The search module is not installed.
Liquid crystal displays( IPS technology, MVA, PVA)
Sergey Yaroshenko
When creating LCD displays, three main technologies are used: TN + film, IPS and MVA. Since TN + film technology was discussed in detail in the previous article, we will focus on its technological competitors.
TN + film technology
Twisted Nematic + film (TN + film). The “film” part in the technology name means an additional layer used to increase the viewing angle (approximately up to 160°). This is the simplest and cheapest technology. It has been around for a long time and is used in most monitors sold in the last few years.
Advantages of TN + film technology:
- low cost;
- minimum pixel response time to control action.
Disadvantages of TN + film technology:
- average contrast;
- problems with accurate color rendering;
- relatively small viewing angles.
IPS technology
In 1995, Hitachi developed In-Plane Switching (IPS) technology to overcome the disadvantages inherent in panels made using TN + film technology. Small viewing angles, very specific colors and unacceptable (at that time) response time prompted Hitachi to develop new technology IPS, which gave good result: decent viewing angles and good color rendition.
In IPS matrices, the crystals do not form a spiral, but rotate together when an electric field is applied. Changing the orientation of the crystals helped achieve one of the main advantages of IPS matrices - viewing angles were increased to 170° horizontally and vertically. If no voltage is applied to the IPS matrix, the liquid crystal molecules do not rotate. The second polarizing filter is always turned perpendicular to the first, and no light passes through it. The black color display is perfect. If the transistor fails, the “broken” pixel for an IPS panel will not be white, as for a TN matrix, but black. When voltage is applied, liquid crystal molecules rotate perpendicular to their initial position parallel to the base and transmit light.
|
LCD TVs appeared on the market quite a long time ago and everyone has already gotten used to them. However, every year more and more new models appear, differing appearance, screen diagonal, interface and more. In addition, there are also models of liquid crystal displays that differ in their special update speed, types of LEDs and backlighting. However, let's talk about everything one by one. To begin with, I propose to understand what it is – LCD monitors.
Probably many of you have heard the concept of LCD panels. LCD is an abbreviation that stands for: Liquid Crystal Display. Translated into Russian, this means liquid crystal display, which means LCD and LCD panels are one and the same.
The technology for displaying pictures is based on the use of crystals in liquid form and their amazing properties. Such panels have a huge number of positive qualities thanks to the use of this technology. So let's figure out how it works.
Widget from SocialMartHow does an LCD monitor work?
The crystals used to create these monitors are called cyanophenyls. When they are in a liquid state, they develop unique optical and other properties, including the ability to position themselves correctly in space.
Such a screen consists of a pair of transparent polished plates, onto which transparent electrodes are applied. Between these two plates the cyanophenyls are located in a certain order. Voltage is supplied through the electrodes on the plates, which is supplied to sections of the screen matrix. There are also two filters located parallel to each other near the plates.
The resulting matrix can be manipulated, causing the crystals to transmit a beam of light or not. In order to obtain different colors, filters of three basic colors are installed in front of the crystals: green, blue and red. Light from the crystal passes through one of these filters and produces the corresponding pixel color. A certain combination of colors allows you to create other shades that will match the moving picture.
Types of matrices
LCD monitors can use several types of matrices, which differ from each other in their technology.
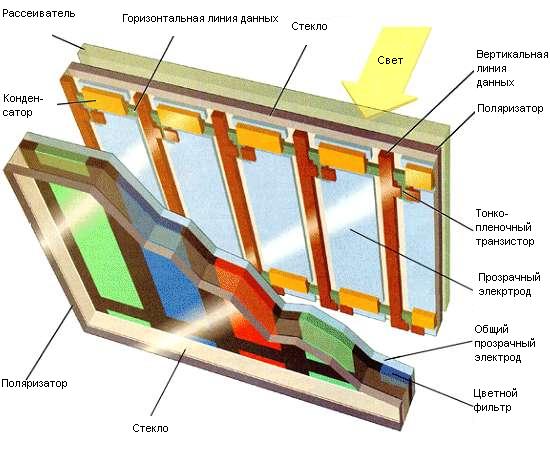
TN+film. This is one of the simplest standard technologies, which is distinguished by its popularity and low cost. This type of module has low power consumption and a relatively low update frequency. You can especially often find a similar module in older panel models. The “+film” in the name means that another layer of film was used, which should make the viewing angle larger. However, since today it is used everywhere, the name of the matrix can be shortened to TN.
A similar LCD monitor has a large number of shortcomings. Firstly, they have poor color reproduction due to the use of only 6 bits for each color channel. Most shades are obtained by mixing primary colors. Secondly, the contrast of LCD monitors and viewing angle also leaves much to be desired. And if some subpixels or pixels stop working for you, then most likely they will constantly glow, which will make few people happy.
IPS. Such matrices differ from other types in that they have the best color reproduction and a wide viewing angle. The contrast in such matrices is also not the best, and the refresh rate is lower than even that of a TN matrix. This means that if you move quickly, a noticeable trail may appear behind the picture, which will interfere with watching TV. However, if a pixel burns out on such a matrix, it will not glow, but, on the contrary, will remain black forever.
Based on this technology, there are other types of matrix, which are also often used in monitors, displays, TV screens, etc.
- S-IPS. Such a module appeared in 1998 and differed only in its lower response update frequency.
- AS-IPS. Next type matrices, in which, in addition to the update speed, the contrast was also improved.
- A-TW-IPS. This is essentially the same S-IPS matrix, to which a color filter called “True White” has been added. Most often, such a module was used in monitors intended for publishing houses or darkrooms, as it made the white color more realistic and increased the range of its shades. The disadvantage of such a matrix was that the black color had a purple tint.
- H-IPS. This module appeared in 2006 and was distinguished by screen uniformity and improved contrast. It does not have such an unpleasant black light, although the viewing angle has become smaller.
- E-IPS. Appeared in 2009. This technology has helped improve the viewing angle, brightness and contrast of LCD monitors. In addition, the screen refresh time has been reduced to 5 milliseconds and the amount of energy consumed has been reduced.
- P-IPS. This type of module appeared relatively recently, in 2010. This is the most advanced matrix. It has 1024 gradations for each subpixel, resulting in 30-bit color, which no other matrix could achieve.
V.A.. This is the very first type of matrix for LCD displays, which is a compromise solution between the previous two types of modules. Such matrices best convey image contrast and color, but at a certain viewing angle some details may disappear and the white color balance may change.
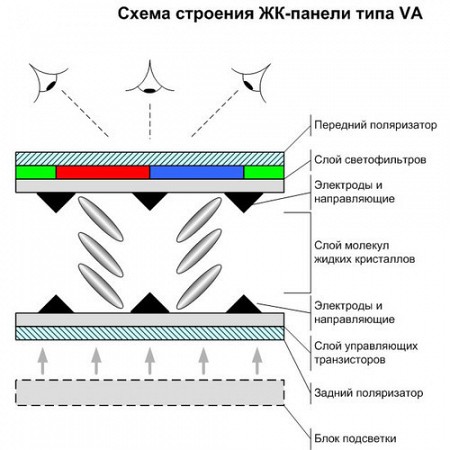
This module also has several derivative versions that differ from each other in their characteristics.
- MVA is one of the first and most popular matrices.
- PVA – this module was released by Samsung and features improved video contrast.
- S-PVA was also manufactured by Samsung for LCD panels.
- S-MVA
- P-MVA, A-MVA - manufactured by AU Optronics. All further matrices differ only in the manufacturing companies. All improvements are based only on the reduction in response speed, which is achieved by applying higher voltage at the very beginning of the change in the position of subpixels and using a full 8-bit system that encodes color on each channel.
There are also several other types of LCD matrices, which are also used in some panel models.
- IPS Pro - they are used in Panasonic TVs.
- AFFS – matrices from Samsung. Used only in some specialized devices.
- ASV - matrices from Sharp Corporation for LCD TVs.
Types of backlight

Liquid crystal displays also differ in the types of backlighting.
- Plasma or gas discharge lamps. Initially, all LSD monitors were backlit by one or more lamps. Basically, such lamps had a cold cathode and were called CCFL. Later, EEFL lamps began to be used. The light source in such lamps is plasma, which appears as a result of an electrical discharge passing through a gas. At the same time, you should not confuse LCD TV with plasma TV, in which each of the pixels is an independent light source.
- LED backlight or LED. Such TVs appeared relatively recently. Such displays have one or more LEDs. However, it is worth noting that this is only the type of backlight, and not the display itself, which consists of these miniature diodes.
Fast response and the required value for watching 3D video
Response speed is how many frames per second the TV can display. This setting affects the image quality and smoothness. In order for this quality to be achieved, the refresh rate must be 120 Hz. In order to achieve this frequency, TVs use a video card. In addition, this frame rate does not create screen flickering, which in turn is better for the eyes.

To watch movies in 3D format, this refresh rate will be quite enough. At the same time, many TVs have a backlight that has a refresh rate of 480 Hz. This is achieved by using special TFT transistors.
Other characteristics of LCD TVs
| Brightness, black depth and contrast | The brightness of such TVs is quite high level, but the contrast leaves much to be desired. This is due to the fact that with the polarization effect, the depth of black color will be as much as the backlight allows. Due to insufficient black depth and contrast, dark shades may merge into one color. |
| Screen diagonal | Today you can easily find LCD panels with both large diagonals, which can be used as home theater, and models with a rather small diagonal. |
| Viewing angle | Modern models TVs have a fairly good viewing angle, which can reach 180 degrees. But older models don't have enough angle, which can cause the screen to look quite dark or the colors to be distorted when looking at the screen from certain angles. |
| Color rendition | The color rendition of such displays is not always quite good. good quality. This again applies mainly to older screen models. But modern models are often inferior to other types of TV. |
| Energy efficiency | LCD displays consume 40% less electricity than other types. |
| Dimensions and weight | Such TVs are quite light in weight and thickness, but today there are panels with less thickness and weight. |
Advantages and disadvantages of LCD TVs
These TVs have a number of advantages:
- Energy efficiency;
- Use of environmental technologies;
- Durability;
- Light weight and dimensions of the TV;
- No glare in bright light;
- Low cost compared to other models of modern TVs.

However, compared to others modern technologies, used in televisions, LCD displays They also have certain disadvantages:
- Insufficient image contrast;
- Low black depth due to the use of additional backlighting;
- Poor color reproduction, especially in older TV models;
- High refresh rate;
- Small viewing angle, especially in older TVs.
In the end, I would like to say that all the shortcomings are mainly present in older models. Modern TV has almost completely gotten rid of such problems and is practically no different from other technologies.
The main purpose LCD matrices – set of screens modern monitors, from technical characteristics which determine the image output and its quality.
For most buyers this is enough brief description advantages of the monitor, from the packaging and demonstration of the main display parameters computer information: brightness, contrast, etc.
Let's expand the range of our knowledge about the design of monitors. Which of them suits us best in terms of quality and price?
What are the criteria for an LCD matrix? is the main element of this device?
We are talking about a “juicy” picture, low response, modern games without stuttering - we really want to get all this when purchasing a new modern liquid crystal display. So, all of the above, first of all, interconnected with the type of LCD matrix, which comes with your monitor.
Today, there are three main types of TFT-LCD matrices. But how are they different from each other?
1. TN + film, or simply TN - the most inexpensive and popular type of matrix, characterized by the shortest response time, sufficient resolution and color rendering, viewing angles up to 170/170 degrees with a decent change in color gradations depending on changes in the viewing angle. Modern models from the main brands Philips, NEC, Sony, ASUS are distinguished by high contrast and a sufficient range of viewing angles. The breakthrough of recent years in the technology of manufacturing monitors based on TN matrices has made it possible to achieve significant results and, today, this line of monitors is the most attractive for users. The monitors are perfectly designed for office work, watching movies, and modern dynamic games, which suits most modern users PC. The most attractive prices for this type of monitor are, for example, 17 inch monitor famous ACER It is possible to purchase within 4 thousand rubles!
2. IPS matrices the most dynamic in displaying colors (color rendition), contrast and brightness are in the middle ranges, but viewing angles are over 170 degrees (without visible changes in color gradations). Increasing the quality of color rendering and saturation of color balance affected the response of the pixels; their response time leaves much to be desired. Therefore, matrices IPS type are now very rare, they have been completely replaced S-IPS matrices, with a short response time, almost equal in level to TN-type matrices.
S-IPS matrices, for all their attractiveness, are quite expensive. Monitors with such matrices are intended for professionals working with graphics, complex video processing and as prestigious models for home use.
3. Matrices type MVA, PVA and their modifications are characterized by the highest contrast when displaying colors (color rendition), as well as fairly wide viewing angles (at the S-IPS level). Compared to S-IPS, there is a slight change in the quality of color balance, especially when displaying black shades. Modern improved matrices A-MVA and S-PVA, more technologically advanced, practically smooth out this drawback. An excellent choice for working with video, graphics, and modern games that require significant resources are displayed dynamically and without visible distortion.
According to your parameters this type matrix is in the middle price category between S-IPS and TN matrices, therefore monitors based on them can be recommended as a universal solution for professionals and ordinary users.
However, it is always better to see once and draw your own conclusion than to read hundreds of pages of holy wars. After looking through Google Images a little, I picked up a few visual illustrations. Unfortunately, the copyright for the images is not respected. In photographs, theoretically, the brightness of the compared models can be different, so we can only reliably say about those that are presented from two angles. Although, I hope that all the shots were taken correctly. In any case, a general understanding can be obtained. So, let's begin.
The most obvious example: Samsung 245B (TN) and Samsung 245T (PVA)
Acer AL2416W (PVA)
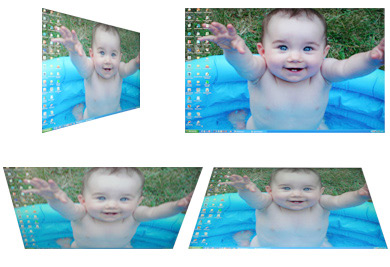
Dell 2407WFP (PVA)
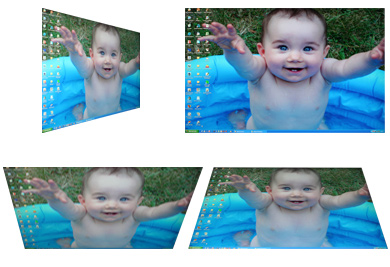
LG L245WP-BN (MVA)

ViewSonic VX2435wm (MVA)

And this, although an old one, is an illustration of the fact that when indicating viewing angles, only the drop in contrast is measured and color rendition distortion is not taken into account at all.
Dell E248 (TN) and Dell 2408WFP (PVA)


NEC24UXi (S-IPS) and DELL 2407WFP HC (PVA)


Dell 2007WFP: S-IPS version (left) and PVA version (right)

LG L203WT: TN version (left) and S-IPS version (right)

The most sophisticated comparison - IPS vs IPS: NEC 2490WUXi vs HP LP2475W

But now you can draw your own conclusions.
I just want to add the following:
- When buying a monitor, you need to clearly understand what tasks it will be used for. If you don't know why you need such an expensive monitor, don't buy it. Focus on your own perception of the picture, so I strongly recommend watching all the monitors live, preferably with special test programs, if the store allows it.
- When monitors on different matrices stand side by side, there is no doubt that *VA is better than TN, and S-IPS is better*VA. But if there is only one monitor on the table, and there is nothing to compare it with, then even a professional is not very easy to determine the type of matrix by eye. With TN it is still quite simple, but you will definitely have to guess between IPS and PVA. And here is a huge “monitor - matrix type” correspondence table compiled by the collective mind of iXBT.
- In addition to viewing angles, there are also important quality parameters, but it is the angles that most spoil the impression of TN matrices.
- Good monitor calibration also greatly affects color quality. And if nothing can be done about viewing angles, then bright and saturated colors can be achieved on TN. Moreover, progress does not stand still.
