Windows 8 came out last year, but it still has frequent program compatibility errors. This usually happens when you try to launch an already familiar program (when you had another operating system installed) or cannot launch new program in Windows 8.
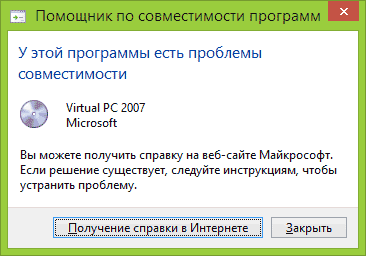
The error windows look like this:
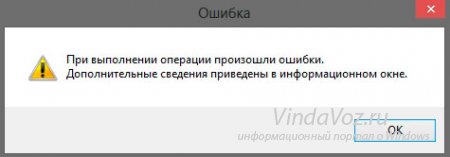
After this, users usually get upset and either lose interest in it or look for a way to fix it.
There are 2 ways to solve this problem:
1) Find on the Internet (Windows Store) a version for Windows 8 and preferably a newer one. More and more manufacturers are now redesigning their products to be compatible with Windows 8
2)
Run the program in compatibility mode operating system.
This option is not the most reliable, but it can work. But it is possible that the program will work correctly in this launch mode.
So, how to run and install the program in compatibility mode for Windows 8?
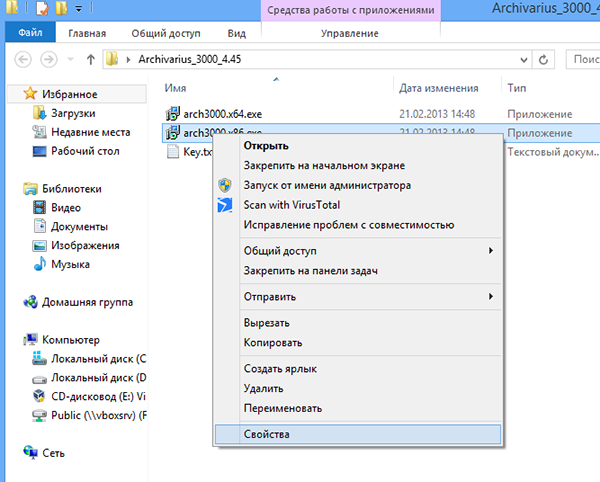
1. Right click on the icon of the program that we want to run/install and select Properties
2.
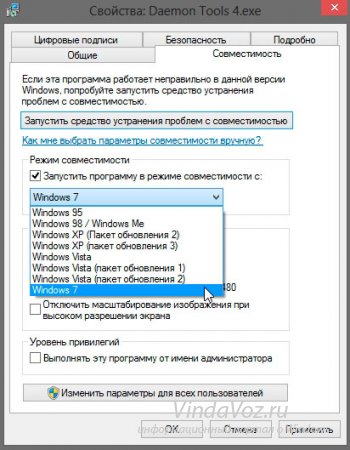
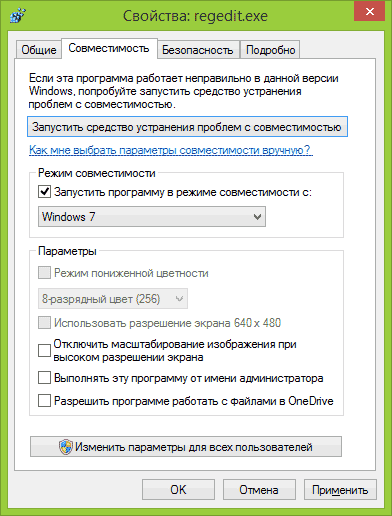
Go to the tab Compatibility, put a tick " Run the program in compatibility mode" and select the operating system for compatibility from the list:
You can also check the box “ Run this program as administrator", so that it will definitely work:
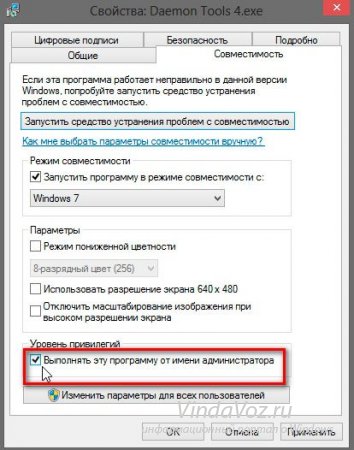
Click Apply And OK. Then we try to launch it. If it worked out, then I congratulate you. If not, then try the first method and look on the Internet for a version for Windows 8.
As you have seen, launching and installing the program in compatibility mode with Windows 8 is not at all difficult.
A lot of time has passed since the release of Windows 8. Many developers software have already managed to make appropriate adjustments to their products, thus eliminating the possibility of an incompatibility conflict. At least this is true for all popular applications.
As for lesser-known programs, among them you can still find quite a few that do not work correctly or produce errors during installation. One reason for this may be a compatibility issue. Fortunately, desktop versions of Windows 8 already have a ready-made solution - compatibility mode.
Using this tool, you can eliminate a number of problems caused by incorrect operation of programs created for earlier versions of Windows. If the program refuses to install at all and displays a critical error at the very beginning of the installation, first of all pay attention to the bit capacity of the application.
If you are using 32-bit Windows, you will not be able to install a 64-bit application. On this moment There are three main ways to solve the incompatibility problem.
Automated Program Compatibility Assistant
Typically, when installing applications, Windows 8 automatically checks the program for possible compatibility issues. If a problem is detected, the operating system will launch a special utility - Program Compatibility Assistant.Depending on the complexity of the problem, this utility will suggest one action or another. The Program Compatibility Assistant can resolve some problems, such as those related to User Account Control, on its own, without user intervention, and it can also automatically launch a program in mode simulating earlier versions of Windows.
In some cases, the appearance of the Assistant may be caused by a program registration error and nothing more. If the installed program or driver works well and does not cause conflicts, but the Assistant displays messages about the application failure, you need to close it by clicking “This program is installed correctly.”
Windows Compatibility Center
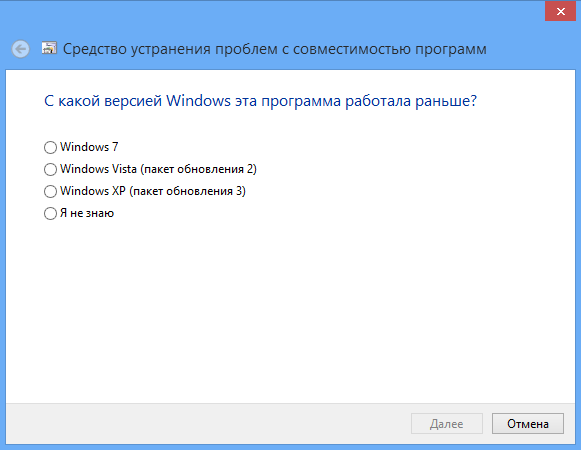
If you have any suspicions that incorrect work already installed program associated with an incompatibility issue, you can try to solve it in manual mode. To do this, go to and then to the Troubleshooting section. In the window that opens, click on the link “Run programs designed for previous versions of Windows.” Select the application that is not working correctly from the list provided. If desired application is not in the list, specify it manually through the standard Review.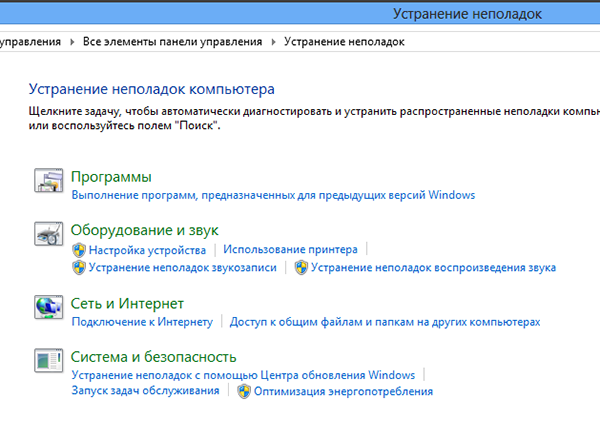
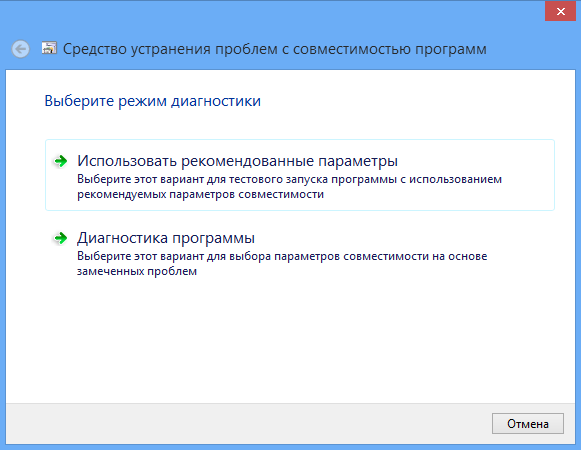
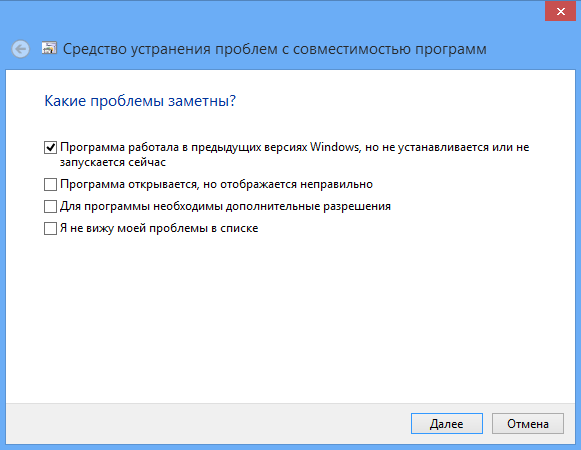
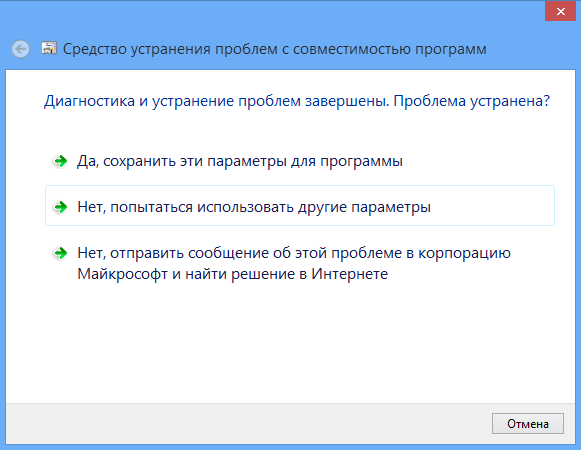
Next, the Wizard will ask you to select a diagnostic mode. The first mode involves correcting errors based on recommended parameters, the second - based on problems noticed by the user, for example, if you indicate that the program worked in earlier versions of Windows, the Wizard will ask you to indicate which version, etc. Once the diagnostics are complete, the Wizard will offer to apply new settings to the problematic application.
Changing the compatibility mode in the installer properties
If you are just going to install an application and you know that it is not supported by Windows 8, you can try installing it in compatibility mode with earlier versions of the operating system.To do this, click on installation file right mouse button, in context menu select Properties, go to the “Compatibility” tab and, by checking the “Run the program in compatibility mode for...” checkbox, specify the operating system version.
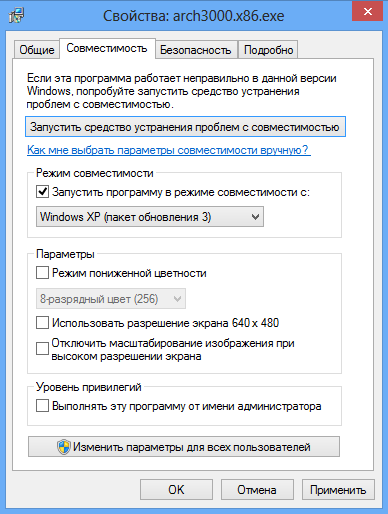
Windows 8 supports compatibility modes with Windows 95, 98, Me, XP (SP2 and SP3), Vista (SP1 and SP2) and 7. In addition, you can configure display settings (if the application is not compatible with newer displays), as well as set the privilege level . If there is no “Compatibility” tab in the properties window, it means that compatibility mode is not supported by this application.
Conclusion
Unfortunately, not all problems associated with version incompatibility can be resolved using the method described above.In particular, this applies to some drivers and outdated versions of antivirus programs. In this case, the only correct solution would be to update the conflicting software to latest versions.
In some cases, errors that occur during program operation can be eliminated by installing the .NET Framework 3.5 component in Windows 8.
In this material I will tell you in detail about how to run a program or game in compatibility mode with a previous version of the OS in Windows 7 and Windows 8.1, what compatibility mode is and in which cases its use can most likely solve certain problems for you.
I'll start with last point and I’ll give an example that I had to deal with very often - after Windows installations 8, installation of drivers and programs on the computer failed, a message appeared stating that the current version of the operating system is not supported or this program has compatibility problems. The simplest and usually working solution is to run the installation in compatibility mode with Windows 7, in this case everything almost always goes well, because these two versions of the OS are almost the same, it’s just that the check algorithm built into the installer “does not know” about the existence of eight, since it was released earlier, so it reports incompatibility.
In other words, Windows compatibility mode allows you to run programs that have problems launching in the version of the operating system that is currently installed, so that they “believe” that they are running in one of the previous versions.
Attention: you should not use compatibility mode with antiviruses, programs for checking and fixing system files, or disk utilities, as this may lead to undesirable consequences. I also recommend looking to see if the program you need is available in a compatible version on the developer’s official website.
How to run a program in compatibility mode
First of all, I will show you how to run the program in compatibility mode in Windows 7 and 8 (or 8.1) manually. This is done very simply:
After this, you can try to launch the program again, this time it will launch in compatibility mode with the version of Windows you selected.
Depending on which version you are performing the steps described above, the list of available systems will differ. In addition, some of the options may not be available (in particular, if you want to run a 64-bit program in compatibility mode).
Automatically applying compatibility settings to a program
Windows has a built-in Program Compatibility Assistant that can try to determine in what mode a program needs to be run in order for it to work as expected.
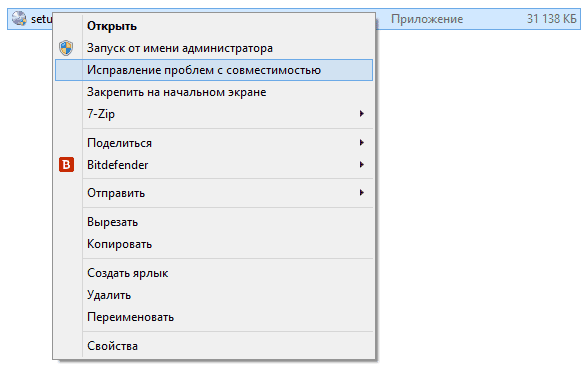
To use it, click right click mouse over the executable file and select the “Fix compatibility problems” menu item.
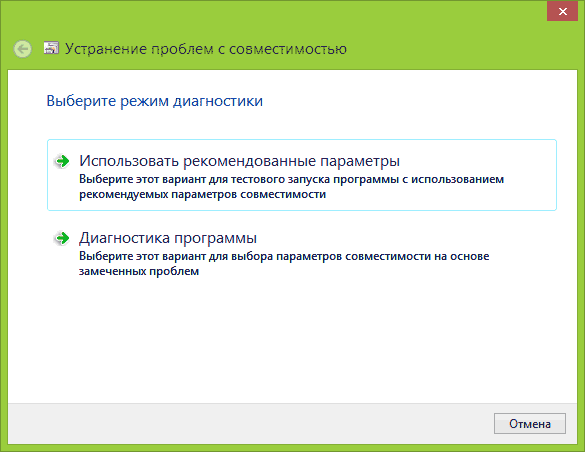
The Fix Problems window will appear, followed by two options:
In many cases, automatically selecting and launching a program in compatibility mode using the assistant turns out to be quite workable.
Setting program compatibility mode in Registry Editor
Finally, there is a way to enable compatibility mode for a particular program using the Registry Editor. I don't think this will really be useful to anyone (at least not to my readers), but the opportunity is there.
So, here is the necessary procedure:
- Press the Win+R keys on your keyboard, type regedit and press Enter.
- In the Registry Editor that opens, open the branch HKEY_CURRENT_USER\ Software\ Microsoft\ Windows NT\ CurrentVersion\ AppCompatFlags\ Layers
- Right click on free space on the right, select "New" - "String Parameter".
- Enter the full path to the program as the parameter name.
- Right-click on it and click “Edit”.
- In the Value field, enter only one of the compatibility values (listed below). By adding the value RUNASADMIN separated by a space, you will also enable the program to run as an administrator.
- Do the same for this program in HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\AppCompatFlags\Layers
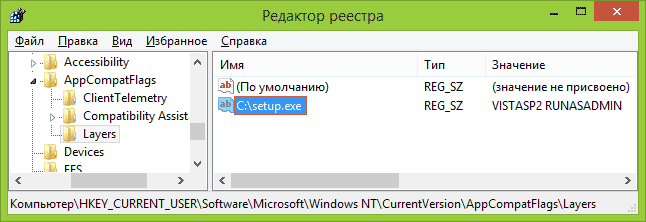
You can see an example of use in the screenshot above - the setup.exe program will be launched as Administrator in Vista SP2 compatibility mode. Available values for Windows 7 (on the left is the version of Windows in compatibility mode for which the program will be launched, on the right is the data value for the registry editor):
- Windows 95 - WIN95
- Windows 98 and ME - WIN98
- Windows NT 4.0 - NT4SP5
- Windows 2000 - WIN2000
- Windows XP SP2 - WINXPSP2
- Windows XP SP3 - WINXPSP3
- Windows Vista- VISTARTM (VISTASP1 and VISTASP2 - for the corresponding Service Pack)
- Windows 7 - WIN7RTM
After changes made, close Registry Editor and restart your computer (preferably). The next time the program starts, it will use the selected parameters.
Perhaps running programs in compatibility mode will help you fix any errors that may arise. In any case, most of those created for Windows Vista and Windows 7 should work in Windows 8 and 8.1, and programs written for XP will most likely be able to run in Windows 7 (or use XP Mode).
This documentation has been archived and is no longer maintained.
Chapter 4: Application Compatibility with Windows 7
The Windows Vista® operating system has made many significant changes to the way it handles program calls to kernel mode, making it more secure than Windows® XP. However, these changes resulted in application compatibility issues that required many programs to be patched to resolve.
The Windows® 7 application model is based on the same core architecture as Windows Vista. Most programs that are compatible with one are also compatible with the other. This alone makes implementing Windows 7 easier than migrating from Windows XP to Windows Vista. If your business, like many others, has adopted Windows XP as the standard, you may need to upgrade to updated versions of key applications. The widespread availability of Windows Vista compatible versions and proven compatibility techniques make this task easier.
However, there is a possibility that older applications may not work correctly with new Windows 7 security technologies, such as User Account Control (UAC) or Windows Resource Protection (WRP).
This chapter provides simple procedures for checking your applications' compatibility with Windows 7, as well as some of the most common compatibility issues and resources to help you resolve them.
Application Compatibility Testing
This section covers testing the compatibility of applications with Windows 7. It describes two scenarios in which testing can be performed. The scripts are designed to test an application on a Windows 7 computer.
Testing an application on a Windows 7 computer
1. Install on Windows computer 7 and log in as administrator.
2. Install the application you are testing. If you are prompted for confirmation during installation, click Permit(allow) to continue. If the installation is successful, proceed to step 6.
Note This step is optional if you are using an MSI file to install the application.
Attention! If the program's installer prompts you to run it right away, refuse because otherwise the application will run with the same elevated rights that were used to install it.
3. If the installation fails and you are not prompted for confirmation, right-click the installer EXE file and select Run this program as administrator(run as administrator), then repeat the installation. If the installation is successful, proceed to step 7.
4. If errors occur related to the operating system version, application registration, or file copying, right-click the installer EXE file, select Compatibility(compatibility) and specify the compatibility mode Windows XP Professional SP3.
5. Repeat step 2. If the application still does not install, go to step 8.
6. Log in as a user who does not have administrative privileges.
7. Launch the application. If the application does not launch as expected or errors occur, turn on compatibility mode Windows XP Professional SP3 for the application EXE file, and then try to launch it again.
8. If the application starts successfully, run the full set of tests that you typically use on computers running Windows XP SP3. If the basic functionality tests pass, the application will run fine on Windows 7.
9. If an application does not install, does not start, stops responding, produces errors, or fails any of the basic functionality tests, it may have compatibility issues with Windows 7. Please refer to other resources in this chapter to investigate further.
If after following these steps you find that the application works fine, you can conclude that it is compatible with Windows 7.
Known application compatibility issues
This section describes technologies, changes, and improvements in Windows 7 that commonly cause application compatibility issues. Where possible, probable solutions are also given.
Important All third party applications must be tested for compatibility with Windows 7 to ensure they work correctly under Windows 7.
Security improvements
The following are security improvements included in Windows Vista and Windows 7 that may cause compatibility issues with applications developed for earlier versions of Windows.
Account Control. This technology in Windows Vista and Windows 7 allows you to separate tasks and privileges regular user from those of the administrator. User Account Control (UAC) enhances computer security by giving users the convenience of working with normal privileges. They can accomplish more tasks and experience fewer application compatibility issues without having administrative privileges. This helps reduce the risks posed by malware infections, unauthorized software installations, and unauthorized system changes.
One of the most useful features of UAC is the virtualization of parts of the registry and file system in cases where applications running with low privileges attempt to write data to system locations. User Account Control may interfere with applications that are not compatible with the improvements described. For this reason, applications should be tested for UAC compatibility before deployment.
Protection Windows resources. First appearing in Windows Vista under the name "Protection Windows files", Windows Resource Protection technology now protects not only key system files, but also folders and registry keys. Its task is to ensure greater stability and security of the operating system. Applications that attempt to make changes to these protected areas may not work correctly in Windows 7. In such cases, the application must be patched to work as intended. For more information about this technology and its impact on application compatibility, see "About Windows Resource Protection" on MSDN®.
Protected Mode. This Windows® Browser feature Internet Explorer® 7 and later versions help protect Windows computers from installing malware by working with reduced privileges. When the browser is in protected mode, it can only interact with certain parts of the file system and registry.
Although protected mode helps preserve the integrity of computers under Windows control, it can prevent older web and intranet applications from working properly. Such applications may need to be modified to work in a more restricted environment. By default, Internet Explorer® 8 does not use Protected Mode when visiting websites in the Trusted Zone or Intranet Zone.
Operating system changes and innovations
The following changes and innovations in Windows 7 may cause compatibility issues with third-party applications.
New APIs. Application programming interfaces (APIs) expose components of Windows Vista SP1 differently than in the past. Such interfaces are required, for example, antivirus programs and firewalls so that they can provide proper monitoring and Windows protection Vista and Windows 7. To resolve possible problems You should update these applications to versions that are compatible with Windows Vista SP1.
Windows 7 64-bit. 16-bit applications and 32-bit drivers are not supported in a 64-bit Windows environment. Automatic redirection when working with the registry and file system Used only for 32-bit applications. Therefore, any 64-bit applications must fully comply with Windows 7 and Windows Vista standards.
Operating system versions. Many old applications check Windows version. If the check shows that the version is not as expected, they may stop working. In many cases, this problem can be resolved by simply setting the application to compatibility mode with one of the previous versions of Windows.
Most compatibility issues related to operating system version requirements are resolved using new tools built into Windows 7. Features such as the Program Compatibility Assistant can usually handle them automatically. There is more information about the Software Compatibility Assistant and other tools later in this chapter.
Additional information For information about these changes and improvements in Windows 7, see the MSDN topic “Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 Application Quality Cookbook.” It also provides ways to possibly detect and resolve most of these problems.
Tools and resources
This section provides short review Some Windows 7 components and technologies that are designed to resolve application compatibility issues.
Program Compatibility Assistant
This component automatically assigns the appropriate compatibility mode to an application designed for previous version Windows®. When Windows 7 detects a program that requires compatibility mode for Windows 2000, Windows XP Professional SP3, or later, it automatically makes the necessary changes so that the program will continue to work correctly in Windows 7.
Windows XP mode
If the Compatibility Toolkit or other tools fail to ensure normal work applications in Windows 7, you can resort to another option - Windows XP mode. It allows you to install and run without problems Windows applications XP directly from Windows 7. This uses Windows Virtual PC virtualization technology, which creates a virtual Windows environment XP. After installing the application, it launches as usual directly from the desktop Windows desktop 7. The user does not even need to know that the program actually runs in a Windows XP virtual machine.
Windows XP mode can be downloaded separately for Professional, Ultimate and Enterprise editions of the operating system. Windows systems 7. It is a 32-bit Windows XP Professional SP3 environment placed on a virtual hard disk. While this mode completely resolves any compatibility issues, it also means that there will now be two operating systems, and the second one will also need to be configured according to the required level of security. By default virtual Windows machine XP is configured to use a shared network, or NAT. The advantage of this option is that unsolicited network traffic can never get into virtual machine, but it also changes the way Internet Explorer automatically discovers the location of Web servers. When running in Windows XP mode, Internet Explorer accessing websites through NAT may classify a number of external websites as being in the Internet zone, so you must limit the settings for this zone to match the settings for the Restricted Sites zone. Trusted websites can then be added to the Trusted Sites zone. To start using Windows mode XP, download it from the "
Each brings a lot of good a new version the most popular operating system on the planet. But there are always programs that refuse to cooperate with the new Windows - either installation attempts end in failure, or installed application won't start.
All about program incompatibility
Often the problem arises in the first months of the release of a new OS: developers do not always regularly release versions of programs that are fully compatible with the next generation of Windows. The main way to resolve incompatibility is to try installing the updated version from the official website.
But there are always applications that do not want to work with the new Windows, and there is no longer any chance of updated versions being released. The most "problematic" categories:
- drivers: usually these are old “peripherals” like printers, scanners, and very ancient audio cards;
- small but convenient non-profit programs that ceased development many years ago;
- old, but still very good games;
- representatives of the so-called “accounting” software. These are created a long time ago for ancient operating systems. Windows type 95 and 98, MS DOS. These are still found in municipal offices such as housing offices and accounting departments of small enterprises.
The reasons for program incompatibility with Windows are sometimes the most trivial: for example, a program, out of old habit, “looks” for its own service files in the wrong folder, displaying an error message on the screen.
Windows Compatibility Troubleshooter Tool
This method solves simple problems. It should be used first - most often "Troubleshooting..." will help.
This Windows function called by right-clicking on a program that does not want to run in the OS - the "Fix compatibility problems" item. When you select this mode, Windows will first display a window asking you to use the recommended settings (we agree),
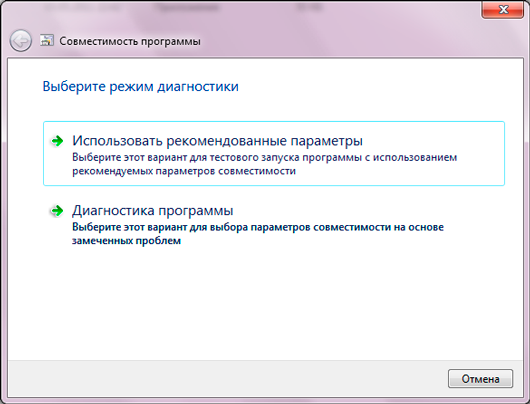
then it will notify you about the results of its work: it will offer to “whisper” to the faulty program that in fact it is not in a cutting-edge environment latest Windows, and in her native “old lady” XP. To try it, just click the "Run program" button.
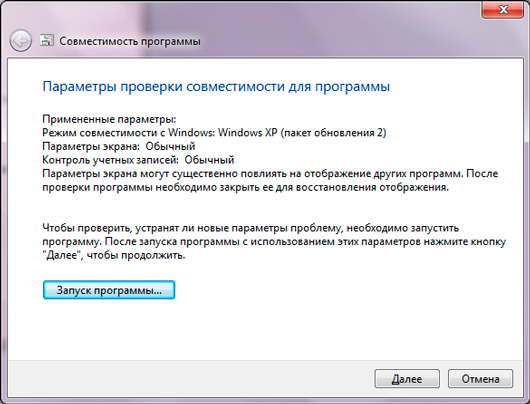
If the program starts working, then you should save the recommended parameters for launching it (the “Next” button) - and from now on, for a successful start, the usual double-click on the shortcut is enough. And if a quick recipe for combining a program and operating system does not help, then there is a more powerful method.
Compatibility Mode Tool
In the case of drivers (and some other programs), the problem is much deeper: they almost always require the appropriate OS version. “Almost”, because skilled hands are sometimes able to independently edit several lines in special inf files - instructions for a computer for installing drivers, but this rarely happens.
As for other programs, you can try to run them without deep skills. Modern operating systems from Microsoft provide a feature called " Windows Compatibility Mode".
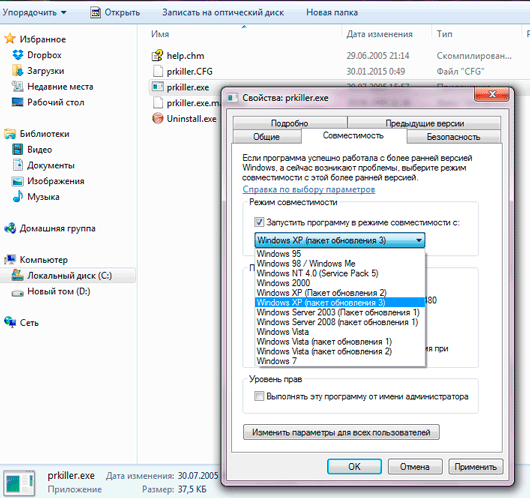
The window carefully suggests options for launching a program that refuses to work. The main selection fields are available after checking the box next to "Run the program in compatibility mode for:". There are a choice of different versions Windows, starting from 95 and ending with Windows 7. You should choose the option in which the program definitely worked in normal mode.
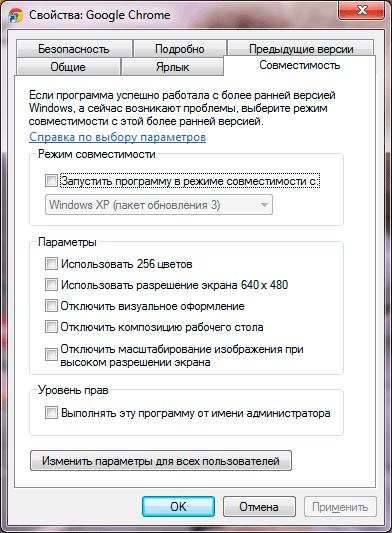
Other parameters of the Windows Compatibility Mode tool are intended for very rare cases - they are visible in the screenshot. Some games from the early 90s require 256 colors instead of the current 16-plus million. For some reason, other programs refuse to work on modern HD screens and require the ancient VGA resolution - 640 by 480 pixels - to function. In especially difficult cases, you can try to disable the “pretty” interface features such as translucent panels and full scaling.
However, to run old programs, most often it is enough to select the appropriate version of Windows, the options for which are indicated in the drop-down menu. After applying the settings, you need, as usual, to double-click with the left mouse button on the faulty program - and get the result of the settings!
Finally
Let us warn you once again about the rare compatibility of drivers with a “foreign” operating system. No compatibility mode can help an old device work in a new environment if the manufacturer of this device has not taken care of it. Sometimes manual editing of special files included in drivers can help, but this is a topic for a separate article.
Finally, in some cases, a folk method of combining incompatible things will help. If the application refuses not only to run on the new OS, but even to install, then try the following recipe:
- Copy all program files from the old computer to external storage(for example, on a flash drive).
- By inserting a flash drive with files of an incompatible program into new computer, copy them to HDD.
- Launch main executable file(extension is usually *.exe) double click, and if that doesn’t work, right-click - Properties - Compatibility - and then everything, as in the previous section.
There are cases when an intractable program submits to such non-standard cunning of the user, and again begins to properly perform its duties.
