» we looked at some aspects of the work wireless wifi adapters, and today we will analyze a few possible options for building a network. Simple construction wireless network or connecting it to an existing wired network, combining two segments of a wired network - all this requires the appropriate equipment. Looking at any price list, we often see only wireless adapters and access points. Only the Access Point group often includes routers, as well as various devices with advanced functions (Client, Brigde, WDS, WDS + AP). Ordinary access points can only combine wireless clients and connect them to a wired network, while access points with the Client function can act as a client to connect to a neighboring AP, and AP Brigde or WDS allow you to combine two wired network segments. The main scope of their application is home networks or a small office, where a quick and easy connection of wireless clients to the network is required at the right time. For large corporate networks, offices with a well-organized network, the requirements are different - the basis is the security and manageability of the network. Therefore, at the service of your favorite network administrator, more advanced equipment is purchased - wireless routers. Typically, a wireless router is a wireless access point, a NAT router, and an Ethernet switch all rolled into one. However, you need to decide in advance on the needs, and then study the proposals. All wireless routers allow you to combine wired and wireless clients into a single network and provide users with Internet access via an ADSL modem connected to it, for example. To make it immediately clear to our readers what are the differences between the operating modes of wireless access points, we present this table:
|
Working mode |
|
|
Access Point Mode. Allows you to connect wireless clients operating in Infrastructure mode. |
|
|
Used in APs and Wi-Fi adapters. In Ad-Hoc (peer-to-peer) mode, each wireless device can communicate directly with each other without using an access point |
|
|
Used in APs and Wi-Fi adapters. In Infrastructure mode, devices operate on a client/server basis. A wireless network consists of at least one access point to which wireless end clients are connected. |
|
|
Bridge-Point to Point |
This mode allows you to connect two wired LANs through a wireless bridge. In this mode, wireless clients will not be able to connect to the AP, since it is configured to work only with a remote AP operating in a similar mode. The main advantage of using this mode is that all possible bandwidth of the wireless channel is used to combine two network segments. |
|
Point to Multi-Point |
Allows you to connect up to six wired LANs. In this mode, wireless clients will not be able to connect to the AP, since it is configured to work only with a remote AP operating in a similar mode. |
|
Allows an AP to connect to a remote AP in Infrasructure mode like a normal wireless adapter. Only wired network clients can connect to this access point, while a remote AP can operate in full AP mode. |
|
|
In wireless "repeater" mode, the AP allows you to extend the range of your wireless network by repeating the signal from a remote access point. To do this, specify the MAC address of the remote AP in the AP settings (MAC-clone option). For the Repeater mode, it is recommended to use APs from the same manufacturer, made on the same chipset. |
It should be clarified that the names of these modes have different manufacturers may vary and occasionally have several implementation options. This article will discuss the various capabilities and functionality of wireless access points using the example of three various devices. At the same time, we tried to focus on real needs and testing conditions.
Access point D-link DWL-2100AP
The dimensions of the D-link DWL-2100AP are relatively small, and appearance recognizable due to the company's traditional two-tone design. As a nice addition, the kit comes with fasteners for vertical installation of the device and wall mounting. The instruction in Russian will help an inexperienced user to understand all the features of the access point.
The front panel has indicators for power, wired (LAN) and wireless network (WLAN) activity.
To connect to local network one RJ-45 connector is used. In addition to it, on the rear panel you can see the SMA connector for connecting the antenna, the socket for the power supply and the reset button recessed into the case, rebooting the device. Management and configuration, as usual, occur through the browser. To access the access point, by default, the IP address is 192.168.0.50 and the login "admin" with an empty password. The web interface is made bright, decorated with beautiful graphic elements, and does not differ from the window of any Windows program.
Upon entering, we are immediately greeted by an easy and not loaded with unnecessary options setup wizard. In addition to supporting standard access point functions, D-link DWL-2100AP supports one of the frequently requested functions - using an access point as a client. In this mode, the AP plays the role of a regular Wi-Fi adapter that can be connected to any Ethernet port on a desktop PC, laptop, network hard drive or digital satellite receiver.
In AP-Repeater mode, the D-link DWL-2100AP can relay the signal from a remote access point to nearby wireless adapters, but it only works with devices built on the same chipset. To combine wired networks over Wi-Fi, you need to use access points in WDS mode (or WDS with AP). It is often found that routers with a built-in access point cannot connect to other APs, and if you connect the DWL-2100AP to it in client mode, then only one computer can be behind it. A standard set of encryption methods is responsible for the security of data transmission: WEP, and the most secure WPA, WPA-PSK WPA2, WPA2-PSK.
To prevent unauthorized access to the network, you can use only the MAC address filter. Practice shows that picking up a key encrypted with the WEP method, as well as replacing the MAC address, is not so difficult, and if you want to protect the network from outside attacks, the use of WPA and WPA2 encryption will help more. Access to the access point management web interface is limited not only by login and password, but by binding to an IP address from which administration can be carried out. The web interface also allows you to view quite informative data transfer statistics and keeps a detailed log of the access point. As a result, D-link DWL-2100AP has all the functions necessary for an undemanding user without any frills. It is easy to set up, operate, and may well provide a minimum level of network protection. We will find out its speed characteristics during testing with more functionally rich brothers.
On this tab, you can change the mode of the access point. In most cases, you can leave the default mode access point(Access point). You may want to change the mode of the access point if you want to use it as a wireless repeater to extend the range of your wireless network. You will also want to change the mode of the access point if you are using it as a wireless bridge, for example, you can use two access points in wireless bridge mode to connect two wired networks located in two different buildings.
Important:
For AP Client and Wireless Bridge modes, the remote access point must also be a WAP54G model. For wireless repeater mode, the remote wireless bridge must be a second WAP54G access point or WRT54G router.
AP Mode
The access point can operate in four modes: access point(Access point), AP Client(Wireless Client) Wireless Repeater(Wireless Repeater) and Wireless Bridge(Wireless bridge). For Repeater and Bridge modes, make sure the network ID, channel, and security settings match those of other wireless access points and devices.
LAN MAC Address
The MAC address of the access point is shown here.
access point. This mode is set by default. This mode connects your wireless computers to a wired network. In most cases, no settings are needed.
AP client. In this mode, the access point is able to maintain a connection with one remote access point within the network coverage area. This option only works if a second WAP54G is used.
This mode allows the access point to act as a wireless client. It cannot connect to other wireless clients directly. A separate network connected through an access point in AP Client mode can be wirelessly bridged to a remote access point.
To use this mode, select AP Client and enter the LAN MAC address of the remote access point in the field Remote Access Point's LAN MAC Address. If you do not know this address, click on the button site survey.
Apartment and office Wi-Fi in practice. Part two
In the first part of the article "" we examined some aspects of the operation of wireless Wi-Fi adapters, and today we will analyze a little possible options for building a network. The simple construction of a wireless network or its connection to an existing wired network, the combination of two segments of a wired network - all this requires the appropriate equipment.
Looking at any price list, we often see only wireless adapters and access points. Only the Access Point group often includes routers, as well as various devices with advanced functions (Client, Brigde, WDS, WDS + AP). Ordinary access points can only combine wireless clients and connect them to a wired network, while access points with the Client function can act as a client to connect to a neighboring AP, and AP Brigde or WDS allow you to combine two wired network segments. The main scope of their application is home networks or a small office, where a quick and easy connection of wireless clients to the network is required at the right time. For large corporate networks, offices with a well-organized network, the requirements are different - the basis is the security and manageability of the network. Therefore, to serve the beloved network administrator, more advanced equipment is purchased - wireless routers. Typically, a wireless router is a wireless access point, a NAT router, and an Ethernet switch all rolled into one. However, you need to decide in advance on the needs, and then study the proposals. All wireless routers allow you to combine wired and wireless clients into a single network and provide users with Internet access via an ADSL modem connected to it, for example.
To make it immediately clear to our readers what are the differences between the operating modes of wireless access points, we present this table:
|
Working mode |
Short description |
|
Access Point Mode. Allows you to connect wireless clients operating in Infrastructure mode. |
|
|
Used in APs and Wi-Fi adapters. In Ad-Hoc (peer-to-peer) mode, each wireless device can communicate directly with each other without using an access point |
|
|
Used in APs and Wi-Fi adapters. In Infrastructure mode, devices operate on a client/server basis. A wireless network consists of at least one access point to which wireless end clients are connected. |
|
|
Bridge-Point to Point |
This mode allows you to connect two wired LANs through a wireless bridge. In this mode, wireless clients will not be able to connect to the AP, since it is configured to work only with a remote AP operating in a similar mode. The main advantage of using this mode is that all possible bandwidth of the wireless channel is used to combine two network segments. |
|
Point to Multi-Point |
Allows you to connect up to six wired LANs. In this mode, wireless clients will not be able to connect to the AP, since it is configured to work only with a remote AP operating in a similar mode. |
|
Allows an AP to connect to a remote AP in Infrasructure mode like a normal wireless adapter. Only wired network clients can connect to this access point, while a remote AP can operate in full AP mode. |
|
|
In wireless "repeater" mode, the AP allows you to extend the range of your wireless network by repeating the signal from a remote access point. To do this, specify the MAC address of the remote AP in the AP settings (MAC-clone option). For the Repeater mode, it is recommended to use APs from the same manufacturer, made on the same chipset. |
It should be clarified that the names of these modes for different manufacturers may vary and occasionally have several implementation options. This article will discuss the various capabilities and functionality of wireless access points using the example of three different devices. At the same time, we tried to focus on real needs and testing conditions.
Access point D-link DWL-2100AP
The dimensions of the D-link DWL-2100AP are relatively small, and the appearance is recognizable thanks to the two-color design traditional for this company. As a nice addition, the kit comes with fasteners for vertical installation of the device and wall mounting. The instruction in Russian will help an inexperienced user to understand all the features of the access point.

The front panel has indicators for power, wired (LAN) and wireless network (WLAN) activity.

To connect to the local network, one RJ-45 connector is used. In addition to it, on the rear panel you can see the SMA connector for connecting the antenna, the socket for the power supply and the reset button recessed into the case, rebooting the device.
Management and configuration, as usual, occur through the browser. To access the access point, by default, the IP address is 192.168.0.50 and the login "admin" with an empty password. The web interface is made bright, decorated with beautiful graphic elements, and does not differ from the window of any Windows program.

Upon entering, we are immediately greeted by an easy and not loaded with unnecessary options setup wizard.
In addition to supporting standard access point functions, D-link DWL-2100AP supports one of the frequently requested functions - using an access point as a client. In this mode, the AP plays the role of a regular Wi-Fi adapter that can be connected to any Ethernet port on a desktop PC, laptop, network hard drive, or digital satellite receiver.
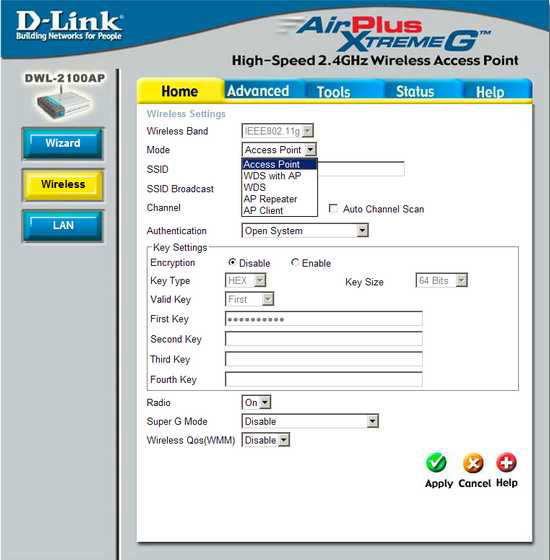
In AP-Repeater mode, the D-link DWL-2100AP can relay the signal from a remote access point to nearby wireless adapters, but it only works with devices built on the same chipset. To combine wired networks over Wi-Fi, you need to use access points in WDS mode (or WDS with AP). It is often found that routers with a built-in access point cannot connect to other APs, and if you connect the DWL-2100AP to it in client mode, then only one computer can be behind it.
A standard set of encryption methods is responsible for data transmission security: WEP, and the most secure WPA, WPA-PSK WPA2, WPA2-PSK.
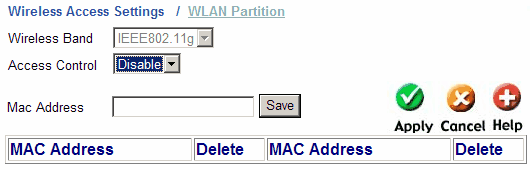
To prevent unauthorized access to the network, you can use only the MAC address filter. Practice shows that picking up a key encrypted with the WEP method, as well as replacing the MAC address, is not so difficult, and if you want to protect the network from outside attacks, the use of WPA and WPA2 encryption will help more. Access to the access point management web interface is limited not only by login and password, but by binding to an IP address from which administration can be carried out.
The web interface also allows you to view quite informative data transfer statistics and keeps a detailed log of the access point. As a result, D-link DWL-2100AP has all the functions necessary for an undemanding user without any frills. It is easy to set up, operate, and may well provide a minimum level of network protection. We will find out its speed characteristics during testing with more functionally rich brothers.
Router TP-Link TL-WR542G

Most of the top panel has many small holes for heat dissipation and, objectively, the device hardly heats up. In the kit, in addition to the device, you can find user manuals in paper and electronic versions, a power supply and external antenna. There are holes for mounting on the wall, but the necessary fasteners are not included. The antenna has a slightly larger than usual dimensions, which has a positive effect on the range of work.

The front panel has power and activity indicators for the wireless segment, the built-in four-port switch, and the WAN port.

Looking at back panel router, you can see the antenna connector, reset button, four LAN and one WAN connector, as well as a power connector.
The main application of TP-Link TL-WR542G is wireless point access and a router to separate and differentiate Internet access. Repeater and WDS modes in this case not provided. For this reason, its use is limited to a network where it is required to make a hybrid network of several wired (there is a built-in 4-port switch) and wireless clients. And given the presence of a built-in switch, it can easily be used only for a wired network, with the future connection of wireless clients.
The web interface is very easy to use, and if the user does not understand any menu item, then he can always read its description on the right side of the html page with more or less detailed description all functions. The traditional setup wizard will help you quickly basic setup networks.
The first menu item "Status" displays the mode of operation of the router and brief data transfer statistics. The LAN, WAN and MAC Clone items are available in the Basic Settings menu. From possible settings item "LAN" - only an indication of the IP address of the router and the subnet mask. The built-in switch is not managed, and therefore DHCP and some other functions are only available for managing WLAN clients.
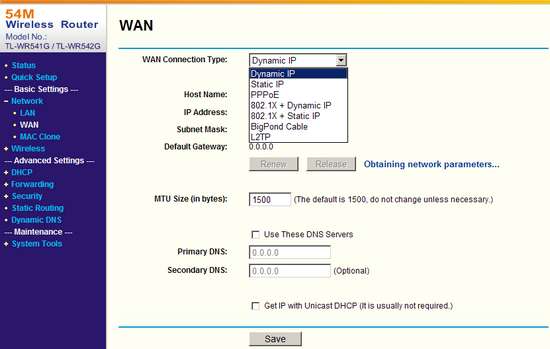
The WAN settings indicate the type of connection and its settings.
In the wireless network settings, the “Wireless” item configures the access point operation mode, filtering by MAC address and shows the number of received and sent packets for each of the wireless clients. Recall that the TL-WR542G only works as an AP (Access Point) in the "Infrastructure" mode (or in another way client-server).

DHCP assigns IP addresses to wireless clients. At this point, you can see the current correspondence between IP and MAC address pairs, as well as assign a static IP binding to a specific MAC address.
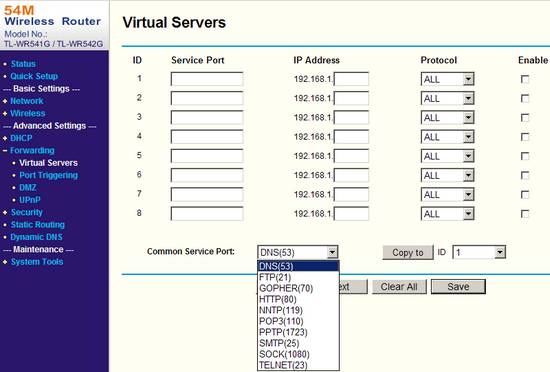
The "Forwarding" group has almost all the settings for creating virtual server and port forwarding.
One of the most interesting and useful groups in the menu - "Security". Available filters by IP and MAC addresses, and URL. Supported remote control from the specified IP address, but when administering the router via the Internet, you need to keep in mind that you must have a permanent external (on the Internet) IP address. The main difference between TP-Link and CNet (see below) is the ability to manually select an access control policy. If in CNet in its filters you can only deny access from certain IP or MAC addresses, then in TP-Link, in addition, you can choose one of two policies that will act by default:
- Allow packets that are not defined in the filtering rules to pass through the router;
- Deny packets that are not defined in the filtering rules to pass through the router.

If you need to define a rule in a filter to allow access to only one or two computers on the network, then it is more logical to choose the "default denial" policy, that is, to allow access only to those who are listed. If it's the other way around, you need to allow access more computers, and deny access to smaller ones, it is more convenient to use the “default permissions” policy, that is, to deny access to those who are listed. When filtering, you can also specify the time range for the rule.

So TP-Link TL-WR542G supports protection against DoS attacks, specifically: ICMP-FLOOD, UDP-FLOOD, TCP-SYN-FLOOD, plus all this there is a function to ignore Ping packets from an external network, and prohibit sending Ping- packets from the internal network to the external. You can enable and configure these settings in the "Advanced Security" item.
Static routing and automatic registration DNS is configured in the corresponding items "Static Routing" and "Dynamic DNS".
In a separate group "System Tools" there are settings that do not affect the quality and speed of communication (changing the time, password), some functions for managing the router (resetting settings, firmware and restarting the device), as well as statistics. TL-WR542G maintains a detailed log of its work and statistics on received and sent information separately for TCP and UDP packets for each IP address.
Router CNet CWR-854

The dimensions of the CNet CWR-854 are small and, despite the possibility of mounting on the wall, there are no necessary fasteners in the kit, but there is one meter-long Patch cord cable. Indicators of device operation and network activity are located on the top panel.

The main visible difference between CNet CWR-854 and TP-Link TL-WR542G is the presence of two antennas. With the exception of this feature, the set of connectors for both devices is the same.
As practice shows, the presence of two antennas is not the main factor that can affect the speed and range of a wireless network. In the case of the CWR-854, the range leaves much to be desired, which you can observe during testing. And it proves that one should not believe not only the declared technical specifications but also to the eyes. Any wireless equipment must be selected either by experience, recommendations, or by testing everything directly on the spot.

The web interface menu is also divided into subgroups with more detailed settings, and the first thing that meets us when we access the router is the traditional settings wizard.
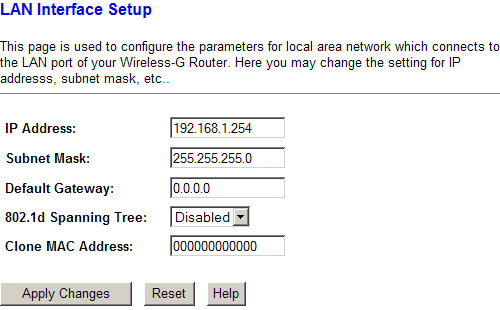
LAN Settings allows you to configure the router to work on an existing local network. MAC address cloning can be done at the same point.
The WAN Settings menu options control the routing method. Available modes include static and dynamic IP, PPPoE and PPTP.
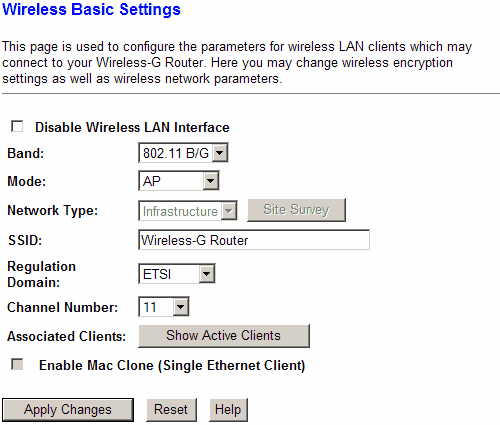
In the “Wireless” menu group, the operation of the router as an access point is configured. CNet CWR-854 can also work as a client in "Client" and "WDS" modes. There is no “Repeater” mode, similar to D-link, which allows you to relay the signal from a remote access point.
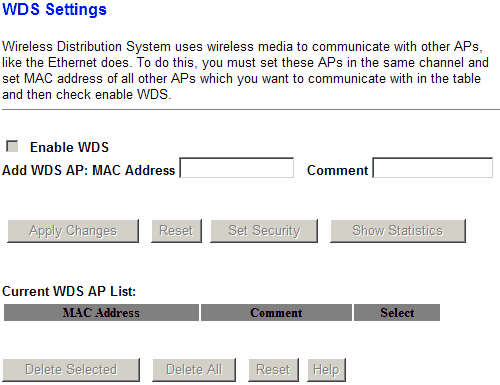
If in “Client” mode you can connect to another access point using a visual web interface, then in WDS mode, as a rule, you need to clearly write down its MAC address.
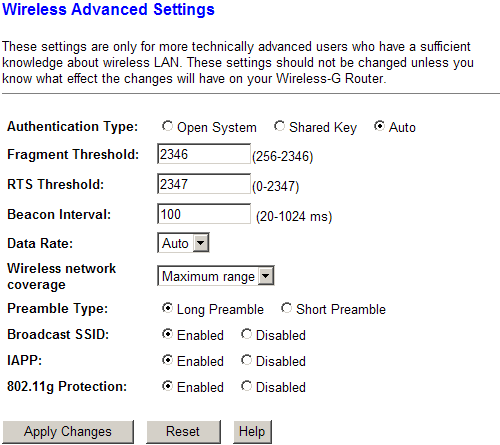
In the "Wireless Advanced Settings" item, more than fine tuning wireless network designed for advanced users.
The "Security" section is responsible for encrypting the transmitted data. The set contains: a standard set of encryption methods, the key length for WEP encryption is up to 128 bits.
To protect against unauthorized access to the control panel of the router, you can use the MAC address filter. It allows how to allow access from specified network cards, and deny access to the settings for clients included in the list.
The “Firewall” item contains the most necessary filters for IP and MAC addresses, restricting access to certain ports and domain name. When adding entries to Port Filtering, each subsequent one was added more and more difficult. The pause between pressing the add button and the actual entry into the list increased, and after adding the 17th entry, the router lost the PPPoE connection and hung. The remaining three entries were added only after the device was rebooted.
CNet has the ability to organize secure VPN tunnels. That is, with the help of this router, you can create secure tunnels between two points via the Internet.
Rarely used and specific functions are located in the "Advanced" section. These include port forwarding, DMZ detection, and dynamic DNS detection. DNS registry services are entered manually.
The last menu group, "Management", has collected items for managing the device and viewing statistics. Only the “DHCP Settings” item stands out from this group, it would be more logical to place it in the wireless network settings, since it automatically distributes IP addresses between them in the specified range.
Testing
Often it is not possible to find objective information about very important issues. Such as: “What is the real speed of work?”, “Will a laptop with an access point in the next room work?”, “I want to give Internet access to only two computers on the network, and prohibit others.” For example this test we have tried to focus on real situations - that is, situations that anyone who plans to use wireless equipment will fall into.
On the example of this table, you can see the differentiation of devices by functionality.
|
Name |
||||
|
Main characteristics: |
||||
|
Wireless standards |
IEEE 802.11b/802.11g |
|||
|
Claimed max. speed, Mbps. |
Up to 108 in SuperG mode |
|||
|
Operating modes |
AP, AP Client, AP Repeater, WDS, WDS with AP |
Access Point (AP) |
AP, AP Client, WDS, AP + WDS |
|
|
Encryption methods |
WEP, WPA, WPA-PSK, WPA2, WPA2-PSK, 802.1x |
|||
|
WEP key length, bit |
||||
|
Antenna type |
external, removable |
Two external, removable |
||
|
Number of LAN ports |
4 x LAN, 1 x WAN |
|||
|
DHCP server |
||||
|
Routing capabilities: |
||||
|
WAN routing |
Dynamic IP, Static IP, 802.1x + Dynamic IP, 802.1x + Static IP, PPPoE, BigPond Cable, L2TP |
Dynamic IP, Static IP, PPPoE, PPTP, L2TP |
||
|
Max. the number of rules for filtering - 8. |
The maximum number of entries is 20. |
|||
|
The maximum number of records is 8 pieces. It is possible to set up a filter by duration. |
The maximum number of records is 8 pieces. You can enter both the entire URL and keywords in the URL. |
|||
As a client side, to identify issues of compatibility and quality of work with various WiFi adapters, D-Link DWL-G510, TP-Link TL-WN551G, and TP-Link TL-WN321G USB adapters were taken. Testing bandwidth passed at a distance of one meter from the access point without any obstacles. Data was transmitted simultaneously in two directions, the value of the average throughput was calculated after a three-minute test of the Ixia Chariot v5.40 program. Under conditions different from these, they will definitely be specified.
The average LAN-LAN data transfer rate through the four-port TP-Link TL-WR542G and CNet CWR-854 switches is no different from that of conventional switches and averages 94 Mbps.

The data transfer rate over the WAN is different for the two routers equipped with it. The difference of 6 Mbps is not significant if an ADSL modem is connected to the router, but it will make sense if you are working with more demanding equipment.
To determine the "range" of the tested samples, we placed access points at a distance of 4-5 meters from wireless adapter so that the signal passes through one reinforced concrete wall.

We see that, it would seem, two antennas should somehow affect the operation of the CNet router, but their number is of little use. TP-Link TL-WR542G has a slightly larger antenna and goes almost flush with the access point from D-link.
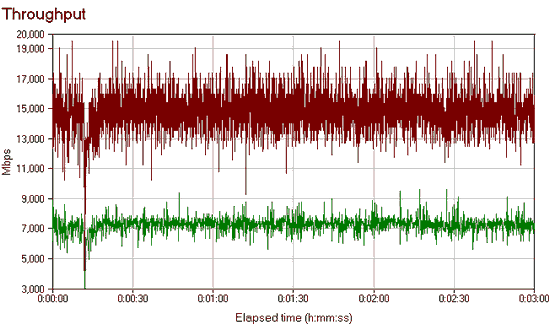

On the graphs, TP-Link shows a smoother data transfer. Unfortunately, there is no D-link DWL-2100AP chart, but we did not observe large drops in speed during its operation.
conclusions
For home users who want to take advantage of the convenience wireless connection, the DWL-2100AP access point from D-link is also quite suitable. If you need to connect an ADSL modem to the network, then you can pay attention to wireless routers. TP-Link TL-WR542G is positioned as a WAN router with a decent level of security, while being limited to a network with a small number of wireless clients, demonstrating stable and high-quality performance. Its ideal place is a small office or a network site where one ADSL modem is required to provide Internet to the entire network. CNet CWR-854, in turn, can provide a more extensive wireless network paired with other access points. According to the test results, this model cannot boast of good consumer qualities, but we recall that it was taken as an example of a device with the most extended functionality. Which device to choose is up to you. We have only shown what you can choose from, what are the differences between access points and different routers. The cost of the devices considered today on this moment is 58-63 c.u. for D-link DWL-2100AP, $54 for TP-Link TL-WR542G, and 84 c.u. for CNet CWR-854. As you can see, the price is not an indicator of the "status" of the device. Cost, speed and quality of work, ease of setup or security - for each of your tasks, you can choose a decent model.
AD HOC MODE
In Ad Hoc mode, clients communicate directly with each other. A peer-to-peer communication is established on a point-to-point basis, and computers communicate directly without the use of routers. This creates only one service area that does not have an interface for connecting to a wired LAN.
In Ad Hoc mode, the connection speed is no more than 11 Mbps, regardless of the equipment used. The actual data exchange rate will be lower and will not exceed 11/N Mbit/s, where N is the number of devices in the network. The communication range is no more than one hundred meters, and the data transfer rate drops rapidly with increasing distance. INFRASTRUCTURAL MODE
In this mode WiFi routers provide communication between client computers. The router can be thought of as a wireless switch. Client stations do not communicate directly. The router has Ethernet ports, through which the basic service area is connected to the wired network - to the network infrastructure. WDS AND WDS WITH AP MODES
The term WDS (Wireless Distribution System) stands for "distributed wireless system". In this mode, access points are connected only to each other, forming a bridge connection. In addition, each point can be connected to several other points. All points in this mode must use the same channel, so the number of points participating in the bridge should not be excessively large. Clients are connected only via a wired network through the uplink ports of the points.
A wireless bridge can be used where cabling between buildings is undesirable or not possible. This solution allows you to achieve significant cost savings and provides ease of setup and configuration flexibility when moving offices. Wireless clients cannot connect to an access point in bridge mode. Wireless connection is carried out only between a pair of points that implement the bridge.
The term WDS with AP (WDS with Access Point) stands for "distributed wireless system, including access point", i.e. using this mode, you can organize not only bridging between access points, but also simultaneously connect client computers. This allows you to achieve significant savings in equipment and simplify the network topology. This technology supported by most modern access points. REPEATER MODE
There may be a situation where it is not possible, or inconvenient, to connect the router to the wired infrastructure, or some obstacle makes it difficult for the router to communicate directly with the location of the wireless client stations. In such a situation, you can use the dot in repeater mode.
Similar to a wired repeater, a wireless repeater simply relays all packets that arrive at its wireless interface. This retransmission is carried out through the same channel through which they were received. When using a repeater access point, be aware that the overlap of broadcast domains can result in a halving of the link throughput, because the original access point also "hears" the relayed signal.
The repeater mode is not included in the 802.11 standard, so for its implementation it is recommended to use the same type of equipment (up to the firmware version) and from the same manufacturer. With the advent of WDS, this mode has lost its relevance, because the WDS functionality replaces it. CLIENT MODE
When moving from a wired to a wireless architecture, you may sometimes find that the available network devices support wired Ethernet network, but do not have interface connectors for wireless network adapters. You can use a client access point to connect these devices to a wireless network. Only one device connects to the wireless network using a client access point. This mode is not included in the 802.11 standard, and is not supported by all manufacturers.
call the master
Reviews
Natalia
Grade:
My laptop began to upgrade to Windows 10 without warning, and after a reboot it didn’t boot anymore ((The guys from CompService helped restore the old Windows 7, for which many thanks to them!
Yuri
Grade:
I picked up a virus encoder that encrypted all the files. Including photos and important documents. I found CompService on the Internet, and on the same day the courier took the laptop to decrypt the files. After 2 days, the laptop was returned to me with the restored files, everything was almost the same as before the virus hit, for which many thanks!
Kirill
Grade:
The laptop got very hot and kept shutting down. The service closest to me was 5 minutes away. After the diagnostics, the master disassembled and cleaned the laptop from dust, replaced the thermal paste and lubricated the cooler. The whole procedure took more than an hour. Now the laptop is working properly. Respect to CompService!
Elena
Grade:
I made an order for the removal of viruses, the master arrived quickly, did everything quickly, efficiently, without complaints. Thank you very much!
Igor
Grade:
I called the master to the house, the system did not boot, a young man came and very quickly reinstalled windows, plus he set up all the programs necessary for work. Satisfied with the quality of service.
Irina
Grade:
It was necessary to set up a router and install an office. Master Pavel arrived on time, quickly set up a router, set up an office. Very pleasant and knowledgeable tradesman! Thank you.
Andrey
Grade:
Pauline
Grade:
Recently, my MacBook has been constantly buzzing, knowledgeable people suggested that this may be due to overheating of the processor, and that it would not hurt to clean it from dust. The next day I took my laptop to service center CompService, and after an hour and a half I was informed that my macbook is ready, and you can pick it up. During the test, they showed me how it works under different loads. Imagine my surprise when the MacBook worked quietly, as it did right after the purchase))) Thanks to CompService for returning silence to my poppy!
