Few marketers and advertisers remember that every square centimeter of advertising space costs money. Somewhere more, somewhere less - but worth it. Whether it's 720 rubles per 1 square centimeter of a page in a federal glossy magazine or 10 kopecks per 1 square centimeter on a 3*6 billboard in the region. What do these numbers say? Yes, only one thing - We must think about the effective use of each square centimeter of advertising media.
Each smartphone is different and has different camera specifications. Modern smartphones should be able to read them. First of all, you need to know when and how it will be scanned: on a large poster or on a product packaging? The combination of these rows and columns creates a grid of modules. The maximum is 177 rows and 177 columns, which means the maximum possible number of modules is 31.
There are 40 preset sizes for you to choose from. They are called versions. Each version is then incremented by 4 rows and 4 columns. Here are some examples showing the difference in appearance for codes containing different amounts of data.
I offer you an article where all the advertising media suitable for the use of QR codes are laid out on the shelves, and key limitations are highlighted, by studying which you can easily increase the efficiency of using each centimeter of advertising.
Purposes of communication with a QR code
- Advertising (more about the product, offers, discounts, participation in prize draws).
- Marketing (voting, feedback)
- Social PR (useful free information)
- Attention capture, curiosity index
- Continued communication online, i.e. transfer from offline to online
- Providing detailed information about a product, service or promotion
- Simplify further communication: fix complex or very long addresses on the Internet or save contact information completely
- Subscribe to newsletter by email
- Poll, collection feedback, indirect control of the effectiveness of the advertising medium
- POS, POP materials (postcards, posters, dispensers) are one of the most effective carriers of QR codes
- Outdoor advertising (not large format) at stops, stations is effective, because forced closed space "offers" to take time plus good optical contact. Features: if this is a subway and you posted a link, make sure the station has operator coverage to follow the link
- Print advertising (magazines, newspapers, booklets, tickets)
- business cards
- Discount coupons, flyers - when buying in a store, you can present the QR code on your phone for scanning and get a discount
- Mailing List (Direct Mail)
- Pointers
Restricted Media
This includes positioning, timing, alignment, and format data, as well as error correction and version information. We're talking about bug fix mode later in the tech series, or you can jump in. It's a misconception that adjusting the surface area of the code will allow you to add more data. Increasing the surface area of your code will never allow you to have more than 177 columns and 177 rows, it just stretches the code to make modules bigger.
If you want to know more about one of these. Or Jump to: == Choose one ==. There is no technical limitation. One simply stretches more than the other, with the only difference being that the physical width and maximum of the module ends up being larger, but the number of modules that store data and their relative position remains the same.
- TV and video advertising
- Website - use in the print version of the material, if your content is often printed and passed to read
- Outdoor advertising (large format) - applicable with restrictions, reasons: usually short contact time with the code and poor optical visibility
- Label/price tag
- transit advertising
- Email distribution
- Modified logo
- wall, roof, field
Criteria for success and applicability of the QR code
When scanning from a distance, this large size is key. It would be impossible for them to get the whole image in the scanner. So the size of your code should be determined by the distance users have to scan it from, but technically there's really no limit to how big or small you can make it.
You most likely have a similar question if you are reading this. You may not want to hear this, but there is no right answer to this question. The good news is that you can figure out the ideal size for your campaign. If your phone scanner can detect every module, it will be able to read your code.
I will consider the main criteria that are imposed on the environment, process, carrier and code itself for their effective use in advertising.
- Time. Duration of contact with the QR code (minimum 10-15 seconds to search and launch the application)
- Distance. Sufficient distance and code size for optical reading (see calculations below)
- Lighting. There must be sufficient lighting for recognition. Some QR readers are equipped with a “Light” function to overcome this limitation (just do not highlight the QR code in the sleeping area with the iPhone).
- carrier stability. A rotating or moving advertising structure does not contribute to the reading of the QR code in any way, the carrier must be fixed.
- code contrast. It can be any color, but a contrast between dark and light squares is required.
- QR code size. QR codes should not be too small either, the minimum size for medium optics is 2.5*2.5 cm, otherwise scanning devices will not be able to focus on the code and decipher its contents.
- "Quiet Zone". One of the critical factors for reading the code is the wide white margins around; size of 4 minimum code modules.
- call to action. The text accompanying the QR code should have a clear motivating call to action.
- Expectations. There should be a clear connection between the content on the link and the placement context.
- Coverage. Initially, there should be a large coverage of the advertising medium, because. the viral distribution of this tool is low.
Critical distances between QR code and reader
Testing and testing again
For a large billboard, the scanner would be hundreds of meters away. Once you have determined the expected crawl distance for your campaign, apply this standard rule. The scanning distance should be approximately 1 foot.
Scan Distance: 5 feet or 6 inches. High error correction will increase the number of rows and columns. This ensures that if the size of the image is increased, the resolution of the image will also increase as a result. If you follow the rules above, this is good practice, Golden Rule.
There are no restrictions regarding size and distances. The main condition is the ability to read the code with a scanning device. The huge QR code on the firewall can be read, for example, from a distance of several meters using standard phone optics.
The minimum size of a QR code for everyday use in advertising — 28*28 mm in size (version 1, contains 441 modules (21×21)). The optimal distance for reading it is 10-15 cm between the code and the reader. Experimentally, I established a relationship between the size of the code and the maximum distance from which it is scanned for different type cameras in the phone (see table). I note that I do not give the third point, but it confirms the linear dependence, which makes it easy to calculate optimal size QR code for almost any distance.
The black and white checkered pixel patterns appear at first glance like a small crossword puzzle and seem to have been put together at random. But if you look closely, some structures can be identified. A number of additional elements guarantee the correct reading of the information.
They indicate the direction in which the Code is printed. Using these strings, the scanner determines how large the data matrix is. Format templates contain error tolerance and data mask template information and make code easier to scan. These templates contain the actual data.
Table of experimental data
| QR code size 2.8*2.8cm |
QR code size 16.5*16.5cm |
|
| Camera 3 MP iPhone 3Gs |
Max. recognition distance 30 cm | Max. recognition distance 150 cm |
| Camera 8 MP iPhone 4s |
Max. recognition distance 70 cm | Max. recognition distance 375 cm |
A QR code placed on a 3 * 6 billboard, with an average distance to the code of 7.2 meters (6 meters high, 4 meters to the billboard) should be:
On the same subject
Because of this, up to 30% of the code structure can be destroyed without affecting the readability of the code. There you can select the type of code you want to generate and then enter the relevant details. Now you just decide which image format you want the code to be in and upload the file easily.
Questions about size
A large selection of them can be downloaded for free from various app stores. If the code is readable, it will be accessed by the automatically encoded address or action. The code consists of black modules arranged in a square pattern on a white background.
- 30*30 cm for good optics
- 50 * 50 cm, if the optics are medium (i.e. 1/6 of the height of the shield!).
Don't Forget the Call to Action
I bring to your attention a list of good “calls to action” stimulating, scanning a QR code:
- Scan and contacts are already in your phone
- Exclusive multimedia, videos and photos
- Fast access
- Special offers, coupons or gifts
- "Secret information
- Follow us on social media(facebook, twitter).
If you have something to add or discuss - I'm ready!
QR codes: introductory course
The processor finds three distinctive squares at the corners of the image and normalizes the image size, orientation, and viewing angle with a smaller square near the fourth corner. The small dots are then converted to binary numbers and verified with error-correcting code.
At the application level, there is some variation between most implementations. They used to be limited to industrial uses, which in recent years have expanded to consumer advertising and packaging as the proliferation of "smartphones" first introduced a barcode reader into every pocket. It may also be used to store personal information for government use. Many of these applications are designed for mobile phone users.
Space on paper, screen, and other media is valuable and should be used sparingly. Some barcodes pack information more efficiently and take up less space than others. In practice, the question arises: for a given amount of information, how much space does a particular barcode format use?
The size of a 2D barcode is measured in the number of grid modules along each side. Each grid module can be either on (black) or off (white). The size of each module is called "X size" (English "X Size"). Each scanner has a minimum "X size" that it can read. This setting is independent of the type of barcode being read. The total size of the barcode will be calculated as the product of "X size" by the number of modules.
This act of linking to objects in the physical world is called a hyperlink or hyperlink object. The higher the error correction level, the smaller the memory capacity. The following table lists exemplary error correction capabilities at each of the four levels. Due to the design of Reed-Solomon codes and the use of 8-bit codewords, a single codeblock cannot contain more than 255 codewords. This means that no more than 15 errors per block can be corrected, which limits the complexity of certain steps in the decoding algorithm.
Under the cut is a translation of a fragment of a Semacode report on choosing the optimal two-dimensional barcode format for mobile applications.
An independent group (R9 Automatic Data Capture group) from the Consumer Electronics Association published a comparison data matrix and QR Code for the needs of the development of the IEC 62090 specification (“Marking the packaging of goods using barcodes and two-dimensional symbols”). The main conclusion - Data Matrix is the most efficient use of space among all two-dimensional symbols.
The format information records two things: the error correction level and the mask pattern used for the character. Masking is used to break up patterns in an area of data that can confuse the scanner, such as large empty areas or misleading features that look like locator marks. The mask patterns are defined on a 6×6 grid that is repeated as needed to cover the entire character. Units corresponding to dark areas of the mask are inverted.
These messages are placed from right to left in a zigzag pattern, as shown below. In large symbols, this is complicated by the presence of alignment patterns and the use of multiple interleaved error correction blocks. 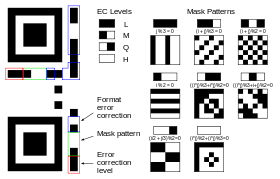
Four-digit indicators are used to select the encoding mode and transfer other information.
The CEA document gives four specific examples, which we summarize in a table:
| QR code | data matrix | Space saving | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Example 1 | 42×42 | 24×24 | 67% |
| Example 2 | 425×25 | 18×18 | 48% |
| Example 3 | 29×29 | 20×20 | 52% |
| Example 4 * | 29×29 | 26×26 | 20% * |
Let's compare the performance of the two formats using independently developed generators:
Independent and our analyzes show that Data Matrix uses 30%-60% less space than QR Code.
After each indicator that selects an encoding mode is a length field that tells how many characters are encoded in that mode. The number of bits in the length field depends on the character encoding and version, as shown below. Alphanumeric encoding mode stores the message more compactly than byte mode, but cannot store lower case and has a limited set of punctuation marks. Two characters are encoded into an 11-bit value using this formula.
Alphanumeric character codes look like this. My main goals are flexible options and absolute correctness. Additional advanced features. Regardless of the language used, the generated results are guaranteed to be identical because the algorithms are translated correctly.
Example

Both barcodes contain the text "http://google.com". Data Matrix is 61% smaller.
Minimum size
For a small amount of data, the minimum barcode size is important to save space. Minimum size of QR Code - 21×21, Data Matrix - 10×10 modules (77% less).I'll add my own

It is strange that they forgot to mention in the report that the QR Code must be framed by a white frame equal in width to the positional marker, which in itself increases the required area when printing.
This makes it easy to quickly build the right application. . Note that all private functions, methods, and fields are hidden as function-local variables, so it's impossible to access them from outside the library. 
Has no dependencies in the box, only relying on the standard library. . Some of the commonly used official terms have non-intuitive meanings, as noted below.
Note that the module can be scaled to fit multiple pixels on the screen or in an image file. A way to measure the size of a character, from 1 to Note that all 40 versions are defined in the same standard, and this term is different from the usual meaning of word version.
