USB Type-C is not only an improvement to the charging port of the device, but also an excellent opportunity to replace the 3.5 mm jack.
What is USB Type-C? What format is this? Now we will understand this using the example of the universal device Promate Unihub-C.
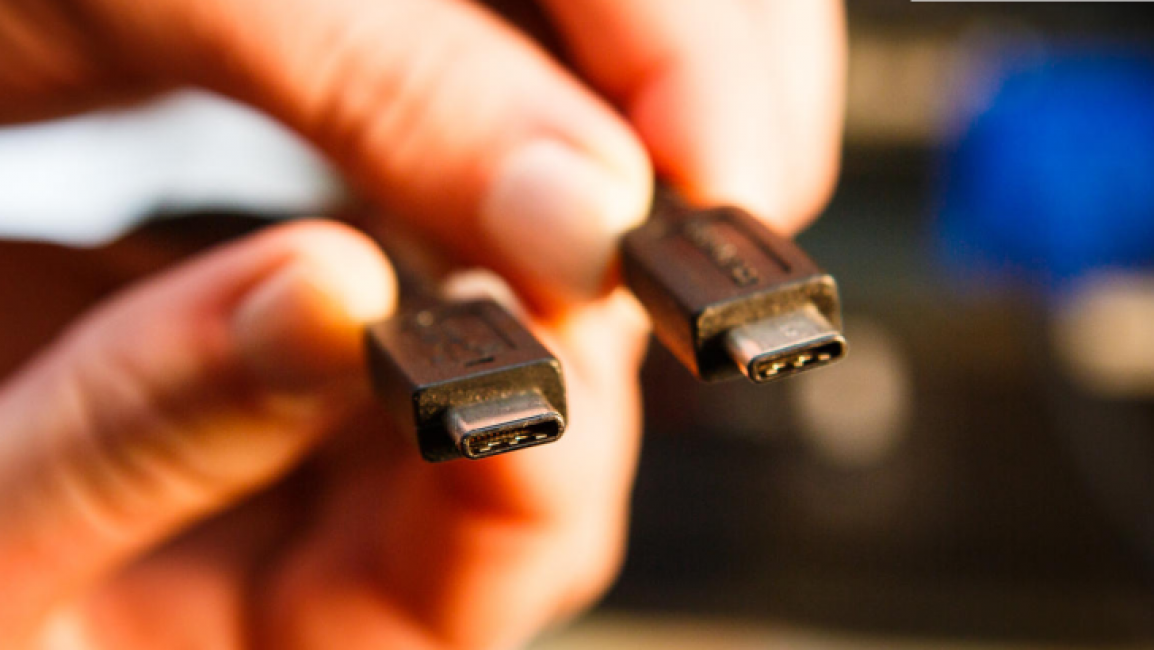

First, a little theory. Today, this format is an actively promoted connector on the market for connecting to peripherals and recharging devices.
These can be not only smartphones, but also some laptop models. The main difference from other formats is balanced plug. It is versatile and works regardless of the connection side.
Development and certification were carried out by the USB Implementers Forum group of companies.
This group includes the largest electronics manufacturers such as Microsoft, Dell, HP, Intel and Samsung.
Many manufacturers supported the innovation, and are already actively are starting to implement it in their new developments.
USB Type-C is the latest, but has already joined the ranks of standard formats and is becoming increasingly relevant.
From the point of view of physical appearance, such a connector differs from the standard designs of the MicroUSB and MiniUSB formats, as more technologically advanced modifications.
The new format specification is based on 24-pin USB device connectors.
We list the new characteristics of the changed format:
- number of signal pins – 24;
- USB format supported – USB 3.1;
- the implementation mode of third-party interfaces is now supported alternatively;
- the data transfer rate has been increased to a maximum of 10 Gbit/s;
- input current consumption is also increased, the maximum volume is 100 W;
- standard dimensions – 8.34x2.56 mm.

Previous USB types
Before the creation of USB 3.1, which supports USB Type-C, earlier versions were used. It all started with USB 1.0, but it did not enter the device market due to inferior development.
It was replaced by a newer one and current version– USB 1.1. She became the first standard version, which all users quickly got used to.
The data transfer speed was only 12 Mbit/s, and the maximum current consumption was 100 mA.

After it they created the USB 2.0 version. It was presented at the beginning of the first quarter of 2000. There were main parameters increased.
Thus, the transmission speed increased to 480 Mbit/sec. The maximum current consumption has also been increased - 1.8A to 2.5V.

USB 3.0 was introduced to the public at the end of 2008 and immediately won the trust of users, as it brought much more improvements than expected.
To distinguish it visually from other versions, it was made blue. Data transfer speed has increased significantly e – as much as 5 Gbit/sec, but the current consumption did not increase much – 5V by 1.8A.

The newest version is USB 3.1. It was developed and released to the device markets in 2013. She received the most maximum improvements to date.
The updated version featured the highest data transfer speed - up to 10 Gbit/s, and energy consumption increased to 100V.

Comparison of characteristics of USB types
Types of connectors
It is unlikely that many users remember such a connector as USB Type-A. Nevertheless, this connector is still used in PCs.
At the beginning of its existence, this connector was very popular, and appearance USB was almost no different from modern plugs.
The connector was more popular USB Type-B Mini. More often, it is used in modern mobile devices ah, cameras and other devices.
With its help, devices can be easily connected to a PC for data transfer. However, only the physical form was changed, and the standard remained the same - USB 2.0.
In order to somehow make the dimensions of smartphones and other mobile devices minimal, the format was optimized to Type-B Micro.
This connector format is used in 99% of smartphones and tablets based on . Even the very first smartphones have this connector.
The next step was to optimize USB to version 3.0, which, as we already said, introduced significant improvements to speed things up.

Devices using USB Type-C
Devices supporting this format are appearing in large numbers.
In the future it is planned to translate everything Android devices for this format. This will speed up the charging process of the device and the speed of data transfer between the device and PC.

Google has announced that their branded devices will already have connectors of this format.
Thus, it turns out that the devices of this company will no longer be so easy to charge or connect to a PC, because the Type-C format has not yet been fully formed on the market.
You can only purchase a USB adapter cable complete with the device itself, since finding it separately is not yet so easy.
Not all stores, which are most often within walking distance from us, are able to purchase such peripherals for sale.
It all follows from this that peripheral wires with a Type-C connector will be available for now only in specialized stores, and only if they are available.
However, there are companies that are already launched the production of USB hubs with Type-C support. For example, the Promate device is .
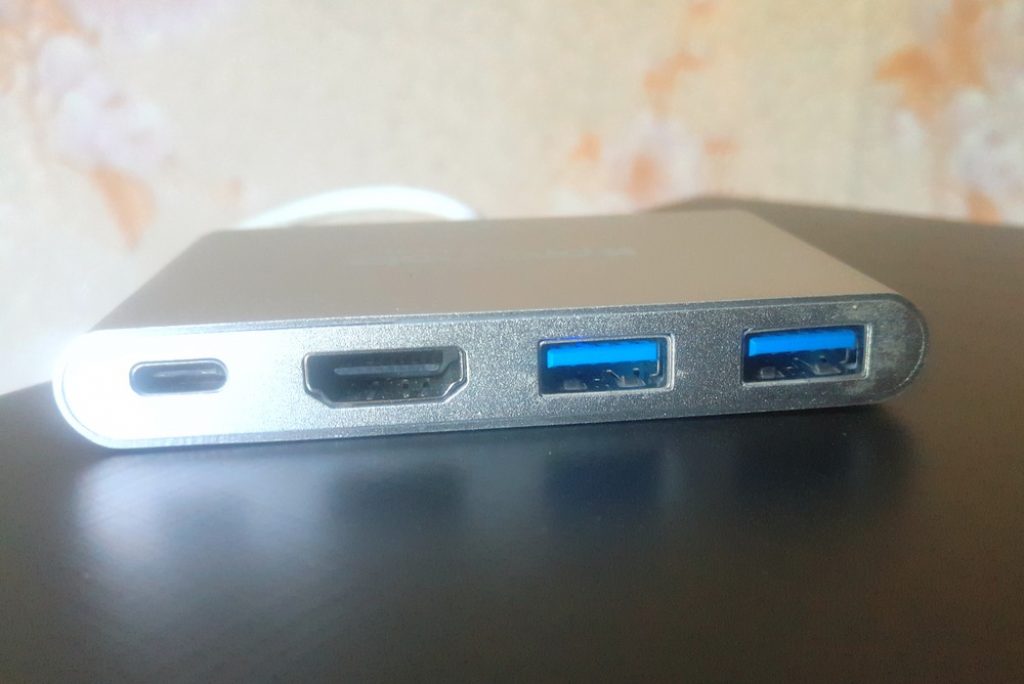

Such a device has several outputs at once - USB 3.1 Type-C with a charging port, two USB 3.0 ports and a 4K HDMI port.
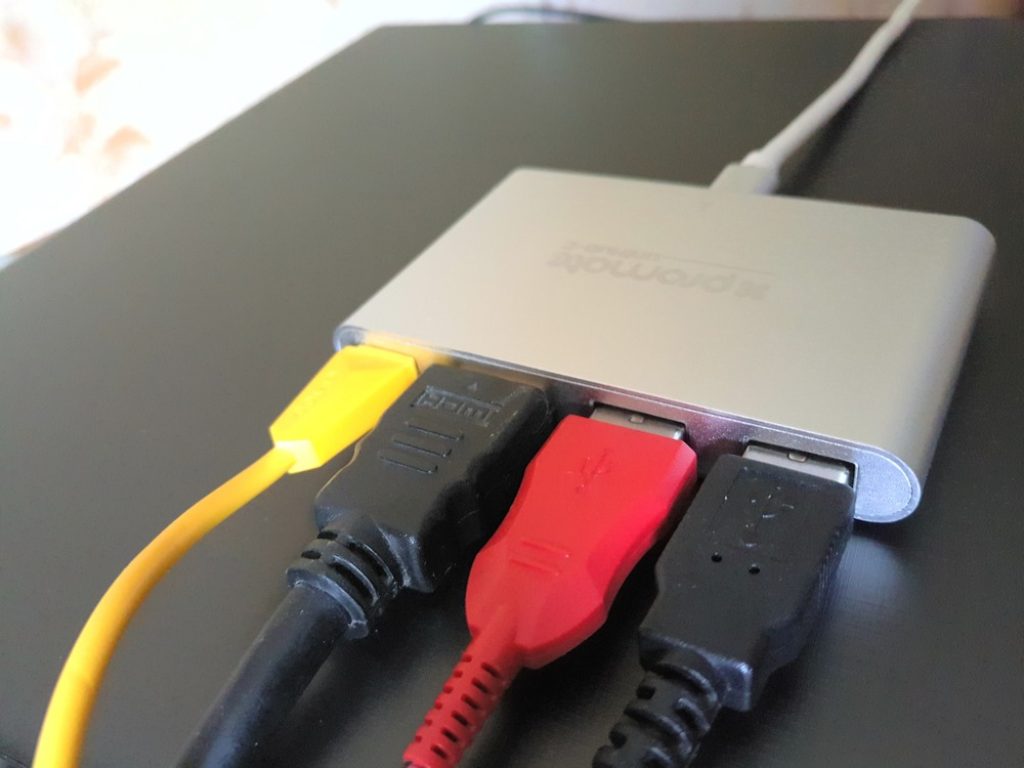

Key Features
- Allows you to charge your MacBook and at the same time be connected to USB 3.0 and HDMI devices
- The HDMI adapter allows you to connect a computer or laptop via USB 3.0 to a TV or any device that supports 4K resolution.
- USB 3.0 connection from either side.
- The hub is capable of working with last generation computers and smart devices that support USB Type-C ports.
- USB voltage - 5V, 900mA, data transfer rate - 5Gbps, support Windows 10/8/7 / Vista / XP, Mac OS X 10.2 (and higher)
Versatility. This format Suitable for absolutely any version of USB. In this case, even USB1 will do, but it’s worth considering that data transfer speed and energy consumption will be minimal.
- Price. The cost of cables and adapters is quite high compared to regular USB cables.
- Unpopularity. Insufficient support from phone and laptop manufacturers.
conclusions

Thus, we learned that many manufacturers are already beginning to transfer their new developments to this format.
It is noteworthy that USB Type-C is set to replace the 3.5mm headphone jack, which greatly upsets many users. Whether this format will take root or not, we will see after a while.
We suggest watching the video to finally understand what USB Type-C is:
Why does a smartphone need USB Type-C? What is USB Type-C and what are its advantages?
What is USB Type-C? Let's look at the example of Promate uniHub-C
The process of mass implementation of the USB interface in PCs and peripheral devices ah began in the late 90s of the last century. Just a few years have passed, and USB has become the de facto standard for connecting peripheral devices, practically displacing other solutions - such as serial and parallel ports, PS/2, etc.
Moreover: the matter is not limited to computers and peripheral equipment. The convenience, ease of connection and versatility of the USB interface have contributed to the spread of this solution in other areas - in particular, in mobile devices, household audio and video equipment, automotive electronics, etc.
Since the process of improving PCs, mobile devices and other equipment is ongoing, from time to time there is a need to refine the USB interface in order to improve key characteristics (in particular, throughput), expand functionality, introduce new connector sizes, etc. All this allows you to adapt the existing solution to the changing needs of the industry.
One of the most notable innovations in recent years is the introduction of the SuperSpeed mode, which appeared in the USB specification version 3.0. The final text of this document was approved at the end of 2008, and over the next couple of years this decision became widespread.
However, a lot of time has passed since then, and the time has come for further improvements. In the coming year, the IT industry and you and I will see a number of, without exaggeration, revolutionary innovations. We will talk about them in this review.
SuperSpeedPlus Mode
In the summer of 2013, the USB specification version 3.1 was approved. The main innovation that was legalized this document, became the SuperSpeedPlus mode, which allows you to double the bandwidth of the USB data transfer bus: from the previous 5 to 10 Gbit/s. For compatibility with older equipment, it is possible to operate in SuperSpeed mode (up to 5 Gbit/s). Thus, a USB 3.1 connection will allow (at least theoretically) to transfer data at speeds in excess of 1 GB/s and practically reach the HDMI version 1.4 interface (whose bandwidth is 10.2 Gbit/s).
What does this mean in practice? A bandwidth of 10 Gbps is quite enough to broadcast high-definition video (Full HD) with a frame refresh rate of up to 60 Hz or stereoscopic recordings in a similar resolution with a frequency of up to 30 Hz. Accordingly, USB 3.1 can be considered as a full-fledged alternative to specialized interfaces (such as DVI and HDMI) for broadcasting video signals high resolution from PCs and mobile devices to monitors, projectors and other devices.
USB Type C connector
One of the revolutionary innovations that will affect the PC sphere, as well as peripheral and mobile devices in the near future, is the introduction of a new type of USB interface connector. The specification for USB Type C plugs and sockets was developed by the USB 3.0 Promoter Group, and the final text of this document was approved in August 2014. The design of USB Type C connectors has a number of important features that it makes sense to talk about in detail.

Firstly, USB Type C plugs and sockets are symmetrical in shape. In a USB Type C socket, the plastic tab is located exactly in the middle, and the contact pads on it are located on both sides. Thanks to this, the plug can be connected to such a socket either straight or inverted by 180°. This will greatly simplify the life of users, who will finally be freed from the need to determine the correct orientation of the plug at random (which is especially important when connecting cables to system unit installed under the table).

Secondly, the USB Type C specification requires the use of symmetrical cables, which are equipped with the same plugs on both sides. Accordingly, the sockets installed on the host devices and on the peripheral equipment will be the same.

And thirdly, the USB Type C connector will not have mini and micro versions. It is expected that USB Type C sockets and plugs will become common for desktop and laptop PCs, peripheral equipment, household equipment, mobile devices, power supplies, etc. Accordingly, to connect devices of any type you will need only one unified cable.

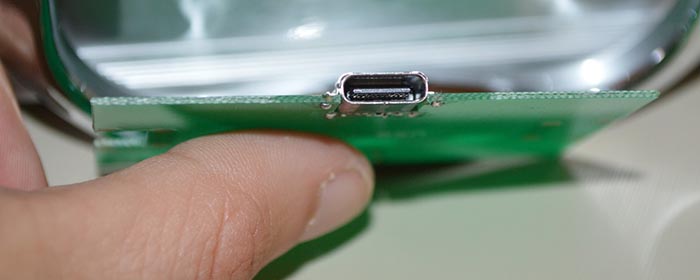
The dimensions of the USB Type C socket are approximately 8.4x2.6 mm, which allows you to easily place it in the case of even small-sized devices. There are several design options for sockets for surface mounting printed circuit board, and in a special cutout (the latter option allows you to reduce the thickness of the device body).
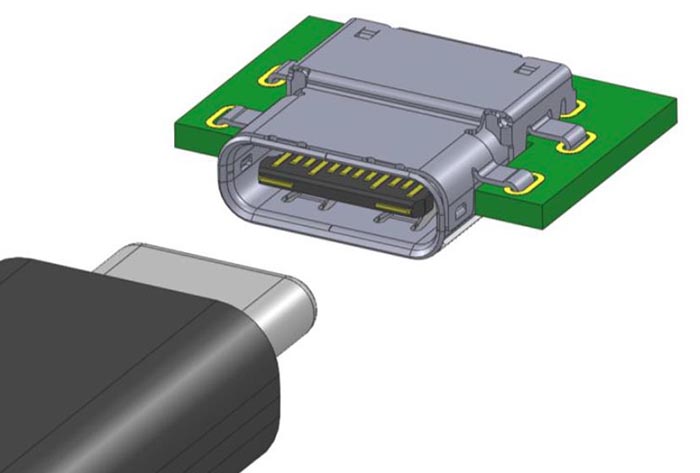
The design of USB Type C plugs and sockets is designed for 10 thousand connections and disconnections - which corresponds to the reliability indicators of USB connectors of currently used types.
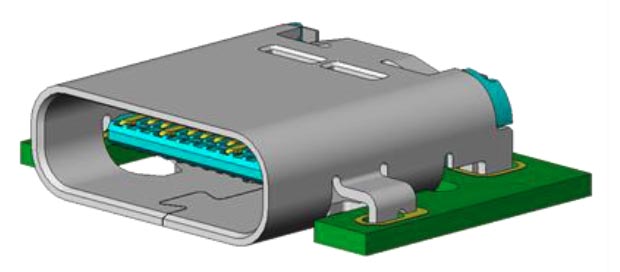
The first public demonstration of USB Type C connectors and cables took place at the 2014 IDF Fall Forum, which took place in early September in San Francisco (USA). One of the first mass-produced devices equipped with a USB Type C connector was the tablet announced in mid-November.
Of course, the physical incompatibility of the USB Type C connector with older types of outlets is not the best news for end users. However, the developers from USB 3.0 Promoter Group decided to take such a radical step in order to expand functionality USB interface, and also create a foundation for the future. To connect new devices to equipment equipped with older types of connectors, adapter cables will be produced (USB Type C - USB Type A, USB Type C - USB Type B, USB Type C - microUSB, etc.).
USB Power Delivery 2.0
One of the reasons for the current popularity of the USB interface is the ability to transfer not only data, but also power over one cable. This allows you to simplify the connection procedure as much as possible and reduce the number of wires used. When working with mobile devices, this property of the USB interface makes it possible to transfer and synchronize data from a PC, and at the same time recharge the gadget’s battery by connecting just one cable. The same can be said about low-power peripherals. Thanks to the ability to transmit power via an interface cable, we have long been freed from the need to use external blocks power supply for some peripheral devices - in particular, flatbed scanners, low-power speaker systems, etc. Due to this, it was possible to reduce not only the number of wires on the desktop, but also the occupied sockets under it.
However, the rapid development of mobile devices in recent years has led to a significant change in the requirements not only for the bandwidth of the data bus, but also for the parameters of the power supply supplied via a USB connection. To charge low-power devices (such as MP3 players or wireless headsets), a current of 500 mA is quite sufficient (and this, remember, maximum value for standard USB ports versions 1.1 and 2.0). However, for normal charging modern smartphones and tablets require power supplies capable of delivering a current of 2 A or more.
A similar situation is observed in the segment of peripheral devices. Transmitted by USB power quite enough to provide power to a 2.5-inch external hard drive or desktop flatbed scanner with CIS type sensor. However, supplying electricity to a small jet printer or, for example, an LCD monitor, the USB interface does not even allow version 3.0 (and in it the maximum current was increased to 900 mA per port).
In order to expand the capabilities of the USB interface to provide power to external devices, the USB Power Delivery 2.0 specification was developed. This document regulates the supply of power to devices with a power consumption of up to 100 W, and in any direction - both from the host device to the peripheral device, and vice versa. For example, a laptop will be able to receive power from a monitor to which it is connected via USB.
Of course, the ability to supply power to external devices limited by the design features of a PC or other device that acts as a power source. That is why the USB Power Delivery 2.0 specification provides three profiles - for devices with power consumption up to 10, 60 and 100 W. In the first case, the supply voltage is 5 V, and the maximum current in the load circuit can reach 2 A. The second profile involves using a supply voltage of 12 V, and the third - 20 V. The maximum current in the load circuit in both cases is limited to 5 A.
It should be noted that in order to power a powerful load, both devices must support the appropriate USB Power Delivery 2.0 profile. Obviously, the maximum power will be limited by the capabilities of the device acting as a power source. There are other aspects that need to be kept in mind.
If the current in the power circuit does not exceed 2 A, USB connectors of any currently existing types can be used to connect devices. Connecting a more powerful load is only possible through USB Type C connectors (which were already mentioned above) and the corresponding cables. It is also necessary to pay attention to the fact that, unlike USB Type C connectors, the design of standard cables is designed for a maximum current of 3 A. Thus, to connect a more powerful load you will need a special cable.
The introduction of the USB Power Delivery 2.0 specification will significantly expand the ability to transfer power via the USB interface bus. The implementation of this solution in the future will make it possible to use USB ports desktop computer for recharging not only smartphones, tablets, etc. gadgets, but also mobile PCs - netbooks, laptops, etc. In addition, the range of peripheral devices will be significantly expanded, which can receive the current required for operation via the USB interface bus and, accordingly, do without separate power supplies. This list will be supplemented by LCD monitors, active speaker systems, etc.
Alternate Modes
Another important innovation that will become available with the transition to using the USB Type C connector is support for Functional Extensions. A special case of functional extensions are the so-called alternative modes (AM). With their help, manufacturers will be able to use the physical connection of the USB interface to implement the specific capabilities and functions of certain devices.
For example, the alternative Audio Adapter Accessory Mode allows you to use the physical connection of the USB interface to broadcast analog sound signal on headphones, external speaker systems and other equipment. To a device equipped with a USB Type C connector and supporting Audio Adapter Accessory Mode, you can connect headphones or an external speaker through a special adapter equipped with a 3.5 mm mini-jack jack.
Support alternative modes is one of the properties of a new class of USB devices - USB Billboard Device Class. Manufacturers who intend to develop their own alternative modes will need to obtain a unique identifier (SVID) from the USB-IF organization.
In 2014, the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA) developed the DisplayPort Alternate Mode specification. This solution allows you to use two pairs of USB cable conductors (TX+/TX– and RX+/RX–) to broadcast an uncompressed digital AV stream. At the same time, the possibility of data transmission (in Low Speed, Full Speed and Hi-Speed modes via the D+/D– pair), as well as power supply via the same interface cable, is retained. Thus, by connecting two devices that support DisplayPort Alternate Mode, you can broadcast audio and video signals, transfer data in both directions at speeds of up to 480 Mbps, and also supply power - all over one cable!
Devices that support DisplayPort Alternate Mode can also be connected to equipment that is not equipped with USB ports Type C (in particular, monitors, TVs, etc.). Specification this mode provides options for connecting to DisplayPort, HDMI or DVI interfaces through special adapters.
In November 2014, the MHL consortium announced the development of an alternative mode, MHL Alternate Mode, which will allow broadcasting uncompressed audio and video signals (including high and ultra-high definition) from mobile devices equipped with a USB Type C connector to external equipment (monitors, TVs, projectors etc.) via a standard USB cable. Specialists from Nokia, Samsung Electronics, Silicon Image, Sony and Toshiba took part in the development of the specification.
The introduction of alternative modes will significantly expand the functionality of the USB interface and greatly simplify the procedure for connecting devices of various types.
Conclusion
Completing this review, let us once again list the most important innovations, the process of introducing them into mass-produced devices equipped with USB interface, will begin in the near future.
The SuperSpeedPlus data transfer mode described in the USB specification version 3.1 will increase the maximum throughput of this interface to 10 Gbps. Of course, this is less than HDMI 2.0 and Thunderbolt 2 (which, remember, provide data transfer speeds of up to 18 and 20 Gbps, respectively). However, 10 Gbps is quite enough to transmit uncompressed high-definition video signals with frame rates up to 60 Hz. In addition, representatives of USB-IF stated that in subsequent versions of USB it is quite possible to increase the throughput to 20 Gbit/s - fortunately, the design of the new USB Type C connectors and the corresponding cables contains a certain margin for further development.
The introduction of support for the USB Power Delivery 2.0 specification will significantly increase the maximum power transmitted over a USB connection. Accordingly, the range of peripheral and mobile devices that will be able to receive power via an interface cable will be expanded. The widespread implementation of this solution will significantly reduce the number of cables and external power supplies used, reduce the number of occupied outlets and use electricity more efficiently.
The advent of USB Billboard Device Class devices with support for alternative modes will open up completely new possibilities. At the same time, each manufacturer will be able to create their own modes for devices of certain types, taking into account their specifics.
Of course, one of the revolutionary changes that will affect the spheres of PCs, peripheral and mobile devices, household equipment, etc., will be the introduction of the USB Type C connector, which (as expected) will replace the USB plugs and sockets of currently used types. On the one hand, the transition to a single connector for devices of all types will significantly simplify the lives of users and reduce the number of required cables to a minimum. But, on the other hand, the industry and users will have to go through a very difficult and painful process of generational change. Previous solutions were distinguished by maximum compatibility: the design of conventional USB plugs Type A and Type B allows you to easily connect them to the corresponding sockets of version 3.0. Now, to connect devices of different generations, you will have to use additional devices.
The USB 3.1 specification provides backward compatibility with earlier versions of the interface. However, with the advent of serial devices equipped with a USB Type C connector, users will inevitably face the need to purchase adapters and adapters that provide the ability to connect new devices to older equipment with USB Type A, Type B and other types of sockets. Considering that currently about 4 billion devices equipped with a USB interface are produced annually, this problem will be very relevant for at least the next five to six years.
It should also be noted that it will be possible to fully realize the potential of the USB version 3.1 interface and the USB Type C connector in practice only when users accumulate at least a minimum amount of equipment equipped with these new products. Obviously, in the case of interaction between two devices of different generations, the functionality and maximum bandwidth of the interface will be limited by the characteristics of the USB controller of the older device.
According to experts from the well-known Taiwanese resource DigiTimes, serial models of PCs, as well as mobile and peripheral devices equipped with a USB 3.1 interface and USB connectors Type C will go on sale in the first half of 2015. In turn, leading developers operating systems and software have already announced their readiness to release updates to implement USB 3.1 support in their products.
Earlier this month, Apple's new guru Tim Cook announced a number of new products, the most interesting of which was an improved version MacBook Air. During his talk, Cook focused too much on features and functions that are no longer as unique as Apple would have us believe. So one of the Air's most key and intriguing innovations, a technology with the potential to profoundly change the world of mobile devices over the next few years, has gone largely unnoticed. We're talking about the new USB Type-C connector and the exceptionally wide range of capabilities it offers.
What is USB Type-C?
As the name of the standard suggests, it is an evolutionary refinement of the well-known Universal Serial Bus (USB) format, which is currently one of the most common interfaces in the field of computer peripherals and mobile technologies. Type-C doesn't just provide backwards compatible With previous versions USB, but also combines them in a new, unique way. So one cable (interface) can transmit data, electricity and even video.


The size of the Type C connector is smaller than the chronologically oldest (and most widespread) Type-A standard, but slightly larger than the microUSB (Type Micro-B) format. Unlike its predecessors, however, new standard is more universal - the Type-C cable connector can be connected to the port on either side and there are identical plugs on both sides of the cable. At the same time, this limits backward compatibility with existing Type-A and Type-B formats. In other words, you will not be able to connect a Type-A or B cable to a Type-C port and vice versa.
But the Type-C port can be easily configured so that it can perform many different functions. For example, USB cable Type-C can easily transmit an HDMI or DisplayPort signal, although this moment this possibility is still purely theoretical.
Type-C? Isn't this USB 3.1?
Definitely not! USB 3.1 is latest version data transfer standard, which (at least in theory) should double the peak data transfer rate from 5 Gbps (USB 3.0) to 10 Gbps. In addition, 3.1 is fully backward compatible with previous versions of the standard: 3.0 and 2.0.
In this vein, the Type-C module could offer both USB 3.1 and some of the older standards. For example, USB adapter Type-C Digital AV Multiport, which Apple will offer as an additional accessory for the new MacBook, according to the specification supports “USB 3.1 Gen 1” with a theoretical maximum throughput 5 Gbps, i.e. almost identical to the USB 3.0 standard. And one of the first devices with support for Type-C, which, unlike the MacBook 2015, is already available on the market, the Nokia N1 tablet, uses even more old usb 2.0 for data transfer and charging.
Type-C = USB Power Delivery?
Not again. Power Delivery is part of the latest USB standard specification and is the ability to deliver up to 100W of power to any connected device, although it can also be used to transfer data. For comparison, the most popular now USB standard 2.0, which is used in almost all smartphones and tablets, provides up to 2.5 W of power. This is one of the reasons why you can't charge most modern laptops via USB - they require voltage between 20 and 65 W. However, with the new Power Delivery connector, you can not only safely charge your future laptop via USB, but at the same time watch 4K video transmitted to an external monitor connected with the same cable.
So what is the connection between Type-C and USB Power Delivery? Here we are again talking about the theoretical possibility of support. In other words, the Type-C connector can offer USB capabilities Power Delivery, if the manufacturer of the corresponding module provides this. Otherwise, just because you have a Type-C cable doesn't mean it supports Power Delivery as well.
Type-C today? Or rather tomorrow?
Despite its numerous, beautiful promises, at the moment new MacBook it's still just a bunch of brilliant features. Unlike Apple, however, a number of companies are already offering devices with Type-C support on the market. The first was Nokia with the aforementioned N1 tablet.

SanDisk recently revealed its first flash drive based on the new standard. However, to ensure backwards compatibility with older USB formats, this 32GB device also includes an additional Type-A connector - a practice that will likely be seen a lot during the transition to the new standard.
As part of the January CES 2015 exhibition, a prototype of a docking station for laptops was demonstrated, which offers a Type-C connector for charging and video output to an external 4K display. And LaCie just recently announced that it intends to offer a series of Type-C external hard drives with capacities of 500 GB, 1 and 2 TB.
Have a great day!
