in density. Modern CipherLab models develop models for reading hard-to-recognize, faded and heavily worn barrels. What if the scanner was unable to identify the barcode? Remember the queue in the supermarket, the coveted product is at the checkout, but the barcode cannot be read in any way. Alternatively, you can drive the numbers manually into the database and get information about the product.
However, if the goods are assigned an encrypted Code39 barcode, the cashier will not be able to enter the numbers manually.

To automate trade, you need a high-quality scanner, preferably with a laser reader and support for all major barcode standards (when it comes to linear barcodes). Good equipment will avoid time losses in the process of work. 

Most Popular EAN means European Article Numbering or European Article Numbering. Distinguish between EAN-8 for encrypting small items or EAN-13 (for large items). Encryption on this system means unification. European standardization implies the introduction of information about the country of manufacture, product category, date of manufacture. A barcode is a cipher that contains all the necessary information about a product, where and when it was produced, to which group it belongs. This is very important for customs. Since the product groups differ in excise taxes, etc. Products from the United States, for example, are labeled as UPC-E.
2D barcodes contain significantly more information than linear ones. Decoding in 2 dimensions - horizontally and vertically. This type The SK appeared relatively recently, a little over 10 years ago. This is how multilevel and then matrix barcodes appeared first. Multilevel ones were built on the principle of superimposing several linear ones on top of each other. Matrix covers the encoding both vertically and horizontally. They are more reliable and secure, which allows them to be used in banking for encrypting unique certificates, documents, and assigning keys.
2D Barcode Standards:
- Aztec Code;
- Data matrix;
- MaxiCode;
- PDF417;
- QR code;
- Microsoft Tag
Example two-dimensional stroke code.

Benefits 2D scanner can be considered more informative. Instead of the maximum 30 characters of a linear one, you can encrypt a whole message of 2000 characters or more!
Reader types in barcode scanner
There are 3 types of readers that fit on wired and wireless barcode scanners. Let's dwell on each of them in more detail.
- LED.
Scanners with an LED reader belong to the budget category. Their principle of operation is to use a red LED as a radiation source. In most cases, the minimum resolution is 3 mil (7.62 μm).
One of the most successful models CipherLab 1500 - LED scanner with a reading range of up to 35 cm (depending on the type, contrast and density of the barcode). Among the wireless scanners with an LED reader is the CipherLab 1560. - Laser.
The advantage of laser readers is the ability to work with low-contrast, poorly recognizable and frayed barcodes. Unlike LED scanners, such devices have a significantly higher range (often up to 57 cm), good scanning and decoding speed, and a wide vertical and horizontal viewing angle. A laser reader, like an LED one, is designed only for linear one-dimensional barcodes. Installed on hand-held wired and wireless models of barcode scanners. - 2d (two-dimensional).
The two-dimensional reader is based on the use of a photosensor. The principle of operation is based on the use of an image sensor with a high scanning speed (often up to 60 frames per second) and good resolution. 2D scanners easily handle all types of barcodes known today, making them versatile across all industries. Among the most popular models there are CipherLab 1504, Godex GS550, (hand-held contact) CipherLab 1564 (wireless).
Variants of using scanners in the automation process:
Conclusions:
- Barcode scanners are universal in operation and differ in many parameters: price, interface, protection class, overall dimensions, range, reading speed and width, reader type, etc. However, they all have the same task - to identify the barcode.
- When choosing a barcode scanner, you must first of all carefully consider the type of reader, taking into account the specifics of the enterprise. Everything modern models work with 1C and are easy to configure. To synchronize with a PC, you need special software.
- Bluetooth scanners- a promising line of equipment in its segment. Scanners differ by interfaces: USB-Hid, USB VCom, KW (keyboard wedge), RS232. For ease of connection, the scanner can be connected to a PC or POS monoblock through the stand.
Tags: Add Tags
In the courtyard there is an economic crisis, which entails instability in demand, so the profits of retail stores are falling along with increased competition. In these challenging times, businesses are looking for additional ways to help them stay afloat by increasing operational results (sales) and reducing costs (including operating costs). Retail Automation provides organizations with supportive paths to stay profitable.
In this article, we will talk about barcode scanners. How does the use of these technical tools help the retail business?
Barcode scanner guarding the trading process
It is difficult to imagine a POS terminal that does not include a barcode scanner, because this technical tool is a necessary element of the trading process. And not only retail - these devices are found in other companies that are not related to retail: medical, logistics, service. This speaks of the versatility of the application and the wide possibilities that barcode scanners for 1C have. Surely you saw in the store how the seller scans the purchased item, which is subsequently automatically displayed on the monitor with the list of purchases. Outwardly, a cash register barcode scanner looks simple and unremarkable, so many underestimate the functionality of such devices.
Varieties of barcode scanners
The device can be categorized as:
- Wired or wireless;
- Slotted, multi-plane or embedded.
The budget option is wired models, because they are used only stationary. In contrast, a wireless handheld barcode scanner allows a warehouse employee to move freely from one room to another without limiting his mobility.
In addition, each type of barcode requires different type technical means. Marking of goods can be:
- Linear - in the form of parallel stripes (EAN, UPC, Code 128, Code39, Codabar). It encodes up to 30 characters (symbols);
- Two-dimensional - due to horizontal and vertical coding (PDF 417, Data Matrix, QR, Microsoft Tag, etc.) it contains more data than linear. Originally (ten years ago) two-dimensional codes were multi-level, and then became matrix. Due to their reliability and security, matrix codes are used in the banking industry to encrypt unique certificates, documents, assign keys, but for this you have to buy a 2D barcode scanner. A 2D device is more informative than a linear one, because it encrypts not thirty, but more than two thousand characters!
If you are using linear codes, then, when choosing a laser barcode scanner, proceed from the density and keep in mind that the image can be difficult to recognize, fade and distort. Because of this, it makes sense to purchase devices that can recognize frayed markings.
Also, give preference to models that support reading different standards, because it is not known which one you will encounter in your work. Some codes do not have numeric elements in the image, so the seller at the checkout will not enter it manually if wireless scanner the barcode does not recognize the picture. Remember, barcode scanners in Moscow have become the gold standard for retail automation, don't skimp on them. This will help you avoid time losses in the checkout area, which will have a positive impact on the speed of service and customer satisfaction.
Warehouse barcode scanner: device
The main element that is built into every 1C barcode scanner is the reader, which is directly responsible for the functionality of the hardware. They are of three types:
- LED;
- Laser;
- Two-dimensional.
A USB barcode scanner that is equipped with an LED reader is a budget option. The principle of operation is to emit red light with a minimum resolution of 7.62 micrometers. Read range refers to values that depend on factors such as density and contrast of markings.
A barcode scanner with a laser reader will work with a low-contrast and frayed image, which will be beyond the power of an LED device. The performance characteristics of these devices are due to the following properties:
- Range (more than 55 centimeters);
- High speed of work;
- Large angle of the field of view (in vertical and horizontal planes).
Laser readers are built into wired and wireless barcode scanners. Restricting the use of laser and LED readers - work only with linear one-dimensional barcodes Therefore, barcode scanners for 1C with two-dimensional recognizers are gaining popularity. The mechanism of operation of these devices is based on photosensors with a high decoding speed (over 50 frames / sec.) Of the image on the product label. The wireless barcode scanner is versatile because it has a high resolution... The online store to-shop.ru presents modern models of devices with a two-dimensional reader.
Barcode scanners in Moscow: case studies
Before buying a scanning device, see which case study is similar to the current situation in your company.
Example 1. Supermarket
In supermarkets, they often use budget wired models that have the necessary functionality: synchronization with a computer, transfer of data about purchases to a single accounting database. These devices are versatile, easy to operate and automatically integrate when connected, even with latest versions 1C software products for retail trade automation.
Example 2. Warehouse
The cordless model is a convenient barcode scanner for the warehouse due to the characteristics associated with compactness, mobility and the amount of built-in memory. They are equipped with audio and LED indication of successful completion of the operation, which simplifies the work of warehouse personnel, increases labor efficiency and reduces the number of errors due to human error. These models automatically sync with personal computer at the end of the shift. In order not to lose data for a day of work, the user can configure the storage of data in the device's memory.
Example 3. Traveling and exhibition activities
Companies participating in trade fairs use a handheld barcode scanner with Bluetooth interface... They have wide functionality, work and automatically sync with mobile devices(on OS Android and iOS). Paired with a smartphone or tablet, the 2D barcode scanner acts as a data collection terminal. They are widespread due to their compact size, long operating range and a large battery.
Example 4. Self-service
In self-service systems of stores, multi-plane devices are used for contactless receipt of information about the product of interest to the buyer (price, characteristics, stocks, etc.). Scanning beams decode product markings in any plane, therefore they are able to read information even from large items at a distance.
Example 5. Access control
Many modern enterprises in the service sector (fitness clubs, libraries) have switched from RFID-based systems for accessing premises to barcode readers. Companies do not bear the cost of maintaining administrators who mark newcomers, but at the same time they have real time access to the database of visitors and to all the necessary statistics. In this field, a multi-plane wireless barcode scanner is more commonly used.
EGAIS
Starting this year, all enterprises engaged in retail and wholesale trade in alcoholic products, as well as their production, storage and supply, are required to transfer data on turnover to the Unified State Automated Information System(hereinafter - EGAIS). To optimize their handling of alcohol acceptance and distribution, companies use a 2D barcode scanner to read excise stamps and QR codes.
The price of a barcode scanner for EGAIS in the online store site varies from 8 to 10 thousand and depends on the model, manufacturer and functionality of the device. If you have any questions on how to choose equipment for EGAIS, please contact the support specialists in the corresponding section of our website.
