Barcode scanners - work
Barcode scanners can significantly increase the productivity of the store staff in the event that the point of sale a large number of product names and (or) a large flow of buyers.
Entering goods using a barcode scanner allows you to eliminate duplication of identical goods (when several identical goods of different receipts are entered into the program under different codes). In this case, accounting becomes more streamlined and simpler. Also, entering goods using a barcode scanner is much faster (sometimes up to 2 times).
To sell a product, you need to enter the product and the quantity of the product to be sold. Standard way is to enter the product code.
To enter a product code, you need to know this code. There are many stores that, when entering receipts, assign internal (store) codes to goods - usually 5-digit or sometimes 6-digit (if the number of items is more than 90,000 and 5-digit ones are over). This code is stuck on the product, which allows you to quickly sell.
A similar method (gluing product codes) allows you to streamline accounting quite well (if codes are pasted on all products, sales of goods are carried out quickly).
If the codes are not pasted, when selling goods, the seller will have to use the search by price / name / article, etc. - which is quite effective and in 99% of cases allows you to find the goods, but takes a lot of time. Therefore, in stores with big amount product names without using a barcode scanner, it is recommended to assign an internal store code to each product (and stick it on the product).
Quite often, ready-made barcodes are already pasted on the goods. If the store has a barcode scanner, the step of sticking internal 5-digit codes on products can be omitted, which facilitates the process of entering goods.
Entering goods
When entering barcodes manually, you can use the F10 key instead of the barcode scanner.
So, how is the entry of goods:
We scan the goods. If there is no product with such a barcode, the fields (for the first time) will need to be filled in manually. If the product with this barcode has already been entered, the program will automatically fill in some of the fields:

It remains only to enter the quantity, the amount of the cost and the program will calculate the cost and price itself (based on the standard markup set in the program settings). The price can be edited manually.


So, the goods are listed along with barcodes. After the session where the goods were entered, the goods will be available for sale, and the barcodes will be available for use in retail sales. You can see which barcodes are entered for a particular product in the product card (F1 key):

You can also configure the display of barcodes directly in the list when entering goods:
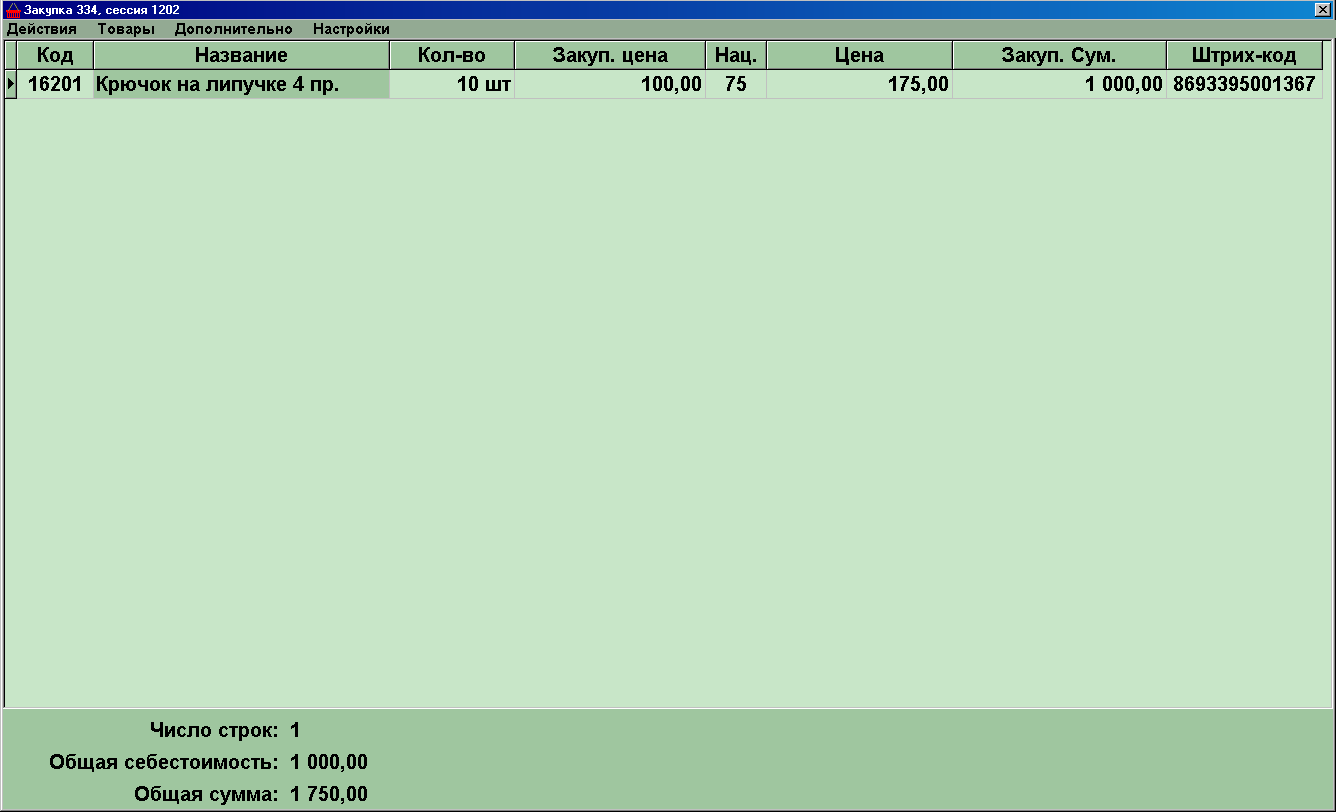
If there are no ready-made barcodes on the purchase goods, there are several options:
1) Paste on these goods internal, store codes of goods (those that are 5-digit or 6-digit), so that sellers can also identify them when selling.
2) After entering for session products that do not have barcodes, barcodes can be automatically generated by the program (Advanced-->Generate barcodes for session products that do not have barcodes"). Then these barcodes can be printed for sticking on goods both on a conventional printer and on a label printer.In this case, it will be much more efficient instead of printing barcodes.
The downside is that for a computer and a program, scanning is equivalent to entering characters from the keyboard. Therefore, before scanning the product, you need to stand on a certain field. The program interface (section "Retail sales") when using a keyboard barcode scanner will look like this:

The seller practically does not need any additional actions, except that before scanning the goods, you need to place the cursor on the "Barcode" field. If several products are being scanned, the cursor jumps automatically:
Since the scanner is keyboard-based, the barcode can also be entered as follows: press F10 and scan the item. The barcode will be entered into the field as if it were entered manually (because for the program the keyboard scanner is just an imitation of keystrokes on the keyboard).
An online store based on the "1C-Bitrix: Site Management" platform allows you to keep quantitative inventory records. To maintain a warehouse and generate a minimum set of documents, you do not need to purchase additional programs.
Warehouse quantitative accounting
The warehouse accounting functionality allows you to register receipts and write-offs of goods to a warehouse, transfer between warehouses, and keep a record of balances. You can take into account goods by barcode and save a lot of your time when shipping or adding goods to the catalog.
Everything for convenient work with goods and balances:
- Documents - all in one section, there is filtering
- Suppliers - section of the online store
- Arrival and shipment of goods with barcodes
- Fast movement of goods to points of issue and warehouses
- All actions: return of goods, write-off of goods, input of balances
You will quickly find all warehouse documents, because they are collected in one special section "Documents". You can easily select the ones you need by using the filters. 
4 main documents:
- Arrival of goods to the warehouse
- Moving goods between warehouses
- Purchase returns
- Write-off of goods
With the help of these documents, you will make all the necessary warehouse transactions with warehouses, with the balance of goods in warehouses, etc. The section is an archive of all inventory transactions.
"Suppliers" - a special section in which you will maintain a list of physical and legal entities with whom you actively cooperate, who you need to contact to obtain materials, components, etc. 
You will quickly find any supplier whenever you need one. It is enough to set his e-mail, phone number, TIN or other known data in the filter.
You can quickly add products by barcode - manually or using special scanners (readers). It is enough to place the mouse cursor in the desired input field, point the scanner at the barcode, and 13 digits of the code will appear in the text field. 
If you receive an item that has already been scanned, you will not have to start the item again.
When you release the goods, you will be sure that you have taken exactly the goods that should be shipped. The barcode scanner confirms the correctness of the choice of goods, thereby preventing the store from losing money due to possible errors.
Warehouse goods management
You have access to all possible actions for managing goods and their balances in warehouses: returning goods, writing off goods, entering balances and much more.
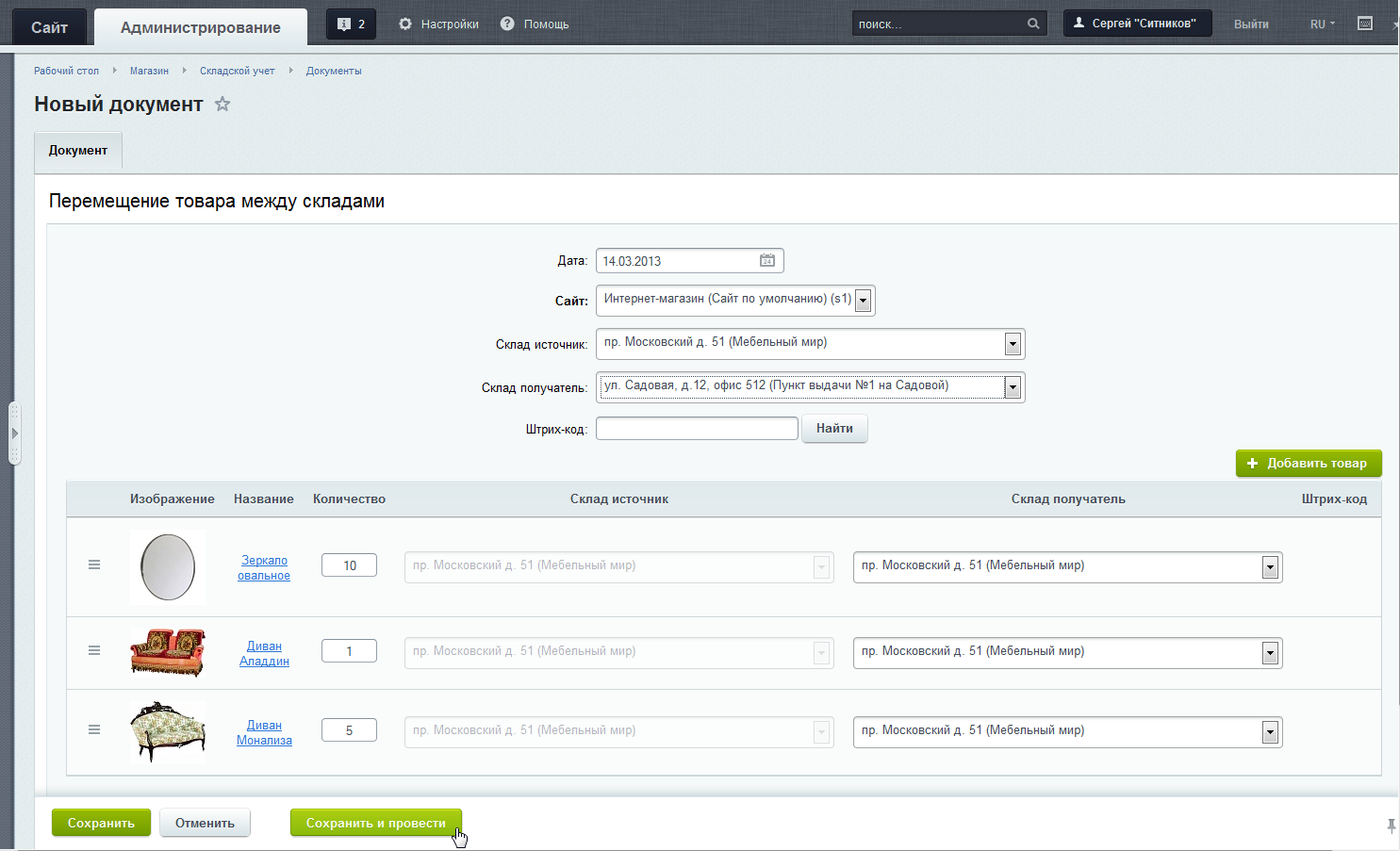
For example, you can:
- quickly move goods from the main warehouse to points of issue
- transfer goods from one point to another
- find out how much and what kind of goods you have in stock
- view the history - when, what goods, how much and who shipped to warehouses
You can build a report for each of your warehouses.
For example, to view the balance of goods in a warehouse, and quickly ship for him those that run out. And you do not need to request this information from the storekeeper.

2 ready reports:
- The balance of goods in warehouses
- Stocks of goods
With the report "Stocks of goods" you are always aware of the balance of goods in warehouses. The filter allows you to select a store, period, product or product category.
For each of the reports there are special filters that can be adjusted by selecting the desired fields for sorting. You can export any report to Excel.
Multi-warehouse
In the online store, you can create several warehouses and set the number of goods in each.

Show your customers how much product you have in stock. In the catalog, the client will see how many products are in stock in a particular store. This is especially convenient for the client if he has chosen the "self-delivery" delivery method.
Multiple storage is integrated with 1C. Thanks to this, you can unload the balances for each of the warehouses from 1C and present this information to site visitors.
Use of barcodes for accounting.
Almost all manufacturers put a barcode on the product packaging. A barcode scanner allows you to read this code and transfer it for further processing, for example, to an invoice for the sale of goods.
The pharmaceutical audit program allows you to implement using a barcode scanner, download barcodes from electronic invoices or enter them manually using a barcode scanner, print barcode labels using specialized printers or on ordinary sheets.
Which option to use: manufacturer's barcodes or your own?
The Farm Auditor program supports two options for working with barcodes:
1) The barcodes of the manufacturer are used, already applied to the packaging with the goods.
2) Inside the pharmacy, their own unique barcodes are used.
Option 1: Use manufacturer's barcodes.
The barcodes printed on the packaging with the goods are usually indicated by the supplier in the electronic invoice and will be loaded into the form auditor program when loading the electronic invoice. If there is no barcode in the electronic invoice, it can be maintained using a scanner in the incoming invoice.
Option 2. The pharmaceutical audit program itself automatically generates its own unique barcodes when uploading an electronic invoice.
For each line in the invoice will be automatically generated new touch code. If such a product has already arrived before, then the barcode generated by the program earlier will be used for it.
Both accounting methods have their advantages and disadvantages. In the second option, when accounting by own barcodes, it will be necessary to print and stick labels with barcodes; for this, it will be possible to use a special printer for printing barcode labels.
In the first option, when accounting for the manufacturer's barcodes, there is no need to print barcodes for each item, however, for some suppliers, you will have to indicate barcodes when goods arrive using a scanner. Sometimes a situation arises when manufacturers apply the same barcode to different products. When selling such goods, the pharma auditor will display a warning and prompt you to select the correct product from the list.
If you're just getting started with barcodes, try starting with the manufacturer's barcode accounting option. This method is used in the program farm - auditor by default. You can switch to using your own barcodes at any time.
To switch between barcode accounting modes:
- Select the menu Tools - Options. The settings window will appear.
- In the settings, select one of the options for using barcodes: Use manufacturer's barcode or Create your own.
- Click the OK button for the settings to take effect.
Receipt of goods. Manual and automatic entry of barcodes in the incoming invoice.
If in the settings of the pharma-auditor program it is specified to create your own barcodes, then in the process of uploading a new electronic invoice barcodes for all products will be created automatically, all that remains is to print them. If such a product has already arrived before, then the barcode generated by the program earlier will be used for it.
If the manufacturer's barcodes are used and there is no information about barcodes in the electronic waybill, then, in this case, upon receipt of the goods, you will have to specify the barcodes manually using a scanner.
Realization of goods using a barcode scanner.
To sell goods using a barcode scanner:
1) open the invoice.
2) swipe the scanner over the barcode printed on the package. The pharmaceutical audit program will find a product with desired barcode and add it to the invoice.
3) If you read the barcode of the same product again, then the number in the column quantity of product in will increase by 1.
4) After all the necessary goods are added to the invoice, to complete the sale, click the Quick sale button or the F2 button on the keyboard.
If the program cannot find a product with the desired barcode, then the message "Item with this barcode was not found" will be displayed.
If for some reason several products with the same barcode are found, the Pharm program will display a message with a list of found products and prompt you to select the right one.
Inventory. Search for the desired product using a barcode scanner.
When inventorying a product, it is often necessary to find the right product among a large list with leftovers.
To search for goods by barcode in the inventory document, it is enough to scan the barcode printed on the package with the goods. The pharmaceutical audit program will find the desired product and place the cursor on the quantity column. It remains to enter the required amount of goods from the keyboard.
The barcode was invented in 1951 and, it would seem, has already firmly entered our lives, however, as my practice shows, many users do not know what it is, even many IT specialists do not know what a barcode scanner and a data collection terminal are . And it seems that all this is difficult to understand and implement, but in fact it is quite simple. And one of the goals of this article is to show how easy it is to work with barcoding, to clarify the logic and sequence of operations in an automated warehouse.
This article does not pretend to be true: on some projects, the issue of automation is solved differently than the option given in the article. My company had about 30 such projects where it was necessary to bring the warehouse to an efficient, working condition. And I developed a work scheme that became for me the standard for warehouse automation. On the one hand, it is simple, on the other hand, it meets the basic requirements.
The warehouse operation scheme presented in the article is scalable, but the essence remains the same in any case. This scheme of work is suitable for both reseller companies and manufacturing companies that have a warehouse and keep records of goods or materials.
We will talk about warehouse accounting using special equipment, software and hardware. I will tell you what devices are used, at what point, how to act in certain situations.
This article is intended primarily for IT professionals, for programmers and for those who have at least some technical skills. Firstly, the article uses terms that are often not clear. ordinary users. Secondly, there are also BPMN notations describing business processes that will be understandable to a specialist, but not to a user. In addition, lately IT specialists who opened their stores or advised their clients contacted me three or four times. If you are going to open your own business, which requires a warehouse, or provide advice on the implementation of programs and equipment, this article will be useful to you.
So, let's begin.
Why do you need warehouse automation?
Now my company is often approached by clients regarding implementation, increasing sales, optimizing processes, etc.But at the analysis stage, I, as a rule, also look at how the warehouse works (usually, companies always have a warehouse). And if I see any "failures" in the work of the warehouse, I will certainly notify the company's management.
What is the point of implementing a CRM system and a sales increase system if the goods are not accounted for correctly? What if the client you worked with so carefully, applying innovations, ends up ordering a product from you that will be short or oversorted and out of stock? Does that mean you did a bad job?
Usually the warehouse of small and medium-sized enterprises is at the most primitive level. Warehouse accounting is carried out manually. At the same time, the accuracy of accounting leaves much to be desired. Based on my experience, I will say that manual inventory management is much more expensive for an enterprise than its automation. At manual method collecting and entering data, the information that is needed is often unreliable. And an increase in the cost of servicing the product leads to an increase in the cost of the product itself.
Warehouse automation is a relatively simple technology, the implementation of which does not require expensive equipment or software. Thus, if automation does not directly affect the increase in profits and sales volumes, then it definitely reduces the current costs of the enterprise.
Product barcoding
In accounting systems, it is mandatory to enter data on the barcodes of the item. Otherwise, your accounting system will not recognize the product, and you will not receive a full account. When filling in information about a new item item, there are two options for generating a barcode:- entering a barcode using a scanner - this option is relevant for companies involved in the sale upon receipt of goods with their own barcode
- automatic generation of a barcode in the accounting system - this option is relevant for manufacturing companies and reseller companies in case the goods are received from the supplier without a barcode
Warehouse accounting equipment
Warehouse automation requires special equipment. You will need:- barcode scanners for receiving, assembling and shipping goods;
- data collection terminals for inventory;
- label printers for printing, if necessary, own product labeling
1. Barcode scanner
A barcode scanner is a compact device whose main function is to read information from a product label and transfer it to an accounting system. The barcode scanner is used during the assembly of goods, upon receipt of goods and the sale of goods to the client.
Scanners are different technical specifications: single-plane, multi-plane, etc. They differ in quality, speed, reading range and other indicators.
Barcode scanners are wired and wireless. I recommend using wireless in order not to limit the employee's mobility and not be tied to a place. Yes, they are much more expensive, but they are very convenient.
2. Data collection terminal
Data collection terminals are a specialized device, which is a portable computer with a built-in barcode scanner.
The terminal is intended primarily for the rapid collection, processing and transmission of information about the goods during the inventory, but can also be used when the goods arrive and the goods are assembled for shipment to the client.
The data collection terminal has a beam for scanning; a monitor on which we can see which product has been scanned; and a keypad for entering quantity information and for executing various commands.
With the help of TSD, you can either scan the entire product in a row, or read the barcode of a single item and manually enter the quantity of this product.
The terminal, unlike the scanner, not only reads the barcode, but also accumulates information about the scanned barcodes in its memory. Naturally, there are more expensive devices that can communicate with the database and provide information about the balance of goods, etc. But we are considering the simplest option TSD when we just need to take inventory.
TSDs are different, their cost varies from 25 thousand rubles to exorbitant figures (I saw TSD for 250 thousand). The effectiveness of TSD in this case does not depend on the price. Which TSD do I recommend to use? I recommend the simplest one that performs scanning, storing and transferring data to an accounting system. All newfangled Android systems, with a color display and other advanced functionality, require qualified specialists, thoughtful work with this equipment and good software. Yes, such functions are not needed, since they do not affect the final result. So the simpler the better.
Also, when buying a TSD, you need such components as a stand and a spare battery. TSD is such equipment that is quickly removed from production. You bought it, and then you may not find accessories for it, and you will either have to look for them or buy a new one. Therefore, I recommend immediately stocking up on batteries.
Why do you need a stand? It is connected with the accounting system itself, through which data is transferred from the TSD to the system. In addition, equipment usually does not come with USB cable to connect the stand with a computer, it must also be purchased.
Another important nuance, which must be considered when buying a TSD: you can buy one or two stands for four or five terminals. Why? The terminal itself is constantly used during the inventory, while the stand is used for a short period of time to upload and download data from your system to the data terminal in your accounting system. You can also wait, since the unloading itself takes 10-15 seconds, depending on the speed of the terminal. I recommend that clients purchase 2 racks and 5 RTDs per medium-sized warehouse for a quick inventory.
In addition, TSD can be used for admission or implementation. You can scan all incoming goods with the terminal and upload the data to the receipt document in the accounting system.
3. Label printer
A label printer is a device that prints a barcode image onto a label. A label is formed in the accounting system, which is then printed on a printer.
Labels with barcodes must be printed, as I wrote above, on a product that does not have a barcode. This happens if you are a manufacturer of goods, or you received goods from a supplier that do not have a barcode.
What you should pay attention to when buying:
- performance
- label width. If you have a large product and want to print a large label, then you should choose a printer that can print this width.
- conditions under which the device can operate. It often happens that warehouses are located in an unheated room, and equipment is bought for an office, naturally, it will quickly fail due to temperature changes, humidity, etc. Therefore, if you have an unheated warehouse, always consider the conditions in which it can function device.
- thermal transfer labels - printing is only possible with an ink ribbon in mostly black
- thermal labels - printing on thermal labels is carried out by direct heating of selective points of a moving label with a thermal printer head or scales
Now that the goods have been barcoded, the data on the conformity of the item and the barcode have been entered into the accounting system, the equipment has been purchased, we can conduct automated work of the warehouse. Let's consider in detail how this happens.
Automation of warehouse processes
Conventionally, the work of the warehouse can be divided into three processes:- Goods receipt - includes the following operations: capitalization of surplus, receipt of goods from the supplier, receipt of goods from production.
- Storage and accounting of goods - involves inventory of goods, movement of goods between warehouses and premises.
- Delivery of goods - includes various operations of spending goods: write-off for internal needs, write-off of damage to goods, shipment to the client.
Receipt of goods from the supplier.

How is the operation of receiving goods from the supplier?
- We create an order to the supplier, in which we indicate the goods we need.
- The supplier delivers the goods.
- We read the barcodes of the goods one by one with the scanner and enter them into the database in the Goods Receipt document.
We have already talked about this above, but now we will consider the procedure itself in detail. If the goods arrived without a barcode, then there are two scenarios:
- If we have time and we know what product will be without a barcode, we can prepare in advance or print out the required number of labels at the time of receipt, stick them on the product, and then enter the warehouse by scanning.
- If we need to quickly receive the goods in order to have information about the balance in the database and immediately start reserving the goods for customers, we will receive the goods by quantity, but without passing through the scanner. That is, employees count the goods and manually enter data into the accounting system.
We need to remember the rule: if the goods arrived without a barcode, if we have little time and the goods are not very valuable, we can first enter them by quantity, without swiping through the barcode scanner, and then barcode and stick labels.
When sticking labels with barcodes on goods, there is one useful trick. It is very simple, but makes the job much easier:
If you have placed an order with a supplier, and you know how many goods will come, you print the labels in advance. It happens that the goods are either not completely barcoded, or it is known which goods will not have a barcode - you generate barcodes for such goods in advance in the accounting system and print out all the labels for the goods of future receipt. The number of labels must match the number of expected goods.
Then, upon receipt of the goods from the supplier, you can, in addition to counting them, simply stick labels. If there are no labels and unglued goods left, it means that the quantity of goods corresponds to what you ordered. If extra labels remain (this happens), it means that the goods have not been delivered. If there were not enough labels, it means that they brought a surplus or there is some kind of sorting (perhaps they stuck a barcode on the wrong product). In this case, you need to immediately find out where you made a mistake, or that the supplier did not deliver.
So, for posting goods from a supplier or any other posting, you need a barcode scanner and a label printer. Also, the receipt can be made by the data collection terminal: we read all the barcodes with the terminal, and then we load all the information at a time or in parts into the document for the receipt of goods into the accounting system.
After the product is labeled, you lay it out. About address storage, when your warehouse is divided into sections, and you put a certain product in a certain section and mark it in the system - I will not talk here. To use or not to use an address warehouse - everyone decides for himself. But I do not recommend using it in small and medium-sized enterprises, as employees begin to make mistakes, they cannot correctly calculate the area and volume of their warehouse and the like. Therefore, this article will not consider such an option as address storage, serial accounting, and the like. This is scaling, complication of the system, but this does not affect the essence of the work.
After we have accepted the goods, we store them, we must control the goods, keep records of them, make the so-called inventory and, if necessary, arrange the movement of goods.
Storage and accounting of goods in a warehouse
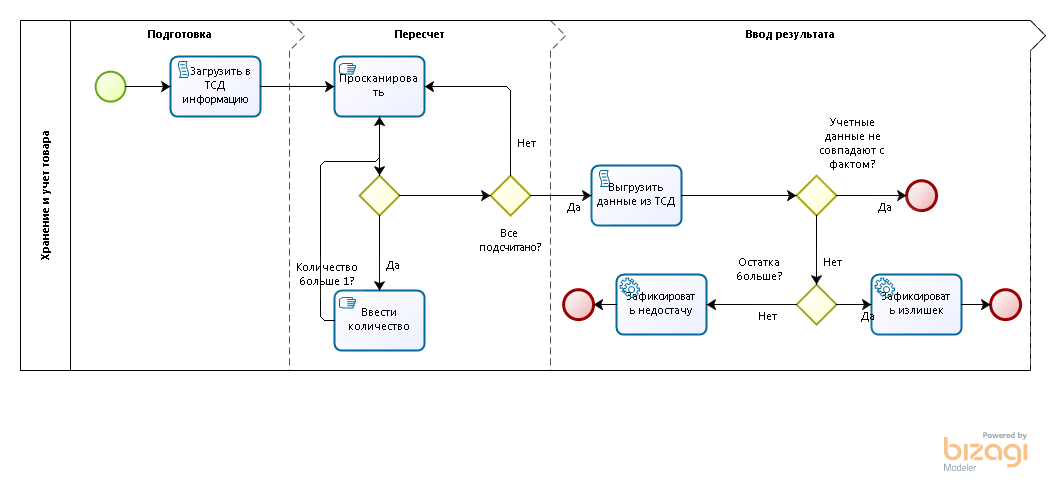
Storage and accounting of goods involves inventory and movement of goods between warehouses and premises. The movement of goods occurs by reading barcodes - here I will not delve into the description. The Transfer document is a simultaneous issue of goods from one source warehouse and receipt to the destination warehouse. You open the Goods movement document and scan the necessary goods into it.
Let's take a closer look at inventory. How does it happen? What equipment is needed for this?
Inventory is a check of the availability of goods on certain date by comparing the actual data with the data of the accounting system.
From my experience I will say that it is wrong to do an inventory on your own. Many companies conduct inventory on their own, arguing that their employees know the product very well, unlike third-party specialists. But this is wrong, because it turns out that the warehouse worker checks himself.
Ideally, if the inventory will be involved third party companies(auditors or 1s-nicknames), or if this is not possible, involve employees of your own company, but from other departments not related to work in the warehouse. Why is it necessary? Because, I repeat, it is impossible for a person to check himself.
There were cases when the inventory (especially if it was the first inventory) was a reason to write off all your flaws, theft, etc. and so on. Especially if a person works for a long time. If, according to the results of the inventory, everything came together, this should make you suspicious, most likely the matter is not clean here, there is a deception of the system by an employee.
I had such a case that the warehouseman “found” the goods after identifying shortages as a result of the inventory. It looked extremely suspicious.
Let me also remind you that the inventory should be carried out on weekends or during non-working hours so that there is no movement of goods. Many companies neglect this, and then look for where the shortage came from.
How is the inventory taking place? An employee or several employees (if there are several employees - the warehouse is divided into sections) read the goods on the racks one by one using the data collection terminal. Each employee goes and scans the goods that he comes across in his section. Then the TSD is installed on a stand and the data is loaded into the accounting system.
Information from the TSD comes in the form of a document Inventory of goods or Recalculation of goods with information about which goods were scanned during this work. Then you need to delete the data from the terminal, after which you can scan the next portion of the data until the entire product is scanned.
What nuances should be taken into account in the automated inventory of goods? If you scan an item in several passes, there is such a problem: when data is loaded from the terminal into the accounting system, the previous data from the Inventory document is deleted.
How do we usually act in such cases? Several Data Inventory documents are created that record who scanned and which rack. Then we take and combine data from several documents into one by copying.
What should the system do next when we have all the data in one document? The system compares the results of the Inventory document with accounting data and provides information on surpluses and shortages. In order for the system to have up-to-date information about the balance of goods in warehouses, following the results of the inventory, you must do the following:
- write off shortages
- capitalize surplus
To summarize, during the inventory, the following actions are carried out:
- scanning goods
- load this data into the Inventory document,
- the system automatically compares the accounting data with the actual ones, and gives us information about the need to create the Write-off and/or Posting of Goods documents.
Issuance of goods

Now consider the option of shipping goods to the client. Typically, the scheme for selling goods to a client looks like this:
- sales manager placing customer order
- after payment for the goods (or meringue, if the company sells goods on credit), the manager draws up a document for the sale of goods
- the warehouse collects and releases the goods ordered by the customer
And with this scheme of work, the warehouseman informs the manager about the shortage of goods after the fact.
- the manager reserves the goods according to the customer's order
- the manager gives the warehouse the task to collect the order
- Based on the order, the warehouse draws up the Order assembly document, where it enters the necessary data on the goods assembled for the order.
If we scanned more than the required amount, the system issues a list of extra positions. If we have scanned a smaller number, we will not be able to close the work on the order until all the goods have been collected. If, in the assembly, the quantity of the assembled goods coincides with the quantity for assembly, the sale of goods and services is created based on this assembly.
If the goods are not enough, the manager is informed about this, the manager already contacts the client about the order, but this is a different business process.
Why is product assembly necessary? If we create an implementation right away, this is wrong, because then our financial obligations to the client come. But in fact, until we see all the goods in stock according to the customer's order, until we have assembled them, we cannot tell the buyer that the goods are really in stock.
You can arrange the assembly of goods not only with the help of a scanner, but also with the help of a data collection terminal. In this case, all assembled goods are scanned at a time, and the data is loaded into the Goods assembly document.
The question often arises at enterprises: What to do with the weight goods that we sell by the piece?
It happens that the goods are credited by weight, and sold by the piece. For example, bolts. Bolts come in kilograms, and you sell them individually. How to be here? Very simple. The system starts two units of measurement of the nomenclature - pieces and kg, the coefficient is indicated, how many pieces are contained in a kilogram. When selling and assembling a product, an employee scans the barcode of this product and enters the quantity of the product to be sold. At the same time, barcode labels do not need to be stuck on each unit of goods. The warehouseman has a sheet with barcodes of goods, on which a barcode cannot be pasted, he scans and drives in the number of bolts.
When writing off, the quantity is written off both in pieces and in kilograms. Then the inventory is carried out already in kilograms, the goods are weighed, and the actual weight is compared with the accounting one. Thanks to the coefficient, you can always know how many pieces are contained in a kilogram, how much one piece weighs. And if 50 kg of bolts arrived, and they sold 1000 pieces of 50 g each, we should have a quantity of 0. If there is nothing left, then everything is in order: 50 kg of bolts came, 50 kg went away.
Conclusion
I hope that the information provided will be enough to design and automate the work of a warehouse at your enterprise or at your client.Sincerely, Kinzyabulatov Ramil.
The use of barcodes to identify goods simplifies the work of the seller and reduces the likelihood of errors when entering information into the program. For successful use barcoding, you need to perform preparatory steps: enter factory barcode values \u200b\u200bfor goods or print your labels with barcodes.
Barcodes can be applied to the goods by their manufacturer. As a barcode, a 13-digit code is usually encoded. digital code. The factory barcode is entered into the program when editing the product description by pressing the "Barcodes" button (in the right upper corner screen). Barcodes can be entered manually from the keyboard, but it is more convenient to do this with a barcode scanner.
Using a barcode scanner.
To use bar codes, you need a scanner that reads the code and transfers its value to the program. Barcode scanners differ in how they connect to a computer. There are connections to the keyboard gap, to the RS232 port, to USB port. The read barcode enters the computer into the keyboard buffer or into the RS232 port (COM port). If the scanner is connected via USB, the barcodes can be loaded into the keyboard buffer or the scanner can emulate the RS232 port and load the barcode into it.
The program can work both with barcodes loaded into the keyboard buffer and into the RS-232 port. For use more convenient work with RS-232 port.
When the scanner works through the keyboard buffer, reading a barcode is equivalent to entering the code from the keyboard and pressing Enter. To process such a code, the barcode entry window must be active in the program. This window appears automatically in the retail section with the appropriate settings or by pressing the F6 key.
When working with a scanner connected to the RS-232 port, it is polled in background, there is no need in the barcode entry window. Those. the program constantly checks the port and, if the code is read, processes it. You must first set the port number for the scanner. This is done in the settings. program parameters. When connecting the scanner via the RS-232 port, a external source power supply, it most likely comes with the scanner. Some computers and most laptops do not have an RS-232 port, so they use USB adapter- RS232. After installing its driver, a virtual COM port appears in the system. Its number can be found in the dispatcher Windows hardware. Some scanner models come with USB interface with RS-232 port emulation, and they do not require an additional power supply.
The barcode scanner can be used not only to read product codes, but also to control the program in the retail section. Special control barcodes for the program are located in the roz_kods.xls file in the program folder, as well as in the UTIL folder on the program CD. With the help of them, the seller can work with the program almost without using the keyboard.
We offer: laser scanner Zebex 30 01 for 3200 rubles. and other models.
Label printing.
If there are no factory barcodes on the goods, then you can print labels with your own barcodes. The program comes with such forms, as a barcode they display the product code. Forms for printing labels with barcodes can be found when registering an invoice and in product reports. If you select labels in MS Word format, MS Office must be installed on your computer. These forms are designed for printing on a conventional printer on A4 paper, it is better to use laser printer. Labels must be cut after printing. You can use adhesive paper.
In the label forms for the invoice, only the goods from the invoice are displayed. In the invoice, you can select individual items and print labels only for them using the "Print document for selected records (Ctrl-F9)" context menu item.
In product reports, labels for all products are displayed through the main menu. You can also display a report with labels for items selected in the directory.
You can also print from the software to dedicated label printers. These printers print on tape with adhesive labels. Applying these labels is much faster and easier than printing with a conventional printer. Forms and tools for printing on specialized label printers are not supplied with the program. Please contact our experts on this matter. As a rule, additional adaptation of such labels to the size and other requirements of the customer is required.
We offer: label printer CITIZEN CLP-521 for 14400 rubles. and other models.
Withdrawal of a check to the fiscal registrar
The program comes with forms for withdrawing a check on fiscal registrars (FR) of the Shtrikh-M company, for example, on Bar-FRK, Bar-M-FRK. The driver for the fiscal registrar, which is supplied free of charge with the device, must be installed on the computer. Forms for check withdrawal are supplied in the program in source codes.
There are also forms for fiscal registrars firm ATOL. To work with the registrar, use "ATOL: KKM driver", which supports the following models of fiscal registrars for free:
- "FPrint-03К"
- "FPrint-5200K"
- "FPrint-02К"
- "FPrint-88К"
- "TORNADO" ("MERCURY-114.1 F" version 04)
- "TORNADO-K" ("MERCURY MS-K" version 02)
- "FELIX-RK" version 01
- "FELIX-R F" version 02
- "FELIX-02K" version 01
- "FELIX-3SK" version 01
- "Trium-F" version 01
- "MERCURY-140F" versions 02 and 03
It is possible to develop similar forms for other FR models. The built-in language of the program allows you to interact with OLE objects of various FR drivers.
Interaction of the program with cash register A is possible MS-100F, AMS-100K. These devices have the ability to communicate with a computer, but the CHON100.DLL library for working with these cash registers from their manufacturer is paid. It has copy protection linked to serial number cash register. The cost of supplementing the program for working with the AMC-100 cash register is approximately 1800 rubles. for 1 cash register.
If you do not need to use a fiscal registrar, then you can print a receipt on a regular or receipt printer.
We offer: fiscal registrar KKM "SHTRIKH-M-FR-K" for 26,000 rubles. and other models.
Data collection terminals.
To put it simply, a data collection terminal (TSD) is a barcode scanner with memory. It accumulates read barcodes, and then they can be loaded into the program into a receipt or expense document, or into an inventory. The program supports direct interaction with Zebex terminals, for example, Zebex PDL-2016 models. This is a relatively inexpensive model with laser scanner. To insert data from the Zebex TSD into the program, create a new document or inventory, click right button mouse or F12 and in the appeared context menu select the item "Import points from the data collection terminal". There are more detailed instructions to work with the Zebex PDL-20 RTD, you can request it from our technical support department.
The use of TSD can be convenient in cases where it is difficult to reach barcodes with a conventional scanner connected to a computer. It can be a warehouse, a showcase, a large trading floor.
You can also equip remote retail outlets with TSD to account for their sales, but in terms of cost and functionality, the option with an inexpensive netbook will be more interesting, for example, Asus EEE, a barcode scanner and our program version "Retail".
For more expensive fiscal registrars based on Windows CE, we have developed the VVS "Mobile Commerce" program, which allows you to keep full records and exchange information with our VVS "Office - Warehouse - Shop" program.
We offer: Zebex PDL-20-16 data collection terminal for 17500 rubles, Zebex Z-2070WL terminal - handheld terminal with WiFi WinCE.NET color touch screen for 31900 rubles. and other models.
Buyer display.
To display to the buyer information about the name and price of the selected goods, the amount of purchase and delivery, a buyer's display can be connected to the computer. Trading rules may oblige the use of buyer displays in the case of using fiscal registrars, you need to clarify this issue yourself.
The program supports interaction with customer displays using various systems commands. We have installed customer displays FIRICH FV-2029M and compatible with it. For other models, verification is recommended.
Customizing the customer's display is done when editing the program parameters.
We offer: customer's display FIRICH FV-2029M Fluorescent display, two line at 4300 rubles. and other models.
Weighted goods
If you are using bulk products, then you may need a scale with the ability to print labels. For example, scales of the CAS LP series. To load them with codes, names and prices of goods, a special report on goods can be added to the program. Data transfer to the balance is possible via text file. More detailed information for communication, see the documentation for the balance.
To process barcodes with weight in the program, you need to configure their processing. This is done when editing the program parameters, the "Additional" tab, then the buttons "Trade equipment", "Weight goods".
We offer: scales with label printing CAS LP for 31,000 rubles and other models.
You can purchase the necessary trade equipment and computer equipment from us or from our partners. We will be happy to consult with you on this matter.
