A laptop's processor is its brain, the component where most of the "thinking" happens. Fast CPU ( CPU) allows you to chew on spreadsheets, web pages, play games or edit photos faster, but a higher power rated processor may take a toll on your time battery life.
When you shop for a laptop, you usually see the name of the processor among the first specifications of each product. However, judging by the name of the processor, without any context, can lead to confusion. For example, is a laptop with a Core i7-7Y75 processor faster than a laptop with a Core i5-7200U? How much speed do you really need?
Most laptops today run on Intel processors, only a handful of laptops use AMD processors for the sake of saving. And while most chips come from one manufacturer, there are more than two dozen various models, which you can see in the new laptop. Fortunately, getting comfortable with modern processors and choosing the best one is not that difficult.
Which laptop processor should you choose?
We'll go into detail about the types of processors and their capabilities below, but if you want a broad understanding, we've included a little cheat sheet below.
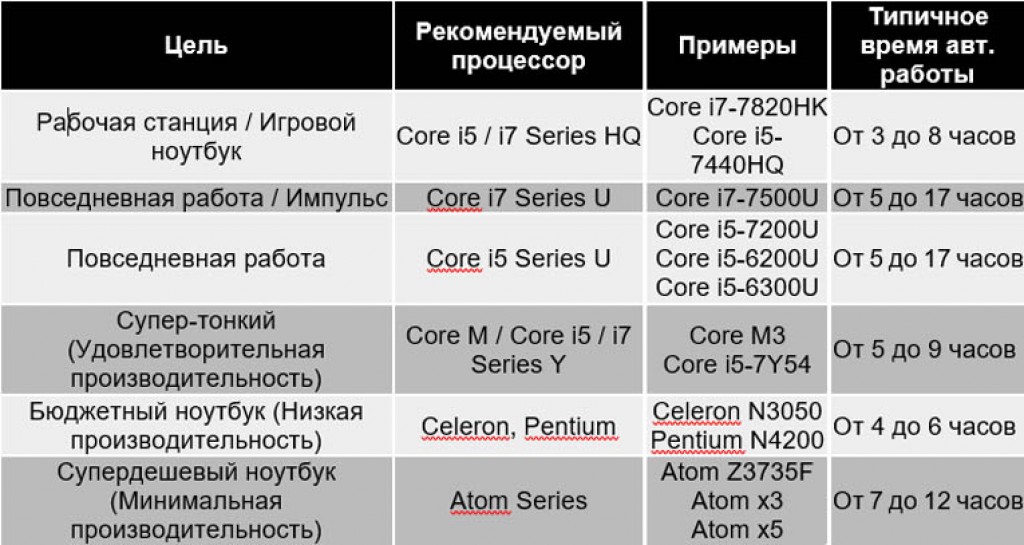
When you look at the specifications, the name of the processor may appear to be a confusing series of numbers and letters.

The first word in the name of the processor is the brand, which is usually “ Intel Core", but you may come across Xeon processors, Celeron, Pentium or Atom. Following the brand, you see a brand modifier, which is most often i3, i5 or i7, but there may be other letters/numbers such as m5, x5, E or N. The first number after the hyphen is the generation indicator; the latest generation is the 7th, so new processors are numbered 7.
Then you'll probably see some combination of two or three numbers and one or two letters, probably U, Y, HQ or HK. The numbers indicate the lineup, and the letters are a line of processors. The line is extremely important because it tells you about the processor's power and power consumption.
Core i3 vsCore i5 vsCore i7
You will see most Intel processors on laptops that cost more than 25,000 rubles, called Core i3, Core i5 or Core i7. As you can see from the numbering, the Core i3 becomes the slowest, the i5 takes the middle, and the i7 becomes the fastest. As a rule, Core i5 models are more than enough for the average, everyday user who does not work with intensive graphics, engineering and scientific topics.
Processor: Cores, frequency and hyperthreading
When you read about any particular processor, you will see that just like a laptop, it has its own specifications. The most important of them are:
Cores (Core): A processor within a processor, each core can perform one discrete task while another core is busy doing something else. Most laptop processors have two cores, but some models increased productivity have four cores.
Hyperthreading: A process in which the processor divides each physical core into virtual cores called threads. Most dual-core Intel processors use Hyper-Threading to create four threads.
Clock frequency: Measured in gigahertz, this is the number of cycles per second that a processor can perform. A higher number is better, but it's not the only factor in processor speed.
TurboBoost: Temporarily increases the processor clock speed from the base frequency to complete a task faster. Most Core i5 and Core i7 processors have this feature, but the Core i3 model does not. The default frequency is listed as the "CPU Base Frequency" while the highest frequency is listed as the "Maximum Turbo Frequency".
Cache: A small amount of random access memory Located directly on the processor chip, the cache stores frequently used data to speed up repetitive tasks. Most processors have a cache of 1 to 4 MB of memory.
TDP (Thermal Design Power): The number of watts used by the processor. More watts means higher performance, but also higher temperatures and therefore higher energy consumption.
Vpro: Built-in function remote control, which is aimed at corporate IT departments. Many business laptops use Vpro processors, but consumer systems do not.
Generations
Every 12-18 months, Intel releases a new generation of processors, which are always slightly faster and more energy-efficient than their predecessors. Unfortunately, not every processor in the series switches to the new architecture at the same time. While Intel launched several processor series Kaby Lake U and Y in September, the manufacturer debuted the remaining 7th generation processors in early January 2017. Kaby Lake refreshes the line of business laptops, gaming laptops and other laptops with quad-core processors that will hit the market in the first months of 2017.
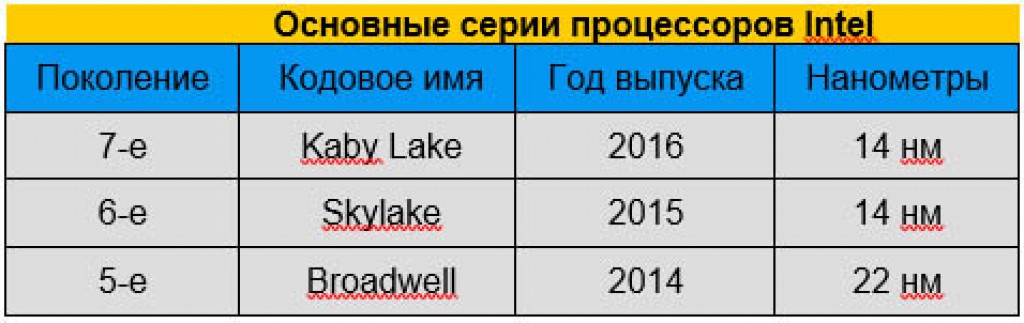
Every two to three generations, Intel "shrinks" its processors, allowing the company to fit more transistors into a smaller processor area, which improves performance at the same heat consumption. Dimensions technological process manufacturing is measured in nanometers and the lower the better.
Processor lines (from most to least powerful)
Choosing the right processor line is much more important than choosing Core i5 vs Core i3. Intel has four main lines, each based on the Core i3, Core i5 and Core i7. Each line has a different TDP (Thermal Design Power), ranging from 4.5W for the Y Series all the way up to 45W for the HQ Series.
Increasing TDP means higher performance, higher heat output and higher energy consumption. However, just because the processor has a very low TDP, it is too early to say that the laptop will be able to offer long battery life. For example, we've tested many laptops with 4.5-watt processors that had below-average battery life because they also had small batteries or power-hungry screens.
XeonE: Only forHigh-End workstations
- Suitable for: engineers, research, professional animators.
- Suffering: Poor battery life, accessibility, weight.
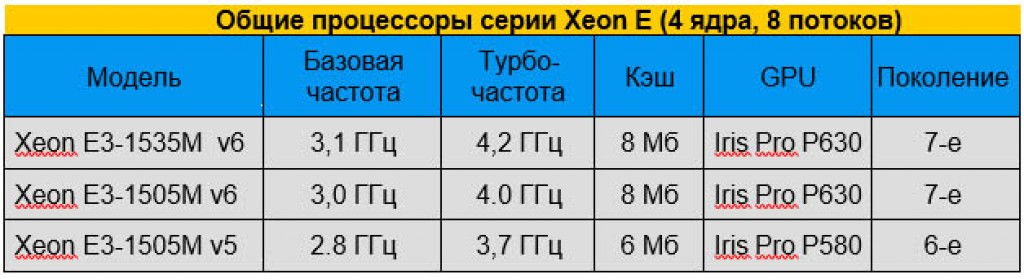
For the highest class of mobile workstations, there are processors from Intel Xeon E3. Laptops with these processors inside are capable of doing more calculations so they can work with 3D animation or run complex simulations, which is important for medical work or engineering. The Xeon E3 has a 45-watt TDP, four physical cores, and HyperThreading and TurboBoost technology. Don't expect long battery life or a low price.
The latest Xeon processors, which now feature Kaby Lake architecture: E3-1535M v6 and E3-1505M v6. Oddly enough, the "v6" at the end of the model indicates that it is the 7th generation while Xeon v5 is used to mark the 6th generation (Skylake) architecture. Since they are made for business, all Xeon processors have Vpro technology built-in.
SeriesHQ/HK: 4-core, High performance
- Suitable for: Gamers, creative professionals, power users.
- Suffer from: Portability, accessibility, battery life.
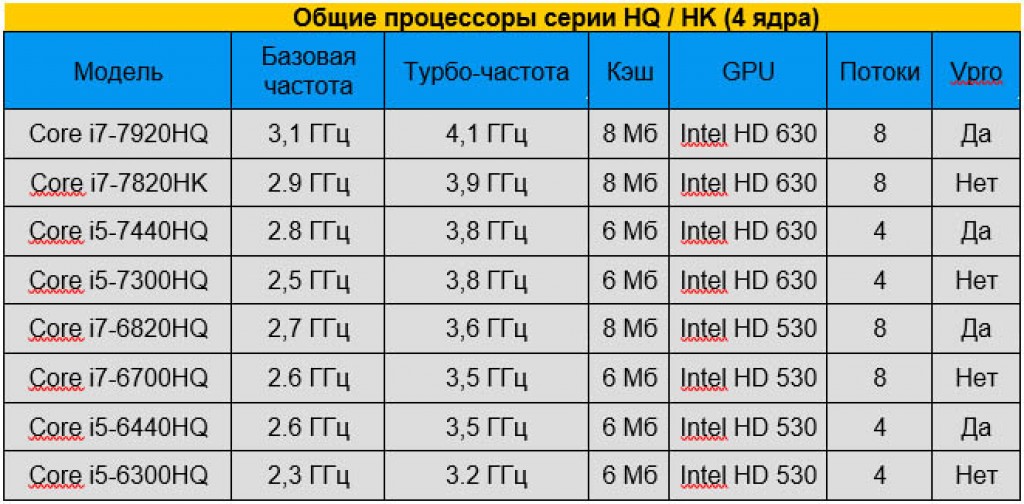
If you are a very active user or gamer, a laptop with an HQ series processor is probably for you. the best choice. HQ series processors have four cores, instead of two, as on U and Y series processors. Thanks to hyperthreading technology, Core i7 machines can offer 8 parallel threads at once. HQ processors also have a 45W TDP, which means laptops with these processors either have poor battery life or a giant battery. Because they generate more heat than U-series CPUs, you won't find HQ processors in ultra-light and thin laptops.
One of the smallest laptops with an HQ processor is the Lenovo ThinkPad T460p with a 14-inch screen and a weight of 1.7 kg. Thanks to the 3-cell battery, the T460p offers a very short 3 hours and 18 minutes, but that time rises to 9:47 with the 6-cell battery.

HK processors are similar to HQ, but they are unlocked, which allows you to increase the clock speed. Intel just launched the 7th generation of HK and HQ processors in early January 2017, so right now, most of the new quad-core laptops are running the sixth generation "Skylake" platform. However, you can expect them on the newest laptops that will debut in the first quarter of this year.
SeriesU: Everyday productivity
- Suitable for: Simple operation, content consumption, long-term operation.
- Suffer from: Gaming performance, graphics capabilities.
If you're looking for a "typical" laptop experience with solid performance and potentially good battery life, Intel processors U series for you. In particular, a Core i5 U series like the Core i5-7200U should be more than enough for most users who need to work with spreadsheets.
Most U-series processors have a TDP of 15 W, which is the sweet spot between performance and battery life, but requires active fan cooling. There are several U-series processors with 28-watt TDUs, although few laptops use them. With a large battery and energy-efficient screen, U-series laptops can get upwards of 10 hours of battery life, while high-end systems can approach 20 hours of battery life.
Intel just released its 7th generation Vpro-enabled U-series processors in January 2017, so new business laptops like Lenovo's 2017 ThinkPads and Dell Latitudes on the new Kaby Lake will arrive in the first months of the year. You'll also see a number of U-series laptops with Iris Plus 640 or 650 GPUs in early 2017. Iris Plus promises significantly improved graphics performance over the base Intel HD 620 GPU.

SeriesY/CoreM: Quiet systems, satisfactory performance
- Suitable for: Portable systems, fanless design, lightweight productivity.
- Suffer from: Battery life, lack of performance.
When you're shopping for a laptop, be wary of the Y series, which you might see behind branded Core i5/Core i7 or Core m3/m5/m7 (in cheap or latest generation laptops). Intel Y-series processors have a very low TDP of 4.5 W, allowing laptop manufacturers to move to fanless designs for super-thin laptops. Unfortunately, most of them also have low-power batteries or powerful screens, which results in worse battery life compared to some U-series competitors.
For example, the slender Acer Spin 7 has a central Core processor i7-7Y75 and lasts only 6 hours and 53 minutes, at the same time, it scored 5777 points on Geekbench performance tests. Meanwhile, the Core i7-7500U-powered HP Sectre x360 weighs about the same and lasts over 10 hours on a single charge, with a Geekbench score of 8,147. The Spin 7 is 5mm thinner than the HP Specter x360, but there are a number of ultra-thin laptops with U-series processors, including the 11.9mm thick ASUS ZenBook 3 and the 10.4mm thick HP Specter.

Laptops with Y-series processors are not smaller or cheaper than laptops with U-series processors. The Spin will cost you about 80,000 rubles, while a customized Specter x360 carries a similar price tag. As of the 7th generation of Intel Kaby Lake processors, Y series processors are sold as Core M3 (base model), Core i5 and Core i7. The 6th generation models have a strict separation of cheap processors, which came with the name Core M3, Core M5 and M7. If you're looking for high performance in a new laptop, make sure your Core i5 or Core i7 CPUs don't have a Y in the model number (Core i7-7Y75).
Despite the shortcomings, we're not ruling out Y-series laptops. The 12-inch MacBook and HP EliteBook Folio G1 are two laptops that offer passable performance and decent endurance powered by Y Series (Core M) processors.
Celeron /Pentium: For those who don't care
- Suitable for: Web surfing, saving money.
- Suffer from: Lack of gaming performance, video editing.
If you are looking for a laptop costing from 15,000 to 30,000 rubles, there is a high probability that you will find a system based on Intel Celeron or Intel Pentium series processors. This budget processors, which provide passable performance for web surfing, email and light work. Celerons are common in Chromebooks because Google's OS doesn't require as much power as Windows does. If you're buying a Windows laptop, only go for Celeron/Pentium processors if price is your primary concern.
Celeron processors have TDPs ranging from 4 to 15 W. Celeron models start with N (eg: N3060) and use 4 to 6 W TDP, while processor models with a U end (eg: 3855U) consume around 15 watts and promise better performance. Battery life varies depending on the system's battery capacity, but laptops with 4- and 6-watt CPUs tend to be cheaper and more reliable.
Less common, but slightly faster, Pentium processors have a TDP range of 6 to 15 W, although most processors are 6 or 7.5 W. One of our favorite budget laptops, the ASUS Vivobook E403SA runs on Pentium processors N3700, which provides the necessary performance for multitasking and over 9 hours of battery life, costs about 30,000 rubles. Some Celeron and Pentium CPUs are 2-core, while others are 4-core.

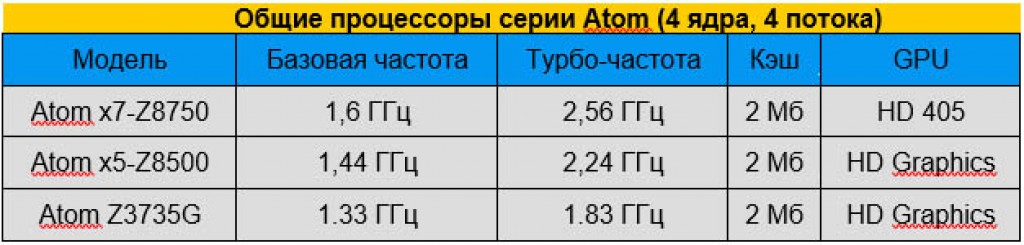
Atom: Good battery life, weak performance
- Suitable for: Saving money, long operating time, light weight.
- Suffer from: Poor multitasking and performance.
This is the cheapest laptop processor in the Intel series, Atoms appear in super-cheap Windows laptops and tablets like the Lenovo IdeaPad 100S and ASUS Transformer Mini T102HA. Almost all Atom processors have four cores and extremely low power consumption, allowing them to offer excellent battery life, along with the worst performance. We recommend purchasing laptops based on Atom processors exclusively as an additional device for an adult or a laptop for a child. The Atom is good enough for surfing the Internet and watching videos, but it struggles with multitasking.

Intel doesn't list TDP for most modern processors this series, Productivity instead says they use 2 to 2.5 watts, about half the power consumption of the Y Series. Perhaps this is why a tiny, one-kilogram laptop like the 100S can last up to 10 hours and cost less than 15,000 rubles.
Integrated Graphics
All Intel portable processors come with their own integrated graphics processing units (GPUs). On most Core i3/i5/i7 processors of any line, the GPUs are called Intel HD Graphics with no. For 7th generation processors, the number starts with 6 (for example: Intel HD Graphics 620), and the GPU of 6th generation processors starts with 5 (for example: Intel HD Graphics 520). Some high-end processors may come with "Iris Plus" graphics, which are not significantly faster and will again be outperformed by discrete graphics chips from Nvidia and AMD.
Integrated GPUs located directly on the CPU eliminate the mixing and matching of brands from laptop manufacturers. Laptops with the Core i7-7600U come with an Intel HD Graphics 620 GPU on board, for example, while the Core i7-7660U CPU is always faster with Iris Plus 640 graphics. For the 7-series U-generation processors, the leading processors end with 60 ( i5-7360U), they are equipped with Iris Plus Graphics 640, while processors with 7 at the end (Core i5-7287U) are equipped with a slightly overclocked Iris Graphics Plus 650.
Overall, integrated GPUs are good enough for productivity, web surfing, video playback, and any casual gaming or gaming at low settings. If you want to edit videos with high resolution, do professional animation or play serious games, you need discrete graphics.
Other laptop components
It's important to remember, however, that the processor is not the only factor that determines a laptop's performance; even the slowest laptop processors can provide a decent user experience when paired with other quality components. For most people, the choice solid state drive(SSD) instead hard drive(HDD) will make the laptop much more responsive than the additional cost of a Core i5 or Core i7. And for high graphics performance of a laptop, having a powerful discrete GPU (graphics processing unit) is even more important than the fastest central processing unit (CPU).
RELATED PRODUCT:
This article will compare laptop processors from two leading semiconductor manufacturers - Intel and AMD. The products of the first of them are equipped with an improved processor part and have more high level speed. In turn, AMD solutions boast a more powerful graphics subsystem.
Division into niches
And Intel for laptops will most optimally fulfill three niches:
- Budget-class processors (they are also the most affordable).
- Mid-level CPUs that combine both high speed and acceptable energy efficiency.
- Chips with maximum level productivity. In this case, performance, autonomy and energy efficiency fade into the background.
If in the first two cases AMD can provide a worthy alternative to Intel, then the latter company has reigned supreme in the premium segment for quite some time. The only hope in this regard is new processor solutions based on the Zen architecture, which AMD should present next year.
Entry-level Intel products
Until recently, this niche from Intel was occupied by products from the Atom line. But now the situation has changed and laptops entry level are now based on Celeron or Pentium processors. The most modest products in this class include only 2 cores, and the most advanced - 4. The following models are relevant for the 3rd quarter of 2016, which are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 - Current CPU models from Intel for entry-level mobile PCs.
Model name | Number of cores, pcs | Technical process, nm | Level 3 cache, MB | Frequencies, GHz | Thermal package, W | CPU cost, $ | HD Graphics video card model |
|
There are essentially no fundamental differences between these CPU models. They are aimed at solving the simplest problems and have a minimum level of performance. Also, this manufacturer of semiconductor solutions has a strong point in the processor part, but the integrated graphics subsystem is very weak. Another strong point of these products is high degree energy efficiency and thereby improved autonomy.

Mid-range solutions from Intel
Core i3 and Core i5 are mid-range Intel processors for laptops. A comparison of their characteristics indicates that the first family is closer to entry-level solutions, and the second, under certain circumstances, can compete with the most productive chips of this company. Detailed specifications of this product family are given in Table 2.
Table 2 - Parameters of Intel processors for mid-range laptops.
Model name | Number of Cores/ logical flows, pcs. | Production technology, nm | Level 3 cache, MB | Frequencies, GHz | Power, W | Video card HD Graphics |
|
The characteristics of CPUs of this class are almost identical. The key difference is the improved energy saving of the 7U54. As a result, autonomy in this case will also be better. Otherwise, there are no significant differences between these processors. The price for all chips of this family is the same - $281.
Premium processors for laptops from Intel
For laptops latest generation indicates that the most productive solutions include i7 family CPUs. Moreover, in architectural terms, they are practically no different from middle-class products. Even the video card models in this case are the same. But a higher level of performance compared to mid-class processors is provided by higher clock frequencies and an increased size of Level 3 volatile memory. The main parameters of chips of this family are shown in Table 3.
Table 3 - Main characteristics of i7 family CPUs.
The difference between these products is that in the second case, energy efficiency is improved, but the performance will ultimately be lower.
AMD entry-level mobile processors
For laptops from the two leading manufacturers of these products, it indicates that Intel, as noted earlier, has a better processor part, and AMD has an integrated graphics subsystem. If the priority in a new laptop is an improved video system, then it is better to pay attention to laptops from a second manufacturer. Specific Models chips technical specifications are given in Table 4.
Table 4 - Most recent AMD processors for entry-level laptops.
Model name | Frequency range, GHz | Level 2 cache, MB | Thermal package, W | Number of cores, pcs | Integrated Graphics |
|
For the most part, these chips have almost identical technical parameters. The key difference here is only in the frequency range and the model of the integrated built-in accelerator. It is based on these parameters that you need to make a choice. If you need maximum autonomy, then we choose products with lower performance. If autonomy comes to the fore, then you will have to sacrifice dynamism for this.

AMD chips for organizing mid-range laptops
FX-9XXXP and A1X-9XXXP are for laptops. Comparison of their characteristics with entry-level products indicates that they already have 4 computing units versus 2, which are available in entry-level products. Also in this case it can be a worthy competitor to entry-level discrete accelerators. But the weak processor part is the factor today that significantly reduces the performance of laptops based on these chips. Therefore, you can only look in their direction if you need the fastest possible graphics subsystem at the minimum cost of a mobile computer. The main specifications of this CPU family are listed in Table 5.
Table 5 - AMD CPU parameters for mid-range laptops.
CPU markings | Clock frequencies, GHz | Graphics accelerator | Thermal package, W |
|

The hardest comparison to make between laptop processors is in the entry-level product segment. On the one hand, Intel solutions in this case have a lower cost and an improved processor part. In turn, AMD offers mobile PCs with an improved graphics subsystem. It is based on the last parameter that it is recommended to buy when choosing an entry-level laptop Pavilion 15-AW006UR from HP. All other things being equal to competing solutions, the video card in this case will have a certain performance margin, and the processor is not that much inferior to the Intel CPU. For a mid-level mobile PC, it is recommended to choose the Aspire E5 - 774 - 50SY from Acer. It has an i5 chip installed - 7200U, which is only slightly inferior to flagship products. And its other technical specifications are at an acceptable level, as for a middle-class laptop. Comparison of laptop processors in the niche of the most productive solutions indicated which is best to buy mobile computers based on 7th generation i7 chips. The most affordable, but also very equipped laptop option is the IdeaPad 510-15 IKB from Lenovo. This is what we recommend buying when choosing the most productive mobile PC. At the same time, the price is quite affordable for this class of devices, and the equipment is excellent.

Results
A comparison of laptop processors from two leading chip manufacturers today clearly and clearly indicates that in most cases the leading positions are occupied by products from Intel. AMD, in turn, lags significantly behind its direct competitor. The only market segment where parity is still maintained is entry-level mobile products, where AMD has worthy alternative. In all other cases, it would be more correct to purchase laptops based on Intel CPUs. The current situation can be radically changed by the release of processors based on the Zen architecture in 2017. But whether AMD will be able to do this - time will tell. Now, in the niche of mid-level and premium mobile PCs, it is most correct to rely on solutions from Intel. Although their price is somewhat high, the level of performance more than compensates for this shortcoming.
And it doesn’t matter at all whether it’s a laptop, pocket smartphone or a NASA supercomputer. However, how many have seen this microcircuit “live”? The curious could satisfy their thirst for knowledge by visiting the nearest store selling computer equipment and carefully examining the display cases with various components. But there are only a few of them. Anyone who knows which processor to choose for a laptop is very well versed in existing models and has seen them more than once. Majority - ordinary users for whom a computer is something like a refrigerator or washing machine, for working with which basic knowledge is quite enough. As a result, a situation often arises when a recently purchased laptop computer turns out to be unable to properly perform the tasks for which it was actually purchased. Because when purchasing, the future owner did not collect information about which processor is the best for a certain range of applications, and bought the model based on cost or appearance. In this article we will try to give advice on which processor is best for a laptop, taking into account a number of characteristics. Obviously, there is no universal answer.
Cores. Give me a couple, or better yet four!
 The basis of any processor is its computing core. This is a set of controllers, transistors, conveyors - in a word, everything that performs calculations. Thanks to the improvement of the technical process of manufacturing microcircuits, it has become possible to place not one, but several cores on a single chip. Actually, now you can find a single-core model only in highly specialized devices. Multi-core solutions have greater computing power, organically sharing data streams among themselves. In this case, memory and controllers are used together, and conflicts do not arise. If we talk about which processor is better for a laptop, then it is absolutely clear that multi-core.
The basis of any processor is its computing core. This is a set of controllers, transistors, conveyors - in a word, everything that performs calculations. Thanks to the improvement of the technical process of manufacturing microcircuits, it has become possible to place not one, but several cores on a single chip. Actually, now you can find a single-core model only in highly specialized devices. Multi-core solutions have greater computing power, organically sharing data streams among themselves. In this case, memory and controllers are used together, and conflicts do not arise. If we talk about which processor is better for a laptop, then it is absolutely clear that multi-core.
One two three four…
However, performance is determined not only by the number of cores. The next key characteristic is the clock frequency. It represents the number of simple operations on binary data that the kernel can perform per unit of time (usually a second).  There is no need to talk too much about which processor is better for a laptop. Of course, the one that is faster, that is, with more high frequency. By the way, its unit of measurement is Hertz (megahertz, gigahertz). It is worth paying attention to the fact that as the frequency increases, the level of energy consumption increases, reducing battery life.
There is no need to talk too much about which processor is better for a laptop. Of course, the one that is faster, that is, with more high frequency. By the way, its unit of measurement is Hertz (megahertz, gigahertz). It is worth paying attention to the fact that as the frequency increases, the level of energy consumption increases, reducing battery life.
Different approaches to solving similar problems
There are several main manufacturing companies. Among them, Intel and AMD should be noted: the lion's share of the market belongs to these two companies. The computer can have a solution installed from both AMD and Intel. Which processor is better for a laptop? There is no answer, since every developer strives to create a quality product.
In simple terms
Despite the abundance of various information on this topic, the choice should be made based on the range of tasks for which you plan to use the laptop. If these are movies, Internet surfing, music and working in office applications, then it is quite enough Intel Atom, Pentium, Celeron and AMD series C and E. If you need a more universal solution, then AMD Phenom or younger Intel Core models are suitable. Maximum performance accounts for Core i5 and i7, as well as the quad-core Phenom.
Performance
First, let's look at the key characteristic of the processor - its performance. For a modern mobile processor, it is determined by three factors: clock frequency, the amount of cache memory of the first (L1) and second (L2) levels, architecture (including the number of cores). Artificial overclocking technologies help optimize processor performance based on the tasks being performed.
When choosing a computer, we are used to first turning to the clock speed of the processor installed in it, which indicates the number of operations it performs every second. But with the advent of mobile multi-core chips, clock speed itself no longer determines system performance. Moreover, it is simply absent from the names of a number of processors - so as not to mislead users. Intel, instead of a nominal increase in clock frequency, proposed TurboBoost technology, implemented in Core i7, i5 and i3 processors: during peak loads, the clock frequency is artificially increased, dynamically increasing performance depending on the resource intensity of the tasks. TurboCore intends to implement similar technology in its processors and AMD soon.
Designed for temporary storage of information, cache memory provides maximum output from the processor clock speed. The fastest memory is the L1 cache on the processor core. L2 cache is characterized by lower speed with increased volume - from 128 KB to 12 MB. The presence of L2 memory built into the processor gives a noticeable increase in performance when working with any applications. It is worth noting that the large amount of second-level cache memory required for resource-intensive tasks significantly increases the power consumption and heat dissipation of the processor.
Number of cores and multitasking
Modern mobile processors for laptops differ not only in clock speed and cache memory size, but also in the number of processor cores. The main advantage of multi-core systems is the ability to perform multiple tasks in parallel. Laptops with multi-core architecture now make up the bulk of offerings, although basic models designed for everyday tasks also include single-core processors with alternative performance-enhancing technologies.
One of the most effective approaches to increasing productivity has been the ability of the processor to solve not one, but several tasks in parallel. At the first stage, it was implemented by creating two logical processors based on one core. Intel's Hyper-Threading technology allows one mobile processor to simultaneously handle two tasks, which significantly increases the speed of multitasking.
The next step in increasing productivity mobile devices become multi-core processors. It was no coincidence that the world's first dual-core processor, Core Duo, was created specifically for mobile PCs: processors with multiple cores in one housing consume much less power and generate less heat. Nowadays, laptops use mobile chips with two or four cores. AMD plans to launch the first triple-core processors for laptops in the near future. They will be more powerful than dual-core ones, but at the same time consume less power than high-performance quad-core ones.
Energy efficiency
Unlike processors for desktop PCs, mobile developments are also evaluated from the point of view of energy efficiency. It is this that guarantees long-term battery life, while simultaneously reducing the heat transfer of the device. The noise level of the cooling system and the laptop as a whole depends on how hot the processor is, and its power consumption determines the battery life.
Intel Celeron Dual-Core, Core i3, Core i5, etc. processors save energy by reducing the processor frequency in standby mode using Enhanced SpeedStep technology. AMD Athlon processors use PowerNow! technology for this purpose. In addition to a decrease in frequency and voltage, when the processor is not fully loaded, the rotation speed of the cooling fan also drops.
Manufacturers do not intend to stop there. One of the most promising trends in the mobile segment has become laptops based on almost full-fledged processors, but with reduced power consumption. Intel solutions labeled CULV (Consumer Ultra-Low Voltage) based on single- and dual-core Celeron, Pentium Dual-Core, Core 2 Solo and Core 2 Duo processors are the basis for highly mobile laptops with long battery life. AMD has also released products based on energy-saving platforms - with Athlon Neo processors. It is assumed that such mini-laptops will become an intermediate link between netbooks and full-featured laptops.
Basic, versatile, productive...
The most common are chips with two cores: they can be found in basic laptops, mid-price systems, and powerful laptops. Single-core processors are still widely used in office systems, netbooks and ultra-light laptops, where the emphasis is on low power consumption, light weight and long battery life. High-performance quad-core processors are designed for premium laptops and powerful gaming systems, and therefore occupy a fairly narrow market segment.
The Intel Atom line of single- and dual-core processors is designed specifically for ultraportables, netbooks, and entry-level notebooks with extremely low power consumption and heat dissipation. minimum sizes. Accordingly, devices based on these processors offer maximum battery life. Almost all “atoms” support Hyper-Threading technology (except for the Z510 processor), and the Nxxx series chips also implement Enhanced SpeedStep technology.
Inexpensive single-core Mobile Sempron and Celeron processors are aimed at the segment of affordable laptops that will do an excellent job of performing basic everyday tasks: their trump card is an advantageous balance between price, performance and power consumption in thin, lightweight devices.
Popular processors Intel Core 2 Duo, Pentium Dual-Core and AMD Turion II with increased L2 cache memory are installed in completely affordable and at the same time competitive and modern machines that can satisfy the most demanding buyer.
Modern mobile Intel Core i3/5/7 chips are structurally close to models for desktop PCs, differing from “stationary” versions in lower clock speeds and power consumption. Among them key features- a built-in graphics chip, the performance of which is sufficient for mid-range games with support for DirectX 10, as well as high-definition video processing and decoding of modern audio formats. These processors also support the most modern video interfaces - DVI, HDMI, DisplayPort. One of the most popular processors in modern mobile PCs is Intel Core i5: it is found in laptops of almost all classes, with the exception of ultraportables.
Focuses on comprehensive support for graphics and multimedia and AMD. Family of single and dual core Athlon processors formed the basis of several platforms that have gained wide popularity due to high-quality mobile graphics - both discrete and integrated into the system logic. With low heat dissipation, laptops based on modern Athlon processors are an excellent option for a mass platform with multimedia applications and wireless communications.
Deciding on the processor
There are no bad ones good processors: each of them is focused on its own segment and specific tasks. If you plan to carry your laptop with you all the time and run it in offline mode, focus on processors with minimal weight and low power consumption. For a home or office laptop designed for basic everyday tasks, single-core processors are suitable. Multi-core chips are designed to support resource-intensive applications, modern multimedia formats and video games.
Single and dual core Intel Atom or Athlon Neo processors - best option for those who value mobility above all in laptops. Atom N series processors were created specifically for portable PCs: the devices equipped with them are thin, light, and have a long battery life. Atom Z-series processors offer the highest performance in their category and are installed in premium ultra-mobile laptops.
Thanks to modern technologies to improve performance, the range of capabilities of modern single-core Intel Celeron and AMD Sempron processors is quite wide: office programs, surfing the Internet, instant messaging and e-mail, films and photographs, simple games and home databases. At the same time, you will not have to overpay for unclaimed capacity.
To support modern multimedia technologies, including high-definition video and the latest audio formats, for video and graphics work, choose processors with multi-core architecture and increased L2 cache: Intel Pentium, Intel Core Duo, Athlon Dual Core, AMD Phenom.
For video game fans, we recommend paying attention to mobile Intel Core i3 and Intel Core i5 processors with DirectX 10 support, as well as AMD Turion II processors. Quad-core Intel Core i7 processors are installed in the most powerful gaming laptops and productive workstations that can handle almost any task.
Laptop processors are quite different from desktop processors. This is primarily due to the limitation of the power of the laptop's power system, especially when running on battery power. The less power a laptop requires to operate, the longer it can run on battery power. Laptop processors are designed to consume as little power as possible. This, in turn, affects performance.
The processor for a laptop is selected based on the purposes and tasks for which the laptop is intended. Based on their purpose, laptops can be divided into four categories. There are budget laptops, ultra portable laptops, ultra-thin lightweight laptops and desktop replacement laptops. Also, it should be borne in mind that for solving most everyday problems it is super powerful processor not needed. In this article we will tell you how to choose a processor for a laptop and provide lists of processors for each category of laptops.
Processors for budget laptops
We will call budget laptops mobile functional computers at a low price. Chromebooks also fall into this category. These computers are equipped with processors with relatively low performance. It should be noted that Chromebooks are equipped with processors designed for tablets. They do not have high data processing speed, but are suitable for solving everyday problems. The variety of processors for budget laptops is unusually large. Budget laptops are sometimes equipped with older processors that were once used on expensive laptops.
The processors from the list below are suitable for solving basic everyday tasks, including surfing the Internet, working with by email, word processing and presentation creation. They are also suitable for playing video and audio files. These processors are not intended for resource-intensive applications. computer games and for complex computer graphics processing applications.
List of processors for budget computers:
- AMD A6-7000 and higher
- AMD A6-9210 and higher
- AMD A8-7100 and higher
- AMD A9-9410 and higher
- AMD E1-7010 and higher
- AMD E2-7110 and higher
- AMD E2-9010 and higher
- Intel Celeron N3350 and higher
- Intel Core i3-6100U and higher
- Intel Core i3-7100U and higher
- Intel Core i5-6200U and higher
- Intel Pentium 4405U and higher
- Intel Pentium 4405Y and higher
- Intel Pentium 4200 and higher
Ultra portable laptops
Ultra portable laptops are lightweight and compact systems designed to handle basic office tasks. This includes word processing, surfing the Internet and preparing presentations. Ultra portable laptops are designed for those who travel a lot. The computing capabilities and availability of additional interfaces for these computers are limited for the sake of portability. This category also includes ultrabooks, portable laptops running on a platform developed by Intel Corporation. Below is a list of processors that are usually installed on ultra-thin laptops.
- AMD A6-9210 and higher
- AMD A9-9410 and higher
- AMD A10 Micro-6700T and higher
- AMD E1-7010 and higher
- AMD E1 Micro-6200T and higher
- AMD E2-7110 and higher
- AMD E2-9010 and higher
- Intel Celeron 3205U and higher
- Intel Celeron N2830 and higher
- Intel Core i3-6100U and higher
- Intel Core i3-7100U and higher
- Intel Core i5-6200U and higher
- Intel Core i5-7200U and higher
- Intel Core i5-7Y54
- Intel Core i7-5500U and higher
- Intel Core i7-7500U and higher
- Intel Core i7-7Y75
- Intel Core M-5Y10 and higher
- Intel Core M3-6Y30 and higher
- Intel Core M5-6Y57 and higher
- Intel Core M7-6Y75 and higher
- Intel Pentium N3530 and higher
- Intel Pentium 4405U and higher
Processors for ultra-thin laptops
Ultrathin laptops are quite powerful mobile computers designed to solve a wide range of tasks. The price and performance of ultra-thin laptops can vary greatly. Typically, their performance is higher than that of ultra portable laptops. But at the same time, they are much smaller and thinner than laptops designed to replace desktop computers.
Below is a list of processors that are installed in ultra-thin laptops.
- AMD A8-8600P and higher
- AMD A9-9410 and higher
- AMD A10-8700P and higher
- AMD A10-9600P and higher
- AMD A12-9700P and higher
- Intel Core i3-6100U and higher
- Intel Core i3-7100U and higher
- Intel Core i5-6200U and higher
- Intel Core i5-6300HQ and higher
- Intel Core i5-7200U and higher
- Intel Core i7-6500U and higher
- Intel Core i7-6700HQ and higher
- Intel Core i7-7500U and higher
Laptops to replace your desktop computer
This category includes laptops that can completely or almost completely replace desktop computer. They are equipped with powerful productive processors, large amounts of RAM, capacious hard drives and usually have large display. Due to this, such laptops are very heavy and bulky, and they have the least portability. Below is a list of processors designed for high-end laptops.
